Abstract
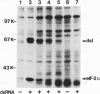
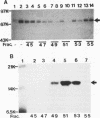
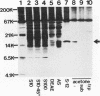
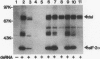
The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 alpha kinase (dsI) has an established role in mediating part of interferon's antiviral effects. Numerous studies have suggested that dsI also has regulatory functions in cells not infected with virus. Our previous results have indicated that the activation of this kinase may be an important regulatory signal in controlling growth arrest of mouse 3T3-F442A fibroblasts prior to their subsequent differentiation to adipocytes. Here, we report that extracts from 3T3-F442A cells cultured under conditions nonpermissive for differentiation exhibit significantly reduced dsI activity and that this reduction is due, at least in part, to the presence of elevated levels of a novel inhibitor of dsI activation (dRF). This inhibitor is also detected in reduced amounts in extracts from cells cultured under conditions which are permissive for differentiation. We have achieved a 1,000-fold purification of dRF activity, and highly purified dRF preparations were found to be greatly enriched for a 15-kDa protein that was greater than 90% pure. Our results indicate that dRF is not a protein phosphatase or protease but a reversible inhibitor of dsI autophosphorylation. In addition, our results imply that dRF is a physiologic regulator of dsI, since dRF activity correlates with the ability of 3T3-F442A cells to undergo adipose conversion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkaraju G. R., Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S., Jagus R. Vaccinia specific kinase inhibitory factor prevents translational inhibition by double-stranded RNA in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10321–10325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amri E. Z., Dani C., Doglio A., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Coupling of growth arrest and expression of early markers during adipose conversion of preadipocyte cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):903–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Levin D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase stimulation by terminal uridylyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7628–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. A., Sharp N. A., Arrand J. R., Clemens M. J. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in interferon-treated cells. Implications for the regulation of protein synthesis and the antiviral state. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90161-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., McNurlan M. A. Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by interferons. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2260345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of mRNA binding to ribosomes by localized activation of dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):79–81. doi: 10.1038/311079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann B., Imbault P., Weil J. H. Spectrophotometric determination of protein concentration in cell extracts containing tRNA's and rRNA's. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exley R., Gordon J., Nathan P., Walker L., Clemens M. J. Anti-proliferative effects of interferons on Daudi Burkitt lymphoma cells: induction of cell differentiation and loss of response to autocrine growth factors. Int J Cancer. 1987 Jul 15;40(1):53–57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. Formation of normally differentiated subcutaneous fat pads by an established preadipose cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Oct;101(1):169–171. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. Spontaneous heritable changes leading to increased adipose conversion in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keay S., Grossberg S. E. Interferon inhibits the conversion of 3T3-L1 mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4099–4103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawisz B. R., Scott R. E. Coupling of proadipocyte growth arrest and differentiation. I. Induction by heparinized medium containing human plasma. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):394–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuri-Harcuch W., Green H. Adipose conversion of 3T3 cells depends on a serum factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6107–6109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Characterization of purified double-stranded RNA-activated eIF-2 alpha kinase from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7638–7641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis: activation by double-stranded RNA of a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1121–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Petryshyn R. A. Activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 alpha kinase by cellular RNA from 3T3-F442A cells. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 1;195(1):41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R. Silver staining of proteins and DNA. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):779–780. doi: 10.1038/343779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Chong K., Galabru J., Thomas N. S., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pairault J., Green H. A study of the adipose conversion of suspended 3T3 cells by using glycerophosphate dehydrogenase as differentiation marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5138–5142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Detection of activated double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3-F442A cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Growth-related expression of a double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14736–14742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Levin D. H., London I. M. Double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2alpha protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:346–362. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Levin D. H., London I. M. Regulation of double-stranded RNA-activated eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase by type 2 protein phosphatase in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6512–6516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Yarden A., Zipori D., Kimchi A. Autocrine beta-related interferon controls c-myc suppression and growth arrest during hematopoietic cell differentiation. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90857-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 in interferon-treated human cells by a ribosome-associated kinase processing site specificity similar to hemin-regulated rabbit reticulocyte kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):600–604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. L., Nilson L. A. Activation of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity on induction of HL-60 leukemia cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3897–3903. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Hoerl B. J., Wille J. J., Jr, Florine D. L., Krawisz B. R., Yun K. Coupling of proadipocyte growth arrest and differentiation. II. A cell cycle model for the physiological control of cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):400–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer M., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Regulation of cell growth by interferon. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1987;6(3):199–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00144264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyszka R., Kudlicki W., Kramer G., Hardesty B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. A type 1 phosphoprotein phosphatase active with phosphorylated Mr = 68,000 initiation factor 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3827–3831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. L., Samuel C. E., Grossberg S. E. Antiviral and antidifferentiative activities of interferon beta and gamma in relation to their induction of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1336–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Ranu R. S., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: purification and characterization of heme-reversible translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3654–3658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallano M. L. Separation of isozymic forms of type II calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase using cation-exchange chromatography. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Oct;30(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise L. S., Green H. Participation of one isozyme of cytosolic glycerophosphate dehydrogenase in the adipose conversion of 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):273–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]