Abstract
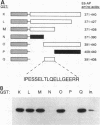
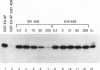
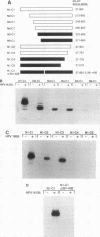
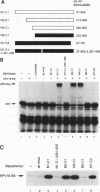
E6-AP is a 100-kDa cellular protein that mediates the interaction of the human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. The association of p53 with E6 and E6-AP promotes the specific ubiquitination and subsequent proteolytic degradation of p53 in vitro. We recently isolated a cDNA encoding E6-AP and have now mapped functional domains of E6-AP involved in binding E6, association with p53, and ubiquitination of p53. The E6 binding domain consists of an 18-amino-acid region within the central portion of the molecule. Deletion of these 18 amino acids from E6-AP results in loss of both E6 and p53 binding activities. The region that directs p53 binding spans the E6 binding domain and consists of approximately 500 amino acids. E6-AP sequences in addition to those required for formation of a stable ternary complex with E6 and p53 are necessary to stimulate the ubiquitination of p53. These sequences lie within the C-terminal 84 amino acids of E6-AP. The entire region required for E6-dependent ubiquitination of p53 is also required for the ubiquitination of an artificial E6 fusion protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S., Kraus V. B., Kroger B., Munger K., Howley P. M., Phelps W. C., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A, simian virus 40 tumor antigen, and human papillomavirus E7 protein share the capacity to disrupt the interaction between transcription factor E2F and the retinoblastoma gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Tidy J. A., Vousden K. H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Vousden K. H. p53 point mutation in HPV negative human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1991 May;6(5):873–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Chau V. Ubiquitination. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:25–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Blake M., Azizkhan J., Nevins J. R. Role of E2F transcription factor in E1A-mediated trans activation of cellular genes. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3547–3552. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3547-3552.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert N. L., Sedman S. A., Schiller J. T. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 increases the degradation rate of p53 in human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6237–6241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6237-6241.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. A cellular protein mediates association of p53 with the E6 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus types 16 or 18. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4129–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for E6-AP, a protein that mediates the interaction of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein with p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):775–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Tomooka Y., Noda M. Identification of a set of genes with developmentally down-regulated expression in the mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91747-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner M. S., Mack D. H., Finicle A. B., Crook T., Vousden K. H., Laimins L. A. Human papillomavirus E6 proteins bind p53 in vivo and abrogate p53-mediated repression of transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Unger T., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. The transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 is inhibited by SV40 large T-antigen and by HPV-16 E6 oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5013–5020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva A., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Chromosomal integration sites of human papillomavirus DNA in three cervical cancer cell lines mapped by in situ hybridization. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D., Rehbein M., Baumeister H., Richter D. Molecular characterization of a novel rat protein structurally related to poly(A) binding proteins and the 70K protein of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1471–1475. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Natural substrates of the ubiquitin proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):615–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. Targeted degradation of the retinoblastoma protein by human papillomavirus E7-E6 fusion proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2425–2431. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S., Zou Z. Q., Pirollo K., Blattner W., Chang E. H. Germ-line transmission of a mutated p53 gene in a cancer-prone family with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):747–749. doi: 10.1038/348747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B. Cancer. A deadly inheritance. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):681–682. doi: 10.1038/348681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 transformation of primary human embryonic fibroblasts requires expression of open reading frames E6 and E7. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):965–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.965-969.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede D., Tidy J. A., Crook T., Lane D., Vousden K. H. Expression of RB and p53 proteins in HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical carcinoma cell lines. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(3):171–175. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew P. R., Berk A. J. Inhibition of p53 transactivation required for transformation by adenovirus early 1B protein. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):82–85. doi: 10.1038/357082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]