Abstract
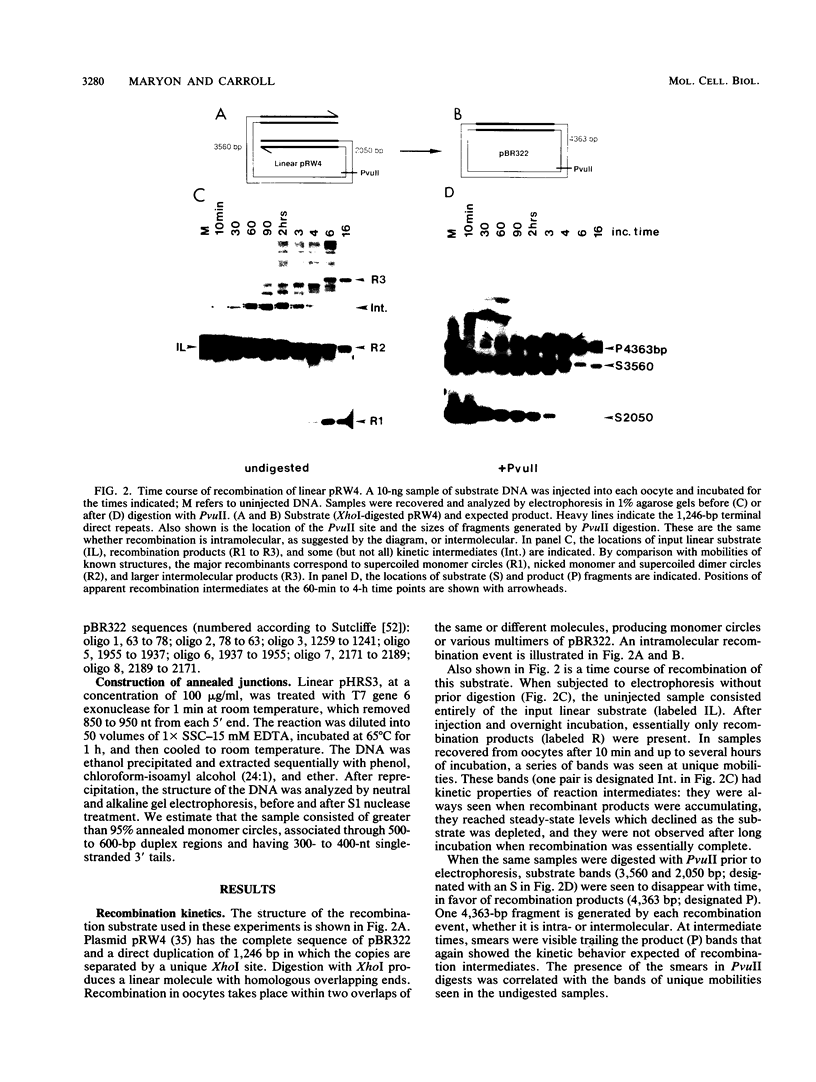
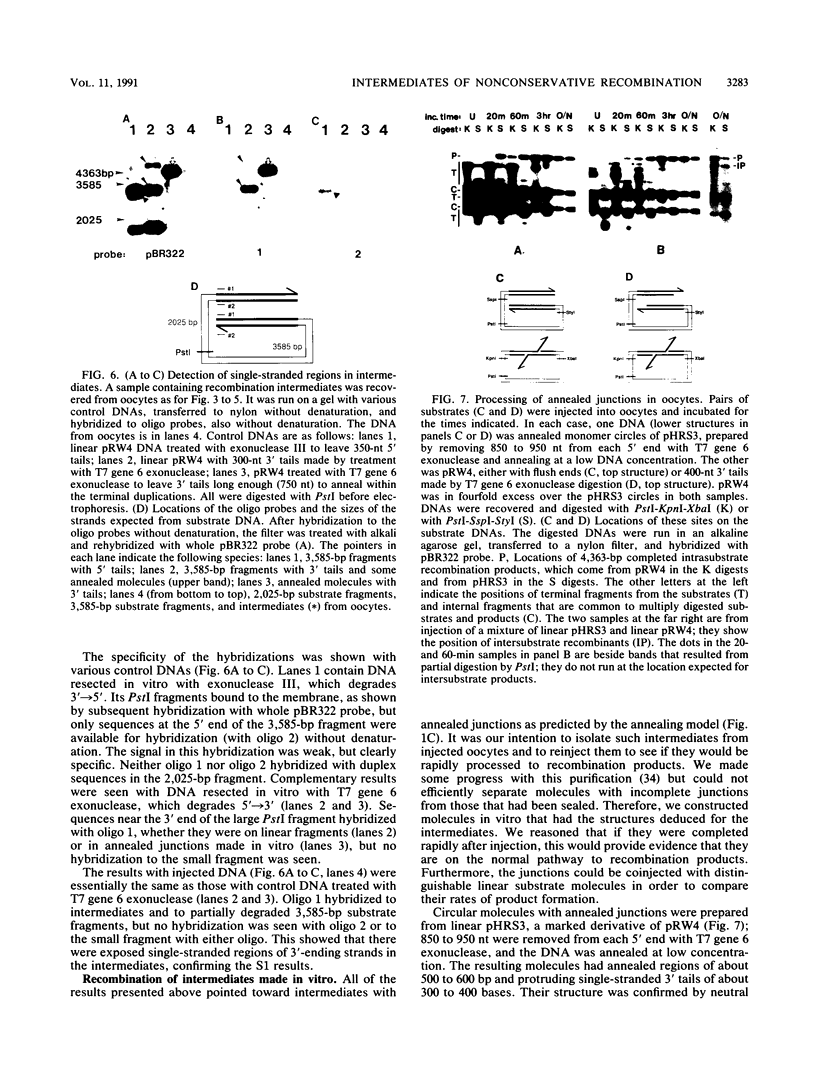
Homologous recombination between DNA molecules injected into Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei is extremely efficient if injected molecules have overlapping homologous ends. Earlier work demonstrated that ends of linear molecules are degraded by a 5'----3' exonuclease activity, yielding 3' tails that participate in recombination. Here, we have characterized intermediates further advanced along the recombination pathway. The intermediates were identified by their unique electrophoretic and kinetic properties. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and hybridization with oligonucleotide probes showed that the intermediates had heteroduplex junctions within their homologous overlaps in which strands ending 3' were full length and those ending 5' were shortened. Additional characterization suggested that these intermediates had formed by the annealing of complementary 3' tails. Annealed junctions made in vitro were rapidly processed to products, indicating that they are on the normal recombination pathway. These results support a nonconservative, single-strand annealing mode of recombination. This recombination mechanism appears to be shared by many organisms, including bacteria, fungi, plants, and mammals.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Eliason S. L. Recombination of homologous DNA fragments transfected into mammalian cells occurs predominantly by terminal pairing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3246–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur M., Potrykus I., Paszkowski J. Intermolecular homologous recombination in plants. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Alani E., Kleckner N. A pathway for generation and processing of double-strand breaks during meiotic recombination in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1089–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90072-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D. Genetic recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6902–6906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Wright S. H., Wolff R. K., Grzesiuk E., Maryon E. B. Efficient homologous recombination of linear DNA substrates after injection into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2053–2061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto E., Lash T., Sriprakash K. S., Radding C. M. Role of exonuclease and beta protein of phage lambda in genetic recombination. V. Recombination of lambda DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1639–1643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto E., Radding C. M. Mechanism for the action of lambda exonuclease in genetic recombination. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 6;229(1):13–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio229013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Williams K. R. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins required for DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:103–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Recombination deficient mutants of E. coli and other bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:67–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Mechanism of transposition of bacteriophage Mu: structure of a transposition intermediate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):867–876. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty M. J., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA. Physical and genetic analysis of the products of plasmid recombination in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):539–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R. A., Detmer K., Rich A. Identification of homologous pairing and strand-exchange activity from a human tumor cell line based on Z-DNA affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Thomas K., Capecchi M. R. Nonreciprocal exchanges of information between DNA duplexes coinjected into mammalian cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formosa T., Alberts B. M. DNA synthesis dependent on genetic recombination: characterization of a reaction catalyzed by purified bacteriophage T4 proteins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):793–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90522-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganea D., Moore P., Chekuri L., Kucherlapati R. Characterization of an ATP-dependent DNA strand transferase from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3124–3130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzesiuk E., Carroll D. Recombination of DNAs in Xenopus oocytes based on short homologous overlaps. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):971–985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Melton D. A. Gene transfer in amphibian eggs and oocytes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:189–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Untwisting B-Z DNA. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):355–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Camerini-Otero R. D. Formation of joint DNA molecules by two eukaryotic strand exchange proteins does not require melting of a DNA duplex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5089–5097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Meyn M. S., Camerini-Otero R. D. Partial purification and characterization of a recombinase from human cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohne D. E., Levison S. A., Byers M. J. Room temperature method for increasing the rate of DNA reassociation by many thousandfold: the phenol emulsion reassociation technique. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5329–5341. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Evans D. H., Morrison P. T. Purification and characterization of an activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that catalyzes homologous pairing and strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichten M., Goyon C., Schultes N. P., Treco D., Szostak J. W., Haber J. E., Nicolas A. Detection of heteroduplex DNA molecules among the products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Intermolecular recombination between DNAs introduced into mouse L cells is mediated by a nonconservative pathway that leads to crossover products. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Repair of double-stranded DNA breaks by homologous DNA fragments during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Degradation of linear DNA by a strand-specific exonuclease activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4862–4871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Involvement of single-stranded tails in homologous recombination of DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3268–3277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosig G. The essential role of recombination in phage T4 growth. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:347–371. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Fungal recombination. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):33–58. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.33-58.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. A., West S. C. Resolution of model Holliday junctions by yeast endonuclease is dependent upon homologous DNA sequences. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90474-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA; a model involving recombination. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jun;59(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Bird A., Barkken A. Ribosomal RNA gene amplification by rolling circles. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):473–487. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin N., Haber J. E. Efficient repair of HO-induced chromosomal breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by recombination between flanking homologous sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3918–3928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin N., Sugarman E., Haber J. E. Genetic and physical analysis of double-strand break repair and recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):519–534. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M. Intermolecular homologous recombination between transfected sequences in mammalian cells is primarily nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3561–3565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Homologous recombination in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):1–28. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.1-28.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., Kobayashi I., Stahl M. M. In phage lambda, cos is a recombinator in the red pathway. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Double-strand breaks at an initiation site for meiotic gene conversion. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):87–90. doi: 10.1038/338087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Morrison P., Kolodner R. Intramolecular recombination of linear DNA catalyzed by the Escherichia coli RecE recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler D. S., Stahl F. W. DNA double-chain breaks in recombination of phage lambda and of yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:169–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. A., Jr Recombination of DNA molecules. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1966;5:315–337. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. Processing of recombination intermediates in vitro. Bioessays. 1990 Apr;12(4):151–154. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. I., Haber J. E. Intermediates of recombination during mating type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):663–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler M. K., Marini N. J., Stowers D. J., Benbow R. M. Stockpiling of DNA polymerases during oogenesis and embryogenesis in the frog, Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]