Abstract
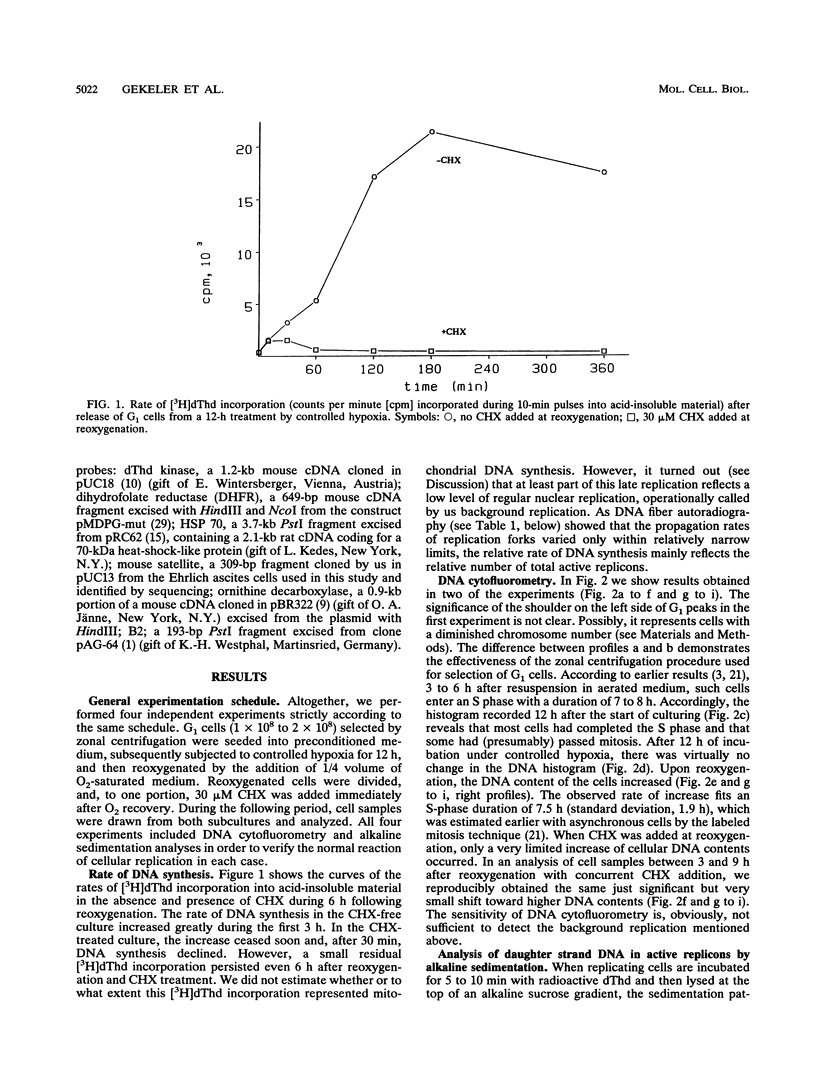
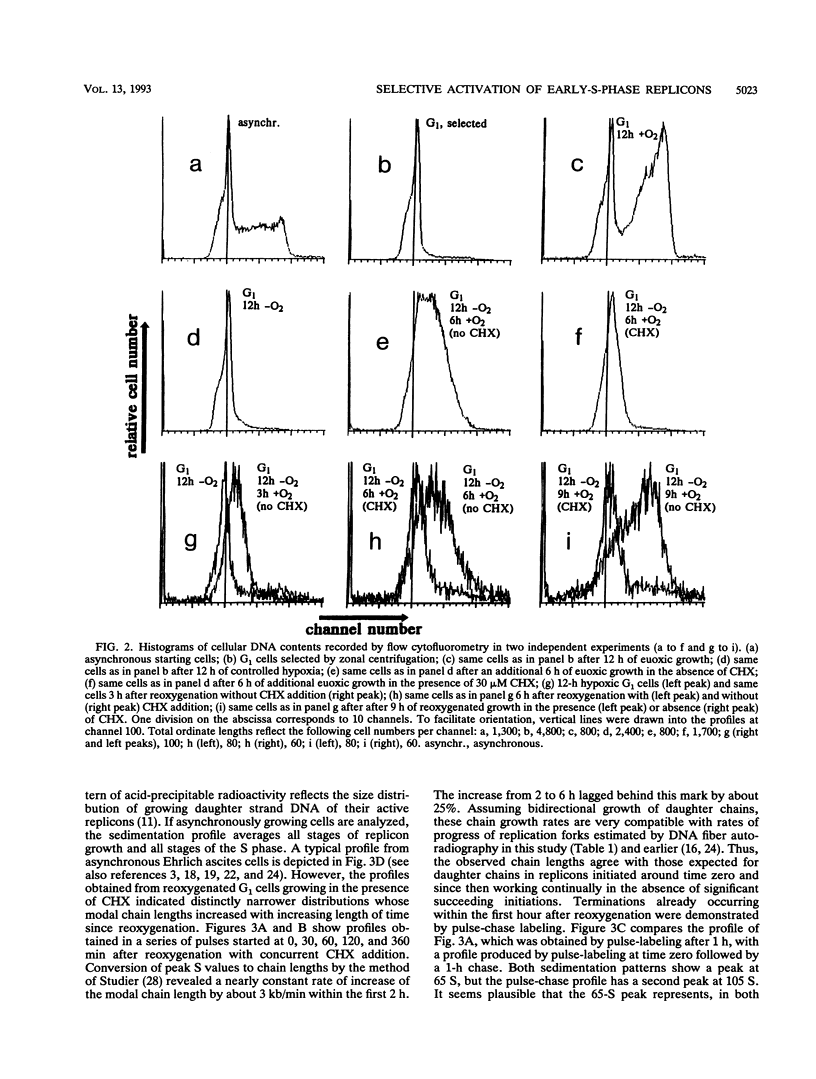
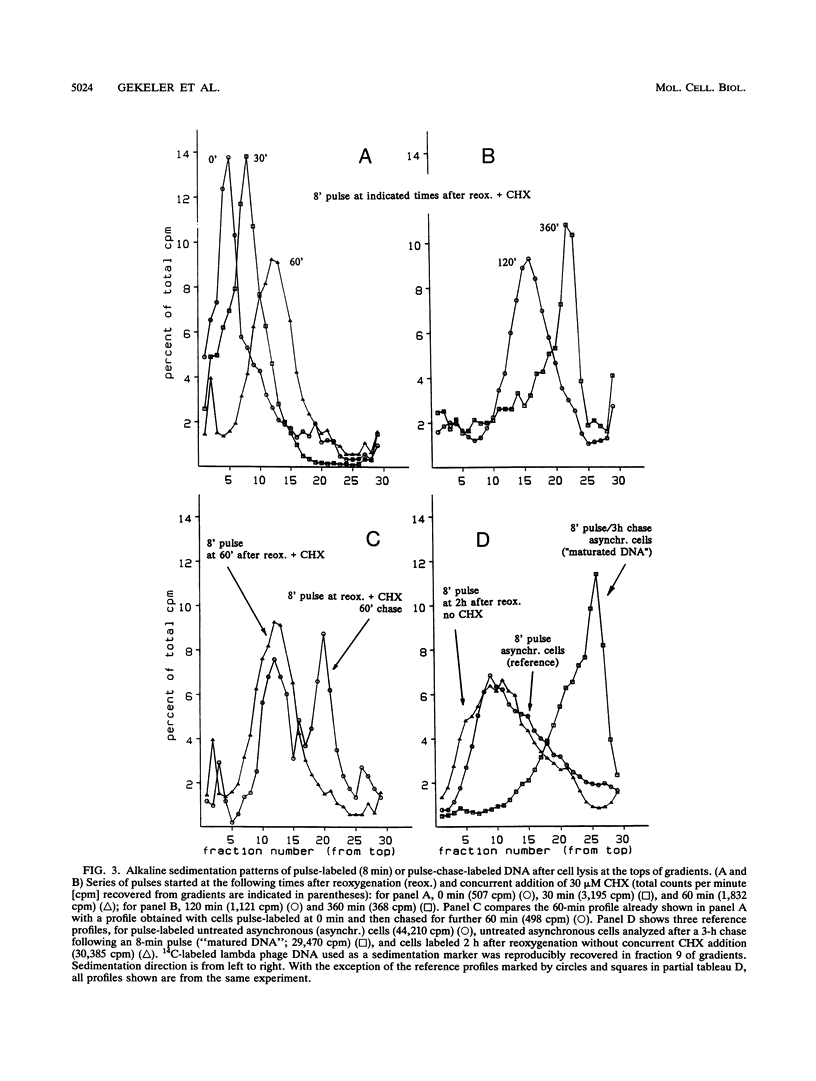
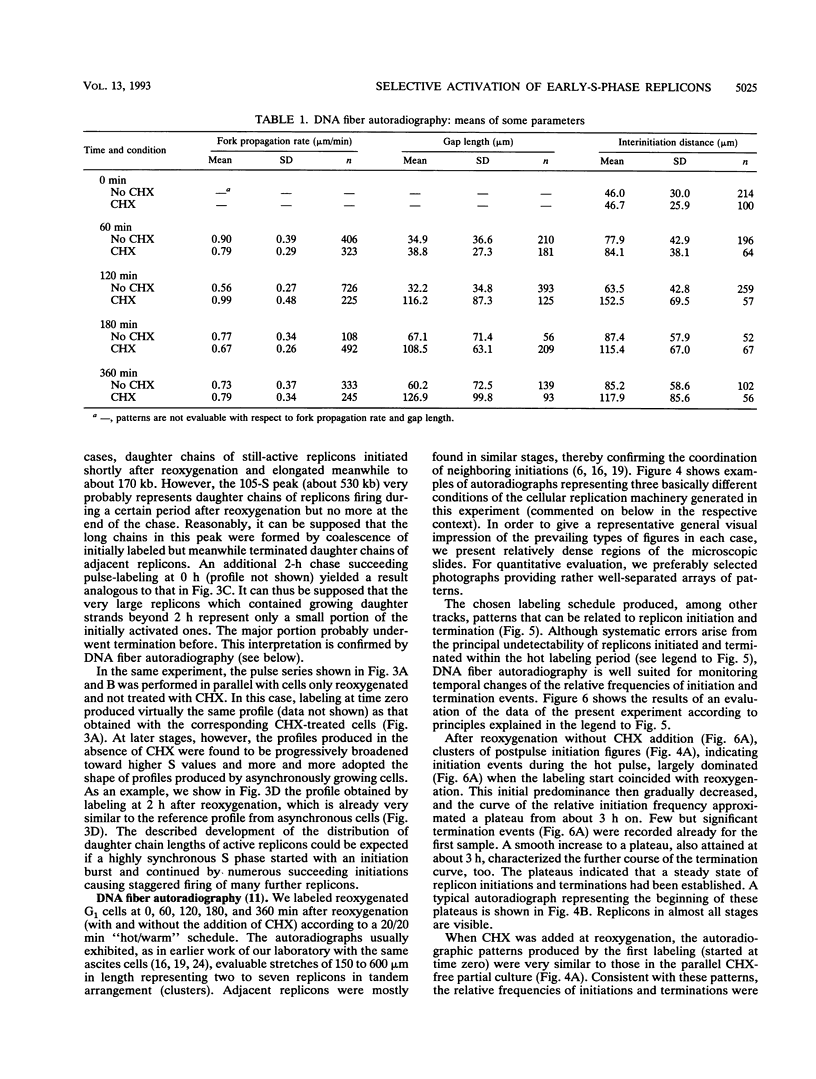
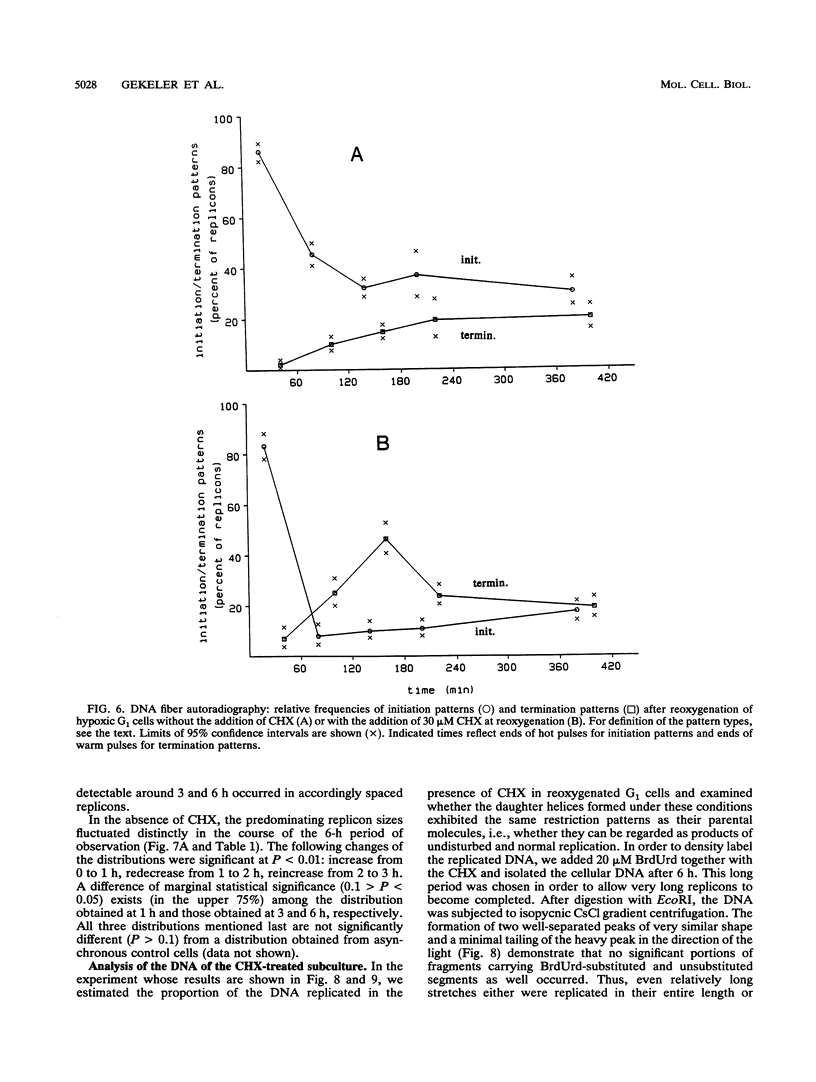
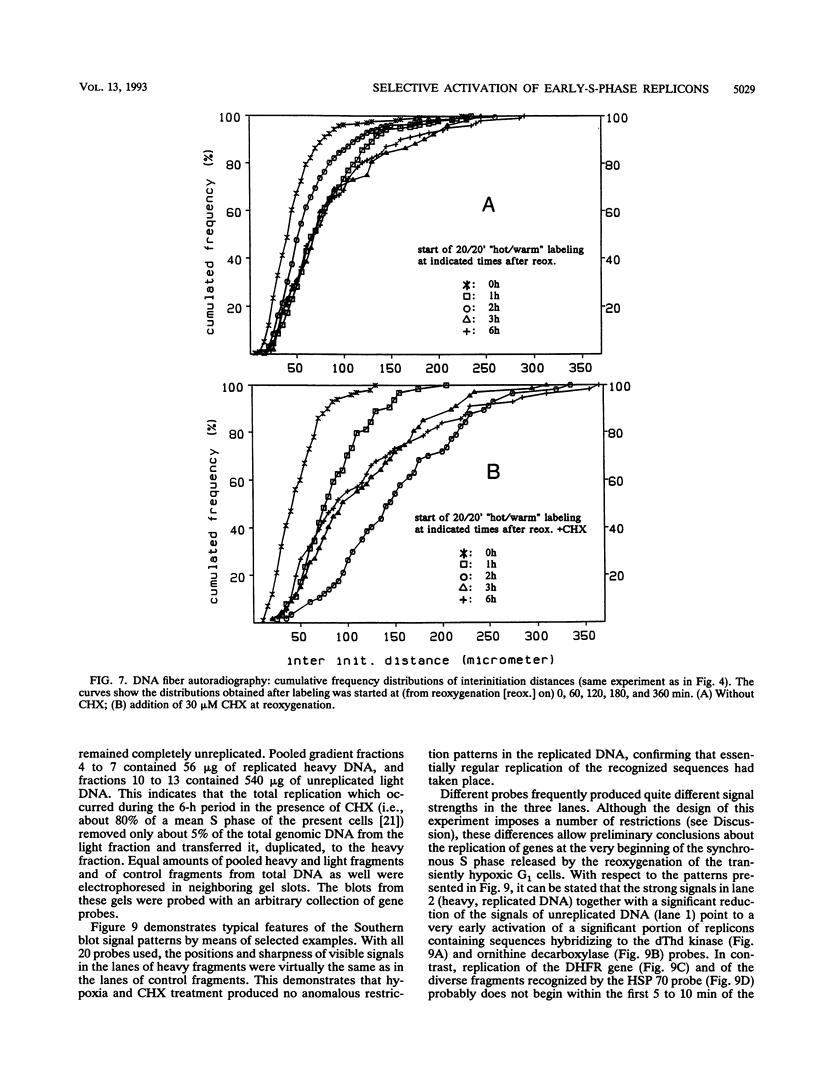
Twelve-hour exposure of G1 Ehrlich ascites cells to controlled hypoxia (200 ppm of O2 at 1 bar) suppressed replicon initiation. Synchronous cycling, beginning with a normal S phase, was released by reoxygenation immediately. The addition of cycloheximide at reoxygenation largely resuppressed, after a short initial burst, succeeding replicon initiations. Alkaline sedimentation analysis of growing daughter strand DNA, DNA fiber autoradiography, and analysis of the newly formed DNA demonstrated that normal chain growth and DNA maturation (replicon termination) in the initially activated replicons continued in the presence of cycloheximide. After 2 to 3 h, a low level of cycloheximide-insensitive background replication emerged out of the then-ebbing single surge of activity of the initially released replicons.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Activation of a Qa/Tla class I major histocompatibility antigen gene is a general feature of oncogenesis in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):756–760. doi: 