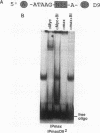
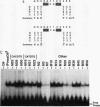
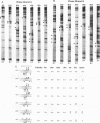
Abstract
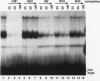
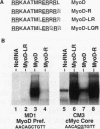
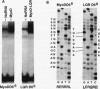
Using an in vitro binding-site selection assay, we have demonstrated that c-Myc-Max complexes bind not only to canonical CACGTG or CATGTG motifs that are flanked by variable sequences but also to noncanonical sites that consist of an internal CG or TG dinucleotide in the context of particular variations in the CA--TG consensus. None of the selected sites contain an internal TA dinucleotide, suggesting that Myc proteins necessarily bind asymmetrically in the context of a CAT half-site. The noncanonical sites can all be bound by proteins of the Myc-Max family but not necessarily by the related CACGTG- and CATGTG-binding proteins USF and TFE3. Substitution of an arginine that is conserved in these proteins into MyoD (MyoD-R) changes its binding specificity so that it recognizes CACGTG instead of the MyoD cognate sequence (CAGCTG). However, like USF and TFE3, MyoD-R does not bind to all of the noncanonical c-Myc-Max sites. Although this R substitution changes the internal dinucleotide specificity of MyoD, it does not significantly alter its wild-type binding sequence preferences at positions outside of the CA--TG motif, suggesting that it does not dramatically change other important amino acid-DNA contacts; this observation has important implications for models of basic-helix-loop-helix protein-DNA binding.
Full text
PDF

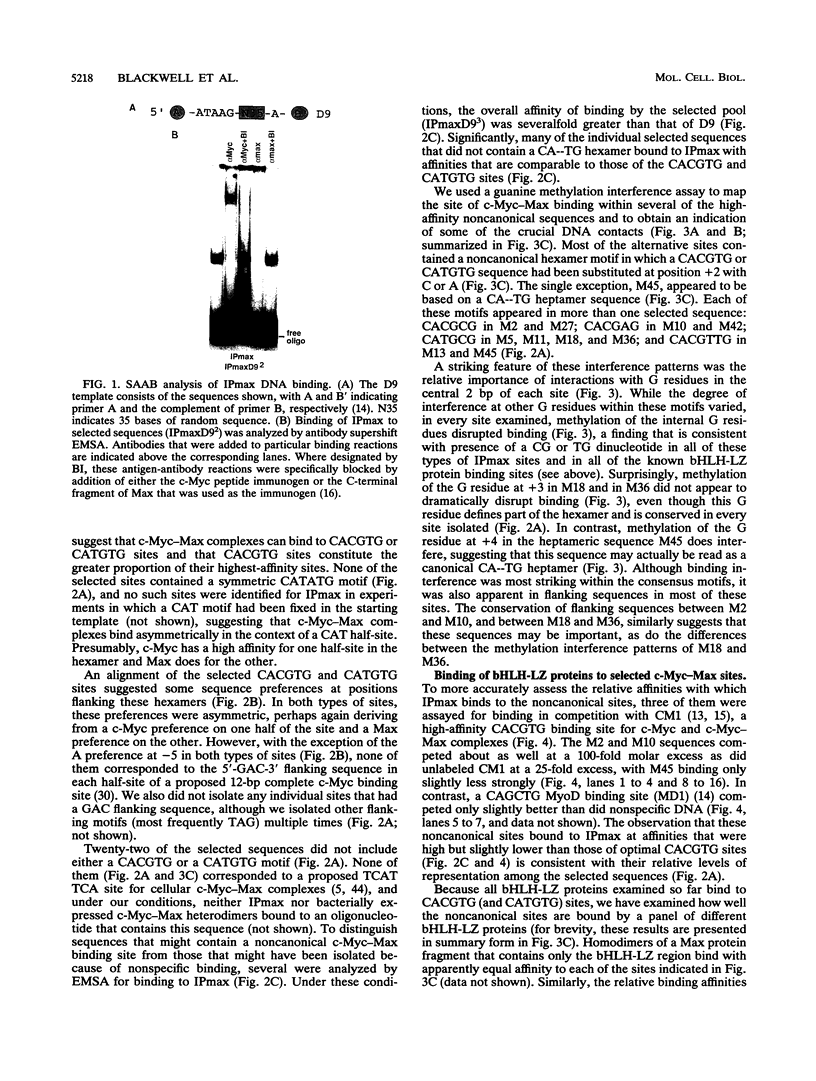





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alex R., Sözeri O., Meyer S., Dildrop R. Determination of the DNA sequence recognized by the bHLH-zip domain of the N-Myc protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2257–2263. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Brooks M. W., Levy N., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Oncogenic activity of the c-Myc protein requires dimerization with Max. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90663-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony-Cahill S. J., Benfield P. A., Fairman R., Wasserman Z. R., Brenner S. L., Stafford W. F., 3rd, Altenbach C., Hubbell W. L., DeGrado W. F. Molecular characterization of helix-loop-helix peptides. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):979–983. doi: 10.1126/science.1312255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Imamura Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. DNA replication origin and transcriptional enhancer in c-myc gene share the c-myc protein binding sequences. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4273–4279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Kadesch T. The leucine zipper of TFE3 dictates helix-loop-helix dimerization specificity. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1057–1066. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Leder A., Kuo A., Leder P. An embryonically expressed gene is a target for c-Myc regulation via the c-Myc-binding sequence. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2513–2523. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S. J., Cole M. D. Casein kinase II inhibits the DNA-binding activity of Max homodimers but not Myc/Max heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):166–176. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S., Hyde-DeRuyscher N., Espenshade P., Cole M. max encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein and is not regulated by serum growth factors. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collum R. G., Alt F. W. Are myc proteins transcription factors? Cancer Cells. 1990 Mar;2(3):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Dolde C., Gillison M. L., Kato G. J. Discrimination between related DNA sites by a single amino acid residue of Myc-related basic-helix-loop-helix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):599–602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Carr C. S., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. TFEB has DNA-binding and oligomerization properties of a unique helix-loop-helix/leucine-zipper family. