Abstract
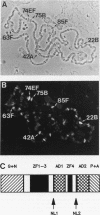
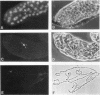
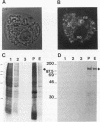
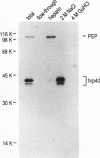
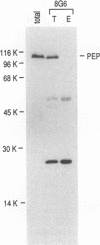
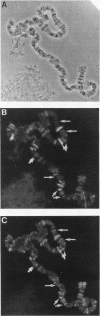
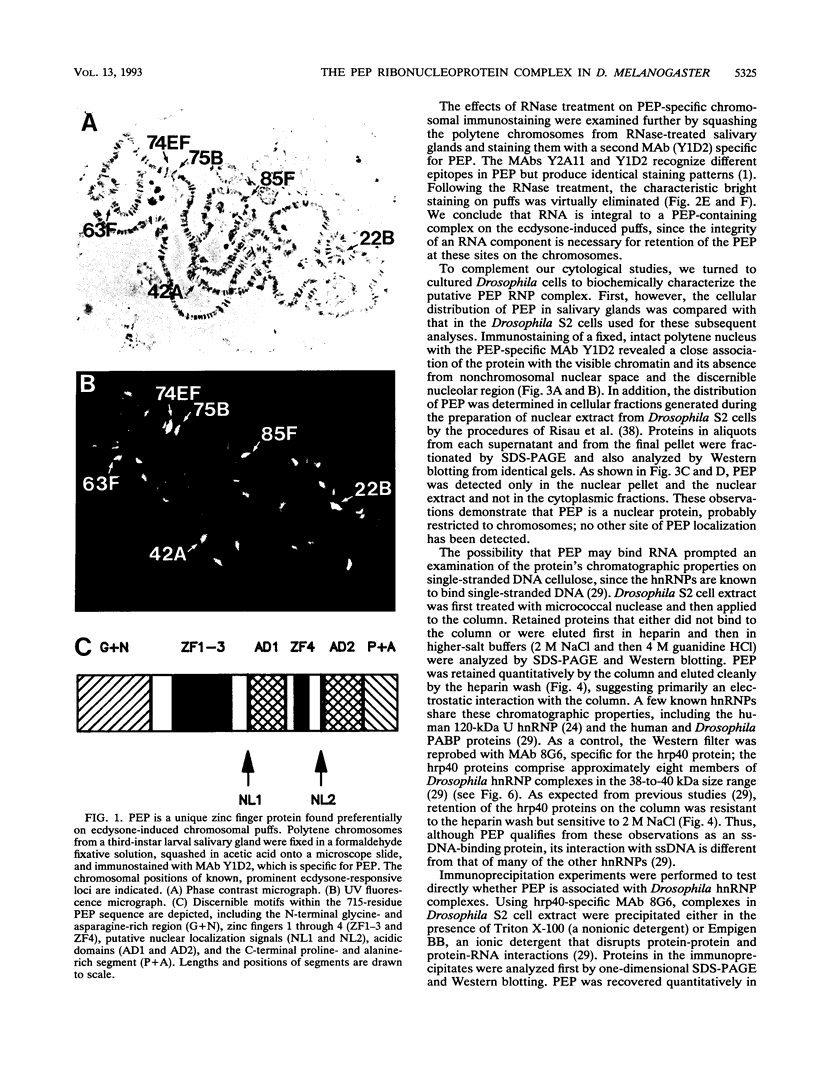
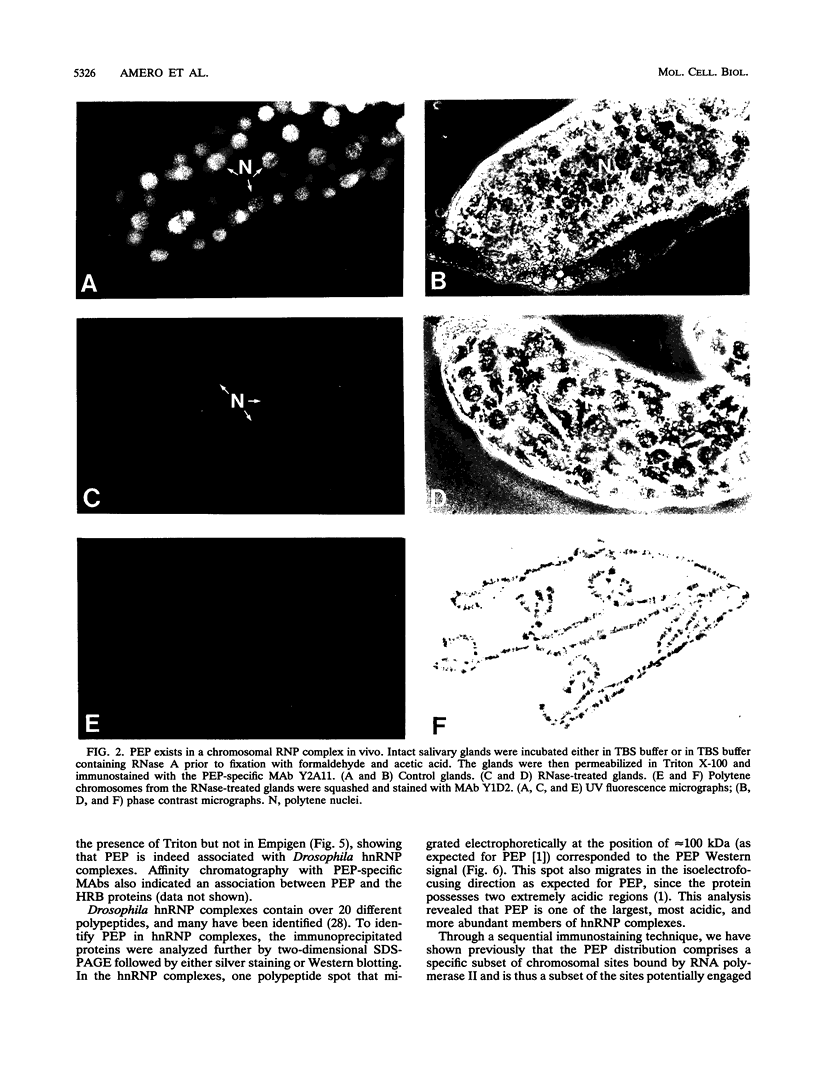
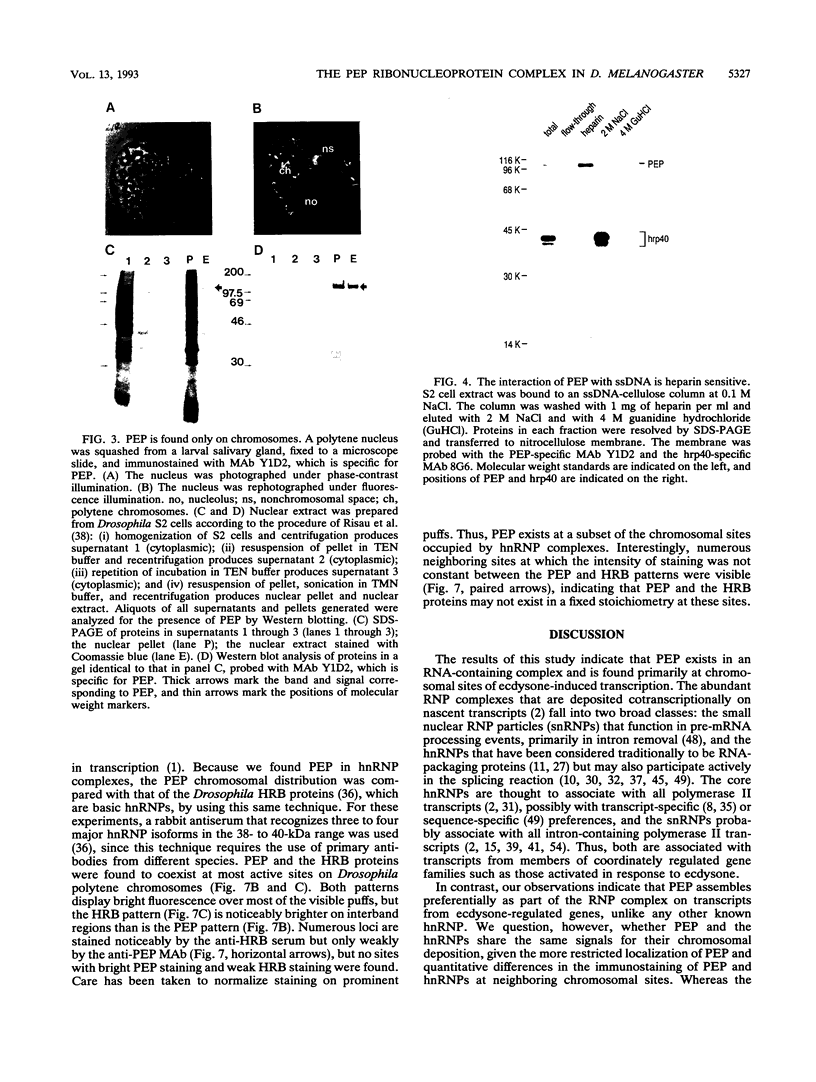
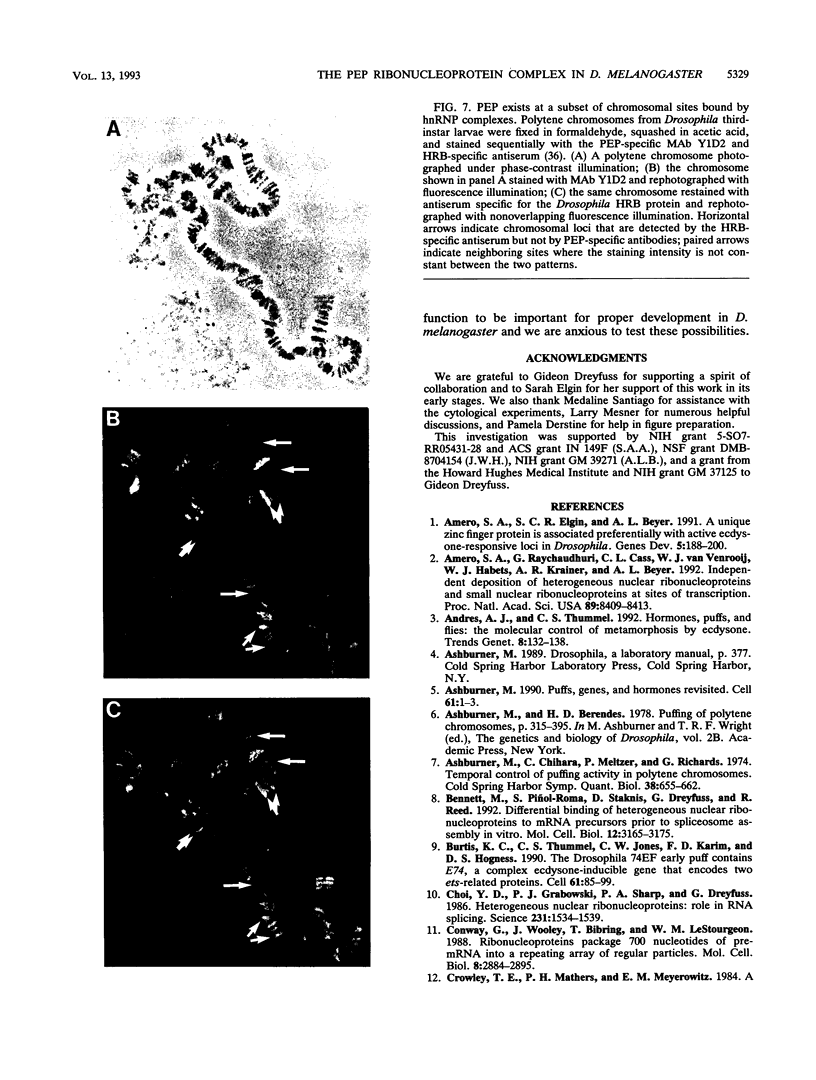
The protein on ecdysone puffs (PEP) is associated preferentially with active ecdysone-inducible puffs on Drosophila polytene chromosomes and contains sequence motifs characteristic of transcription factors and RNA-binding proteins (S. A. Amero, S. C. R. Elgin, and A. L. Beyer, Genes Dev. 5:188-200, 1991). PEP is associated with RNA in vivo, as demonstrated here by the sensitivity of PEP-specific chromosomal immunostaining in situ to RNase digestion and by the immunopurification of PEP in Drosophila cell extract with heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) complexes. As revealed by sequential immunostaining, PEP is found on a subset of chromosomal sites bound by the HRB (heterogeneous nuclear RNA-binding) proteins, which are basic Drosophila hnRNPs. These observations lead us to suggest that a unique, PEP-containing hnRNP complex assembles preferentially on the transcripts of ecdysone-regulated genes in Drosophila melanogaster presumably to expedite the transcription and/or processing of these transcripts.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amero S. A., Elgin S. C., Beyer A. L. A unique zinc finger protein is associated preferentially with active ecdysone-responsive loci in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):188–200. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amero S. A., Raychaudhuri G., Cass C. L., van Venrooij W. J., Habets W. J., Krainer A. R., Beyer A. L. Independent deposition of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles at sites of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8409–8413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres A. J., Thummel C. S. Hormones, puffs and flies: the molecular control of metamorphosis by ecdysone. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90371-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Puffs, genes, and hormones revisited. