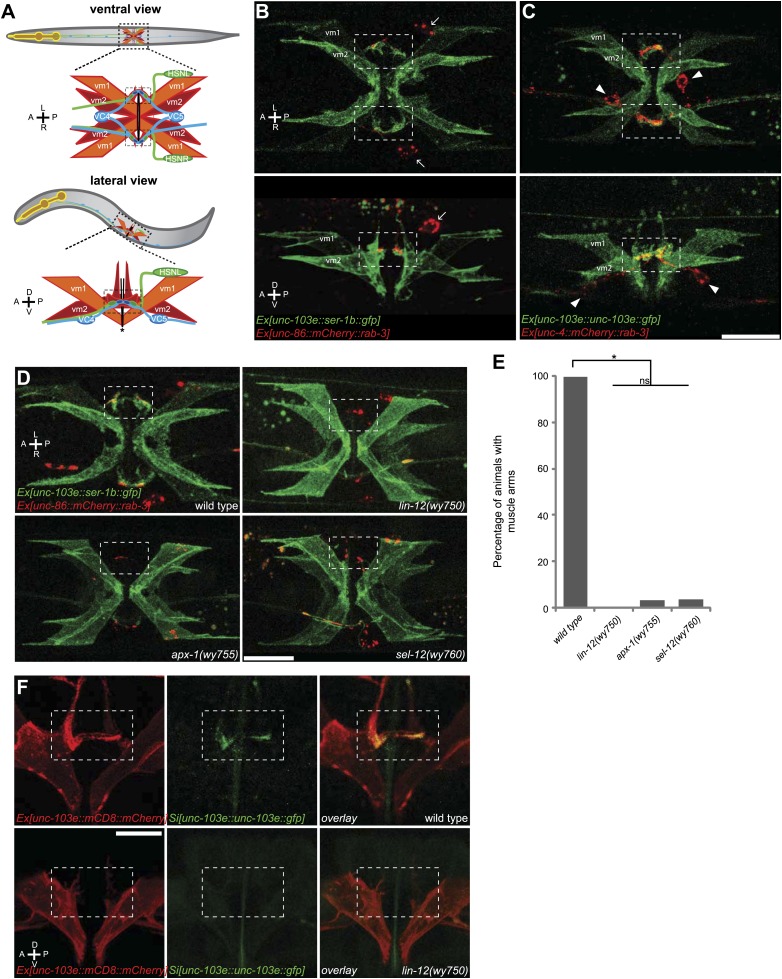
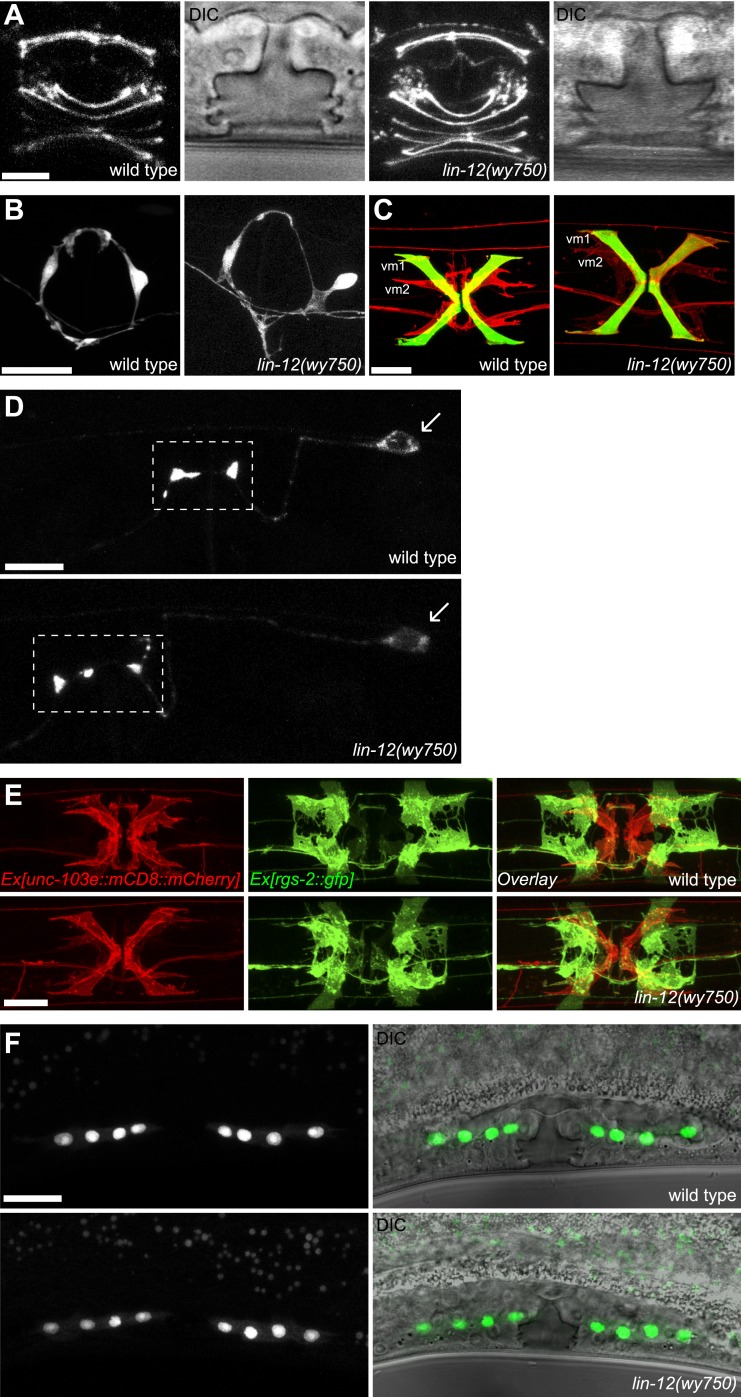
Figure 1. The muscle arms of type 2 vulval muscles (vm2) are missing in lin-12(wy750), apx-1(wy755) and sel-12(wy760) mutants.
