Abstract
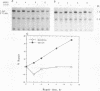
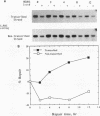
This report describes an unexpected difference in the efficiency of removal of UV-induced DNA damage in the c-myc locus in splenic B lymphoblasts from two inbred strains of mice. In cells from plasmacytoma-resistant DBA/2N mice, 35% of UV-induced damage in the regulatory and 5' flank of c-myc is removed by 12 h. However, in cells from plasmacytoma-susceptible BALB/cAn mice, damage is not removed from this region. In the protein-encoding region and 3' flank of c-myc as well as in two dihydrofolate reductase gene fragments, UV damage is repaired with similar efficiency in B lymphoblasts from both strains of mice. Furthermore, in the protein-encoding portion and 3' flank of c-myc, damage is selectively removed from only the transcribed strand. No repair is detected in the nontranscribed strand. In contrast, DNA repair in the 5' flank of c-myc is not strand specific; in DNA from DBA/2N cells, UV damage is rapidly removed from both the transcribed and nontranscribed strands. In BALB/cAn cells no repair was detected in either strand in the 5'flank, consistent with the results with double-stranded, nick-translated probes to this region of c-myc. In addition to the repair studies, we have detected post-UV-damage formation: in most of the genes studied, we find that additional T4 endonuclease-sensitive sites are formed in the DNA 2 h after irradiation. Our findings provide new insights into the details of gene-specific and strand-specific DNA repair and suggest that there may be close links between DNA repair and B-cell neoplastic development.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer S. R., Piechaczyk M., Nordan R. P., Owens J. D., Nepveu A., Marcu K. B., Mushinski J. F. Altered myc gene transcription and intron-induced stabilization of myc RNAs in two mouse plasmacytomas. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):615–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Evans M. K., Fornace A. J., Jr DNA repair and its pathogenetic implications. Lab Invest. 1989 Aug;61(2):143–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Okumoto D. S., Ho L., Hanawalt P. C. Characterization of a DNA repair domain containing the dihydrofolate reductase gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16666–16672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Smith C. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. DNA repair in an active gene: removal of pyrimidine dimers from the DHFR gene of CHO cells is much more efficient than in the genome overall. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Leys E. J., McEwan R. N., Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Analysis of the mouse dhfr promoter region: existence of a divergently transcribed gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1847–1858. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Shell B. E., Dery C. DNA sequences near the site of reciprocal recombination between a c-myc oncogene and an immunoglobulin switch region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7269–7273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A. The scid mutation in mice causes a general defect in DNA repair. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):479–482. doi: 10.1038/347479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindy M. S., McCormack J. E., Buckler A. J., Levine R. A., Sonenshein G. E. Independent regulation of transcription of the two strands of the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2857–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Ravetch J. V., Kwan S. P., Max E. E., Ney R. L., Leder P. Multiple immunoglobulin switch region homologies outside the heavy chain constant region locus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):585–587. doi: 10.1038/293585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leadon S. A., Snowden M. M. Differential repair of DNA damage in the human metallothionein gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5331–5338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Bohr V. A., Hanawalt P. C. Differential DNA repair in transcriptionally active and inactive proto-oncogenes: c-abl and c-mos. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B. Regulation of expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene. Bioessays. 1987 Jan;6(1):28–32. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Hanawalt P. C. Induction of the Escherichia coli lactose operon selectively increases repair of its transcribed DNA strand. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):95–98. doi: 10.1038/342095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Spivak G., Hanawalt P. C. Selective removal of transcription-blocking DNA damage from the transcribed strand of the mammalian DHFR gene. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullenders L. H., van Kesteren van Leeuwen A. C., van Zeeland A. A., Natarajan A. T. Nuclear matrix associated DNA is preferentially repaired in normal human fibroblasts, exposed to a low dose of ultraviolet light but not in Cockayne's syndrome fibroblasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10607–10622. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumoto D. S., Bohr V. A. DNA repair in the metallothionein gene increases with transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10021–10030. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Sanford K. K., Parshad R., Huppi K., Mock B. Susceptibility and resistance to plasmacytomagenesis: possible role of genes that modify efficiency of chromatin repair. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;137:289–294. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50059-6_43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford K. K., Parshad R., Potter M., Jones G. M., Nordan R. P., Brust S. E., Price F. M. Chromosomal radiosensitivity during G2 phase and susceptibility to plasmacytoma induction in mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;132:202–208. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71562-4_29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacter E., Beecham E. J., Covey J. M., Kohn K. W., Potter M. Activated neutrophils induce prolonged DNA damage in neighboring cells. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Dec;9(12):2297–2304. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.12.2297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Watt R., Marcu K. B. Translocation, breakage and truncated transcripts of c-myc oncogene in murine plasmacytomas. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):401–406. doi: 10.1038/303401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stedman H., Browning K., Oliver N., Oronzi-Scott M., Fischbeck K., Sarkar S., Sylvester J., Schmickel R., Wang K. Nebulin cDNAs detect a 25-kilobase transcript in skeletal muscle and localize to human chromosome 2. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleth C., van Sluis C. A., van de Putte P. Differential repair of UV damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4433–4439. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Okumoto D. S., Sancar A., Bohr V. A. Preferential DNA repair of (6-4) photoproducts in the dihydrofolate reductase gene of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18005–18010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Q., Remmers E. F., Marcu K. B. The first exon of the c-myc proto-oncogene contains a novel positive control element. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3553–3562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]