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2342–2352. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. High affinity DNA-binding Myc analogs: recognition by an alpha helix. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher F., Goding C. R. Single amino acid substitutions alter helix-loop-helix protein specificity for bases flanking the core CANNTG motif. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4103–4109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Determination of the c-MYC DNA-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Predicted structural similarities of the DNA binding domains of c-Myc and endonuclease Eco RI. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.1734524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoff E., Bister K., Klempnauer K. H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by Myc proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4323–4327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma A., Moroy T., Collum R., Weintraub H., Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K. DNA binding by N- and L-Myc proteins. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):1093–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee B., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A. Myc family oncoproteins function through a common pathway to transform normal cells in culture: cross-interference by Max and trans-acting dominant mutants. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1480–1492. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Protein complexes bearing myc-like antigenicity recognize two distinct DNA sequences. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Thomas S. J., Loring G. Induction of apoptosis during normal and neoplastic B-cell development in the bursa of Fabricius. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5857–5861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoulas O., Williams N. G., Kingston R. E. DNA binding activities of c-Myc purified from eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10470–10480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Hopewell R., Gorham B. J., Ziff E. B. Biphasic effect of Max on Myc cotransformation activity and dependence on amino- and carboxy-terminal Max functions. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2429–2439. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bach C. Target Detection Assay (TDA): a versatile procedure to determine DNA binding sites as demonstrated on SP1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3203–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze K., Oellers N., Knust E. Enhancer of splitD, a dominant mutation of Drosophila, and its use in the study of functional domains of a helix-loop-helix protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6152–6156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Antwerp M. E., Chen D. G., Chang C., Prochownik E. V. A point mutation in the MyoD basic domain imparts c-Myc-like properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9010–9014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Garcia K. C. Molecular model for DNA recognition by the family of basic-helix-loop-helix-zipper proteins. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):396–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A., Baltimore D. Mutations that disrupt DNA binding and dimer formation in the E47 helix-loop-helix protein map to distinct domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4722–4726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel A., Cziepluch C., Hamann U., Schürmann J., Schwab M. The N-Myc oncoprotein is associated in vivo with the phosphoprotein Max(p20/22) in human neuroblastoma cells. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3703–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]