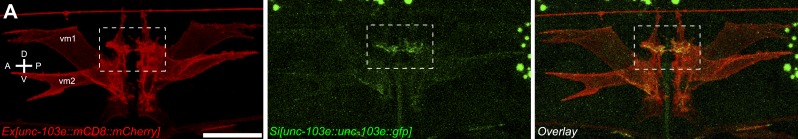
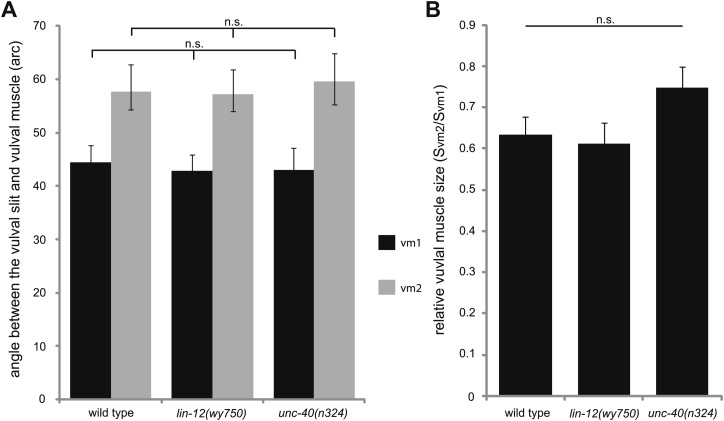
(A) An illustration showing ventral (top) and lateral (bottom) views of C. elegans egg-laying circuit. vm1 (orange) and vm2 (red) are vulval muscles. HSN (green) and VC4/5 (blue) are presynaptic motoneurons. Each of the four vm2 cells extends a dendritic spine-like muscle arm laterally, on which it receives synapses with HSN and VC neurons (boxed areas). Top row of (A–C) are ventral views; bottom row of (A–C) are left lateral views. Anterior (A), posterior (P), left (L), right (R), dorsal (D), ventral (V). (B) Ventral (top) and lateral (bottom) views of vulval muscles labeled by SER-1B::GFP transgene in a young adult. HSN neurons are labeled by a mCherry::RAB-3 transgene. The boxed areas indicate synaptic regions. Arrows indicate the HSN cell bodies. Note that the laterally extended muscle arms on vm2 cells are colocalized with the HSN presynaptic specializations. (C) Ventral (top) and lateral (bottom) views of vulval muscles labeled by a UNC-103E::GFP transgene and VC4/5 neurons labeled by a mCherry::RAB-3 transgene. The boxed areas indicate synaptic regions. Arrowheads indicate cell bodies of VC4 and VC5. Note that the laterally extended muscle arms on vm2 cells are colocalized with the VC4/5 presynaptic specializations. Scale bar is 20 μm. (D) Ventral views of the vulval muscles and presynaptic regions of HSN neurons in wild-type, lin-12(wy750), apx-1(wy755) and sel-12(wy760) animals. The boxed areas indicate synaptic regions. Note the absence of vm2 muscle arms in mutants. Scale bar is 20 μm. (E) Quantification of the vm2 muscle arm defects in wild-type, lin-12(wy750), apx-1(wy755) and sel-12(wy760) animals. * p<0.0001, n.s. no significant difference, chi-squared test, n = 90–114 animals. (F) High magnification lateral views of the synaptic region in wild type and lin-12(wy750). vm2 muscle arms are visualized by a single-copy UNC-103E::GFP transgene. Vulval muscle morphology is labeled by mCD8::mCherry. The boxed areas indicate synaptic regions. Scale bar is 10 μm.