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90205-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Piñol-Roma S., Staknis D., Dreyfuss G., Reed R. Differential binding of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins to mRNA precursors prior to spliceosome assembly in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3165–3175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway G., Wooley J., Bibring T., LeStourgeon W. M. Ribonucleoproteins package 700 nucleotides of pre-mRNA into a repeating array of regular particles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2884–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B. Transcription in polytene chromosomes. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBello P. R., Withers D. A., Bayer C. A., Fristrom J. W., Guild G. M. The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):385–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Immunoelectron microscope visualization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens within spread transcription complexes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigl G., Gram M., Pongs O. A member of the steroid hormone receptor gene family is expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 75B in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7167–7178. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galcerán J., Llanos J., Sampedro J., Pongs O., Izquierdo M. Transcription at the ecdysone-inducible locus 2B5 in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):539–545. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay P. S., Guild G. M. The ecdysone-induced puffing cascade in Drosophila salivary glands: a Broad-Complex early gene regulates intermolt and late gene transcription. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):169–175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild G., Richards G. Gene regulation. Ecdysone and the onion. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):539–539. doi: 10.1038/357539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts R. B., Sage B., O'Connor J. D. Ecdysone titers during postembryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):310–317. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James T. C., Elgin S. C. Identification of a nonhistone chromosomal protein associated with heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster and its gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3862–3872. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Taube W., Lüdecke H. J., Pongs O. Characterization of a putative transcription factor gene expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 74EF in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4455–4464. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Ecdysone coordinates the timing and amounts of E74A and E74B transcription in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1067–1079. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure and binding activity of the hnRNP U protein: binding RNA through RGG box. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2655–2664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Talbot W. S., Segraves W. A., Bender M. T., Cherbas P., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90572-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis E. L., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Characterization of the major hnRNP proteins from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):257–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis M. J., Matunis E. L., Dreyfuss G. Isolation of hnRNP complexes from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):245–255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S. H., Pederson T. Crosslinking of hnRNP proteins to pre-mRNA requires U1 and U2 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3307–3318. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Pederson T. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles probed in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2208–2212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T., Davis N. G. Messenger RNA processing and nuclear structure: isolation of nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles containing beta-globin messenger RNA precursors. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):47–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Swanson M. S., Gall J. G., Dreyfuss G. A novel heterogeneous nuclear RNP protein with a unique distribution on nascent transcripts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2575–2587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri G., Haynes S. R., Beyer A. L. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes and proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):847–855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. Protein composition of mammalian spliceosomes assembled in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8031–8035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W., Symmons P., Saumweber H., Frasch M. Nonpackaging and packaging proteins of hnRNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. Postinitiation transcriptional control in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6041–6045. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass H., Pederson T. Transcription-dependent localization of U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins at major sites of gene activity in polytene chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):911–926. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Szer W., Furdon P. J., Kole R. Antibodies to hnRNP core proteins inhibit in vitro splicing of human beta-globin pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5241–5254. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M., Elgin S. C. Distribution patterns of three subfractions of drosophila nonhistone chromosomal proteins: possible correlations with gene activity. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):971–983. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90308-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Sutton C. A., Lobell R. B., Glaser R. L., Lis J. T. Determinants of heat shock-induced chromosome puffing. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90340-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S. Mechanisms of transcriptional timing in Drosophila. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):39–40. doi: 10.1126/science.1553530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Segraves W. A., Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90266-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]