Abstract
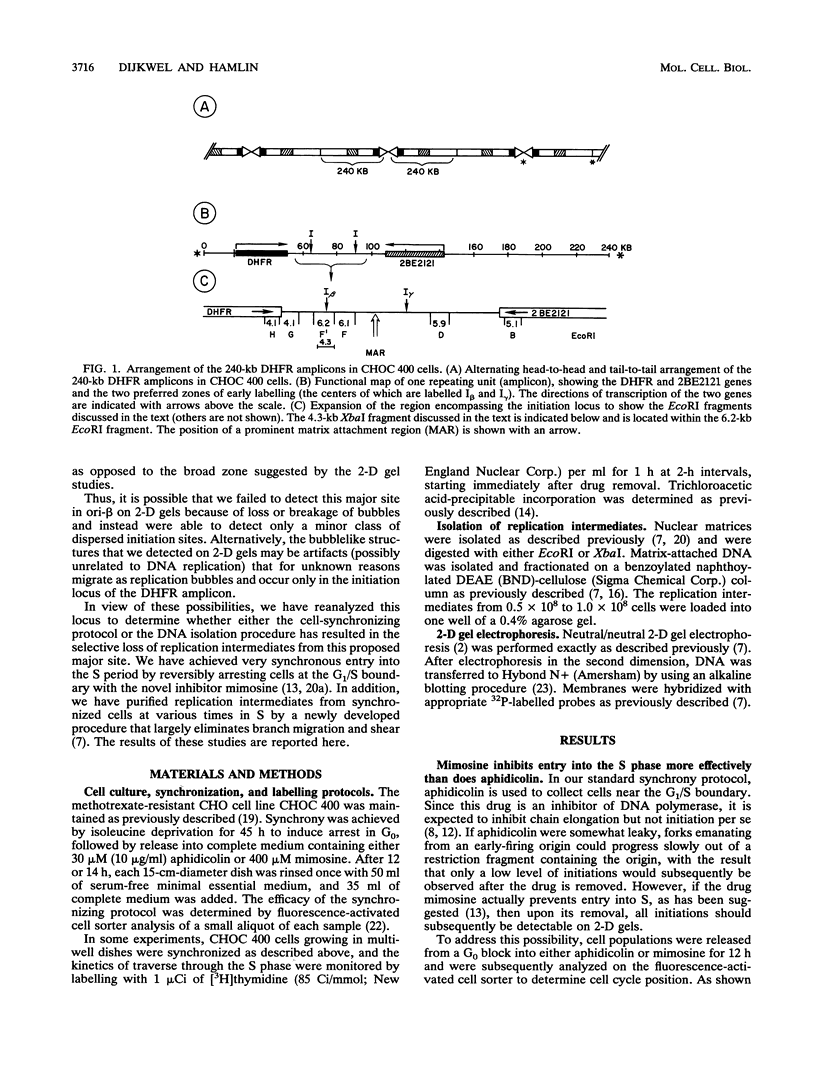
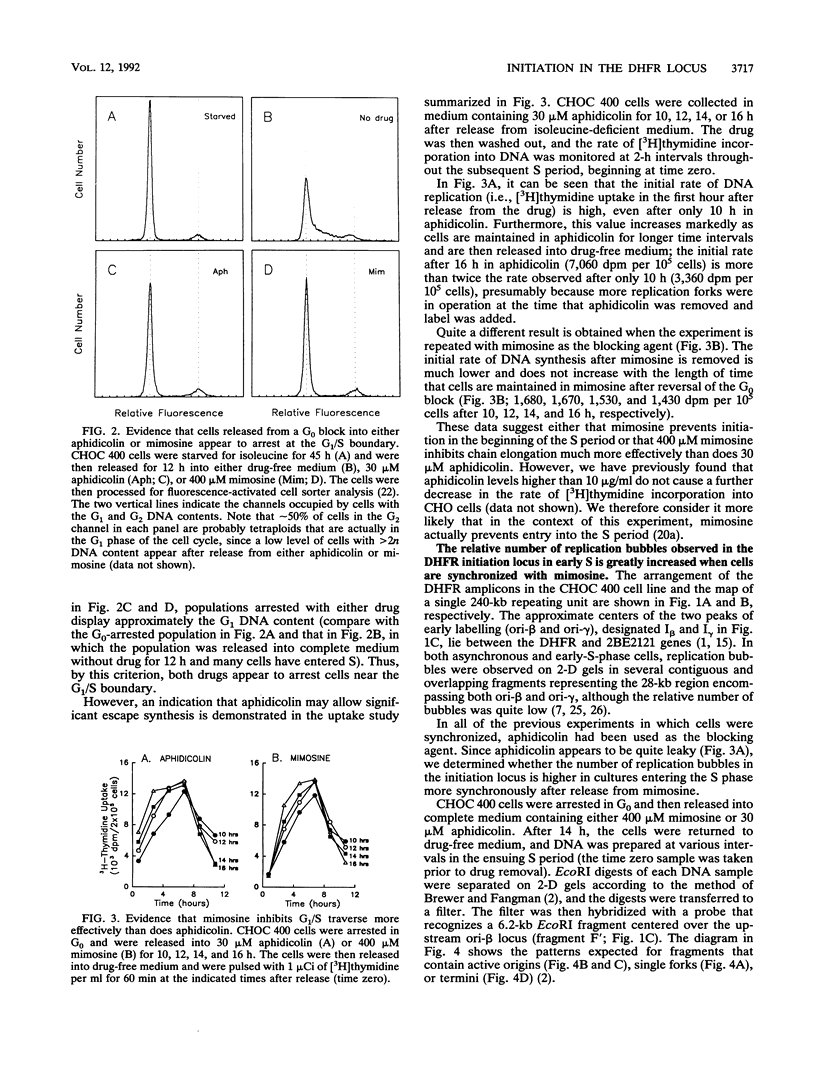
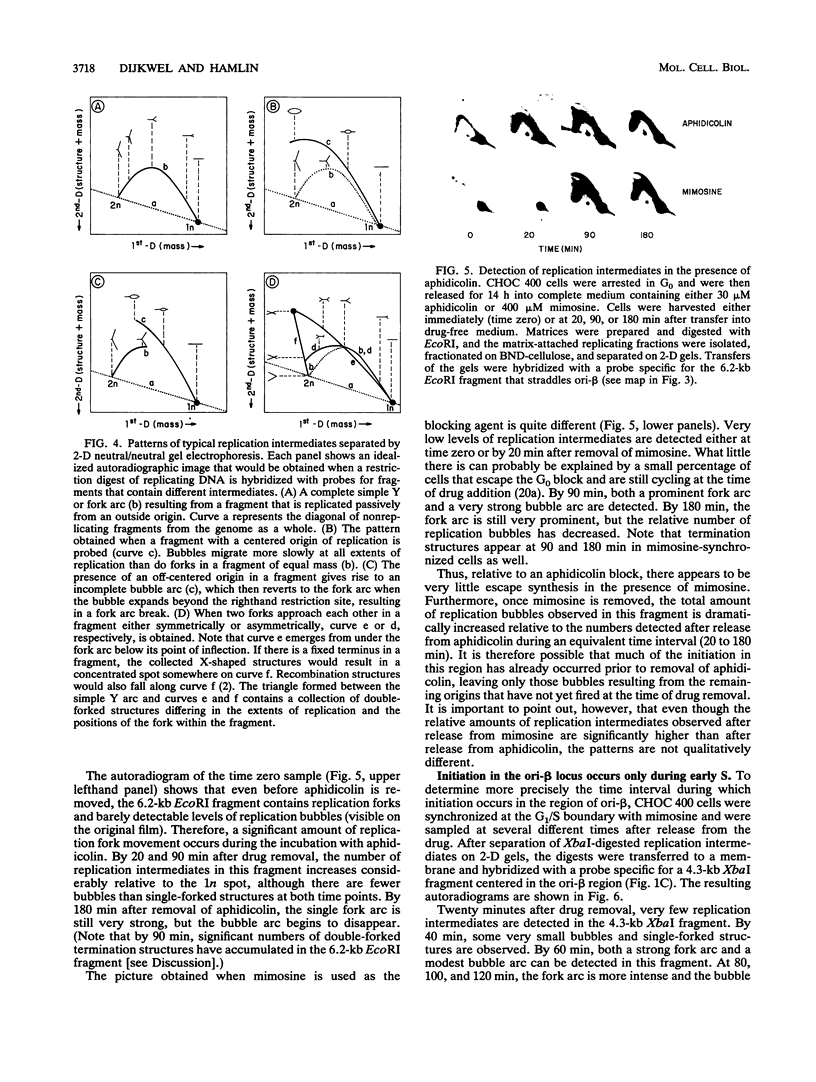
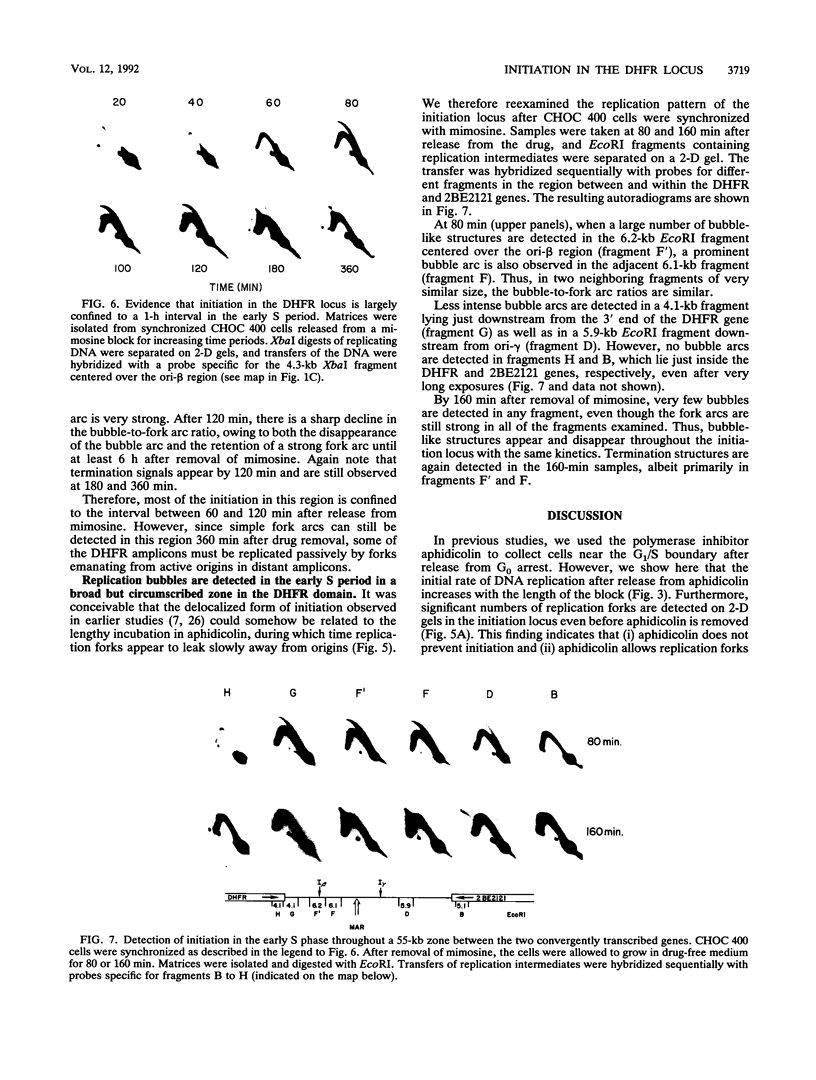
In previous studies, we used two complementary two-dimensional gel electrophoretic methods to examine replication intermediates in the 240-kb amplified dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) domain of methotrexate-resistant CHOC 400 cells (J. P. Vaughn, P. A. Dijkwel, and J. L. Hamlin, Cell 61:1075-1087, 1990). Surprisingly, in both asynchronous and early-S-phase cultures, initiation bubbles were detected in several contiguous fragments from a previously defined 28-kb initiation locus. However, because of the low levels of bubblelike structures observed on gels, it has been suggested that these structures might represent artifacts, possibly unrelated to replication per se. In this study, we have achieved much more synchronous entry into S phase by using a novel inhibitor and have isolated replication intermediates by a new procedure that largely eliminates branch migration and shear. Under these conditions, we find that (i) the relative number of bubblelike structures detected in fragments from the initiation locus is markedly increased, (ii) bubbles are detected at multiple sites scattered throughout the region lying between the DHFR and 2BE2121 genes, and (iii) bubbles appear and disappear in this region with the kinetics expected of an early-firing origin. These data strengthen the proposal that in vivo, initiation can occur at any of a large number of sites scattered throughout a broad zone in the DHFR domain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anachkova B., Hamlin J. L. Replication in the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain in CHO cells may initiate at two distinct sites, one of which is a repetitive sequence element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):532–540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Selegue