Abstract
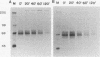
The rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC12 can be induced by growth factors to undergo proliferation and neuronal differentiation. These cells also have excitable membranes that can be depolarized by neurotransmitters or elevated levels of extracellular KCl. Treatment of PC12 cells with growth factors or membrane-depolarizing agents rapidly activates the expression of specific genes whose products are thought to mediate the subsequent biological responses. One such gene, nur77, is a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor gene superfamily. We have identified the Nur77 protein and shown that it is synthesized rapidly and transiently in PC12 cells following stimulation, has a short half-life of 30 to 40 min, and is located in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nur77 is posttranslationally modified, primarily by phosphorylation on serine residues. Phosphopeptide analysis reveals that Nur77 is modified differently upon membrane depolarization than after treatment with growth factors. We hypothesize that the activity of Nur77 is regulated by both differential gene expression and posttranslational modification and that these modes of regulation contribute to distinct downstream responses specific to membrane depolarization and growth factor treatment.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of protein kinase activities in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Tjian R. Biochemical analysis of transcriptional activation by Jun: differential activity of c- and v-Jun. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Moolenaar W. H., Harrison P. H., Moed P., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Ionic responses and growth stimulation induced by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):92–98. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill A. L., Horwitz J., Perlman R. L. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in protein kinase C-deficient PC12 cells. Neuroscience. 1989;30(3):811–818. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson-Jurica M. A., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990 May;11(2):201–220. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Barium modulates c-fos expression and post-translational modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8521–8524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP6, a yeast nuclear gene necessary for synthesis of cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., Trifiro M. A., Plante R. K., Nemer M., Eriksson P., Wrange O. Glucocorticoid receptor binding to a specific DNA sequence is required for hormone-dependent repression of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5305–5314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner T. J., Carroll S. L., Milbrandt J. The NGFI-B protein, an inducible member of the thyroid/steroid receptor family, is rapidly modified posttranslationally. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6454–6459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glineur C., Zenke M., Beug H., Ghysdael J. Phosphorylation of the v-erbA protein is required for its function as an oncogene. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1663–1676. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Gilna P., Waterfield M., Baker A., Hort Y., Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1150–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.3753802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in situ at serine 8, 19, 31, and 40. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11682–11691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazel T. G., Nathans D., Lau L. F. A gene inducible by serum growth factors encodes a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8444–8448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R. Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:281–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Vesque C., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Frank R., Charnay P. The serum-inducible mouse gene Krox-24 encodes a sequence-specific transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3456–3467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. Nerve growth factor induces a gene homologous to the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylin L. M., Bhat J. P., Hopper J. E. Regulated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of GAL4, a transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1157–1165. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Müller D., Kurz C., Renz M. Different types of modification in c-fos and its associated protein p39: modulation of DNA binding by phosphorylation. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):19–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):80–82. doi: 10.1038/348080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Stanton L., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Human proto-oncogene N-myc encodes nuclear proteins that bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4450–4457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Macdonald-Bravo H., Mattéi M. G., Ruppert S., Bravo R. Structure, mapping and expression of a growth factor inducible gene encoding a putative nuclear hormonal binding receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3327–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. D., Helms S., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Rottman F. M., Yamamoto K. R. Hormone-mediated repression: a negative glucocorticoid response element from the bovine prolactin gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1144–1154. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., McFadden G., Greenberg M. E. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):571–582. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90115-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]