10.1038/306756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESE G. The respiration of ascites tumour cells at low oxygen concentrations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 12;57:509–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekeler V., Probst H. Synchronization of replicons in Ehrlich ascites cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Mar;175(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R., Tamm I. DNA replication: direction and rate of chain growth in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):410–418. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R., Tamm I. Initiation of DNA replication in mammalian cells and its inhibition by reovirus infection. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 15;82(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton K. S., Dhar V., Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Didamo V. T., Schildkraut C. L. Replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickok N. J., Seppänen P. J., Kontula K. K., Jänne P. A., Bardin C. W., Jänne O. A. Two ornithine decarboxylase mRNA species in mouse kidney arise from size heterogeneity at their 3' termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):594–598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer R., Müllner E., Seiser C., Wintersberger E. Cell cycle regulated synthesis of stable mouse thymidine kinase mRNA is mediated by a sequence within the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):741–752. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Horwitz H. Discontinuous DNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:233–238. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARZEL K. UBER EINEN IN VITRO IN SUSPENSION WACHSENDEN PERMENENTEN STAMM VON EHRLICH-ASCITESTUMORZELLEN. Med Pharmacol Exp Int J Exp Med. 1965;12:137–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsén K., Granzow C. Chromosome band patterns of near tetraploid Ehrlich-Lettré mouse ascites cells (ELT Bonn) in vivo and in vitro. Hereditas. 1983;98(1):95–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1983.tb00584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K., Mauron A., Barchas J. D., Kedes L. Constitutively expressed rat mRNA encoding a 70-kilodalton heat-shock-like protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3476–3483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Blütters R., Fielitz J. DNA replication in asynchronous and synchronous Ehrlich ascites cells in different conditions of growth. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Nov;130(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Gekeler V., Helftenbein E. Oxygen dependence of nuclear DNA replication in Ehrlich ascites cells. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Oct;154(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Gekeler V. Reversible inhibition of replicon initiation in Ehrlich ascites cells by anaerobiosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Hofstaetter T., Jenke H. S., Gentner P. R., Müller-Scholz D. Metabolism and non-random occurrence of nonnascent short chains in the DNA of Ehrlich ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 24;740(2):200–211. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Maisenbacher J. Use of zonal centrifugation for preparing synchronous cultures from Ehrlich ascites cells grown in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Apr;78(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Schiffer H., Gekeler V., Kienzle-Pfeilsticker H., Stropp U., Stötzer K. E., Frenzel-Stötzer I. Oxygen dependent regulation of DNA synthesis and growth of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 15;48(8):2053–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Schiffer H., Gekeler V., Scheffler K. Oxygen dependent regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase in vivo and possible significance for replicon initiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):334–340. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedinger H. J., Gekeler V., Probst H. Reversible shutdown of replicon initiation by transient hypoxia in Ehrlich ascites cells. Dependence of initiation on short-lived protein. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 1;210(2):389–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte D., Knippers R., Dreier T., Probst G., Probst H. Cycloheximide inhibits cellular, but not SV40, DNA replication. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 9;299(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selig S., Ariel M., Goitein R., Marcus M., Cedar H. Regulation of mouse satellite DNA replication time. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):419–426. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Housman D., Huberman J. A. Effects of inhibition of protein synthesis on DNA replication in cultured mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):485–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Gekeler V., McIvor R. S., Martin D. W., Jr A human purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency caused by a single base change. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2332–2338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]