J. E., Heintz N. H. Isolation of the origin of replication associated with the amplified Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Wu J., Sogo J. M., Nallaseth F. S., DePamphilis M. L. Emetine allows identification of origins of mammalian DNA replication by imbalanced DNA synthesis, not through conservative nucleosome segregation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4351–4360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Matrix attachment regions are positioned near replication initiation sites, genes, and an interamplicon junction in the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5398–5409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter-Gottlieb G., Kaufmann G. Uncoupling of SV40 tsA replicon activation from DNA chain elongation by temperature shifts and aphidicolin arrest. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):763–773. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handeli S., Klar A., Meuth M., Cedar H. Mapping replication units in animal cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Hamlin J. L. An amplified chromosomal sequence that includes the gene for dihydrofolate reductase initiates replication within specific restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Milbrandt J. D., Greisen K. S., Hamlin J. L. Cloning of the initiation region of a mammalian chromosomal replicon. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):439–441. doi: 10.1038/302439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. New views of the biochemistry of eucaryotic DNA replication revealed by aphidicolin, an unusual inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalande M., Hanauske-Abel H. M. A new compound which reversibly arrests T lymphocyte cell cycle near the G1/S boundary. Exp Cell Res. 1990 May;188(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90285-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu T. H., Anachkova B., Hamlin J. L. Repetitive sequence elements in an initiation locus of the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain in CHO cells. Genomics. 1990 Jul;7(3):428–433. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90178-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu T. H., Hamlin J. L. High-resolution mapping of replication fork movement through the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain in CHO cells by in-gel renaturation analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):523–531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Kang H. S., Billheimer F. E. DNA replication in SV40 infected cells. I. Analysis of replicating SV40 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):549–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. The two faces of higher eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):845–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90258-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., White W. C., Rothman S. M., Hamlin J. L. Methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells have amplified a 135-kilobase-pair region that includes the dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6043–6047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawotka K. A., Huberman J. A. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic method for mapping DNA replicons. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1408–1413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K., Rabinovitch P. S., Schwartz S. M. Smooth muscle cell hypertrophy versus hyperplasia in hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7759–7763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B. Detection and mapping of homologous, repeated and amplified DNA sequences by DNA renaturation in agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5413–5431. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






