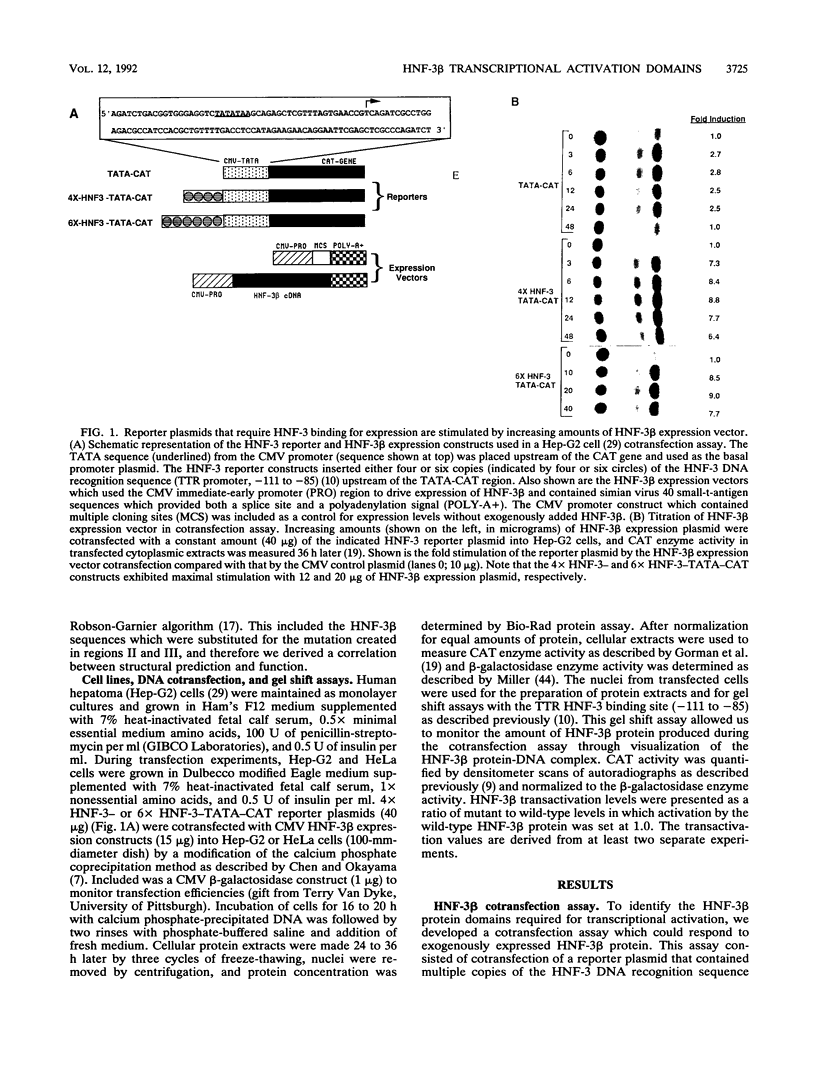
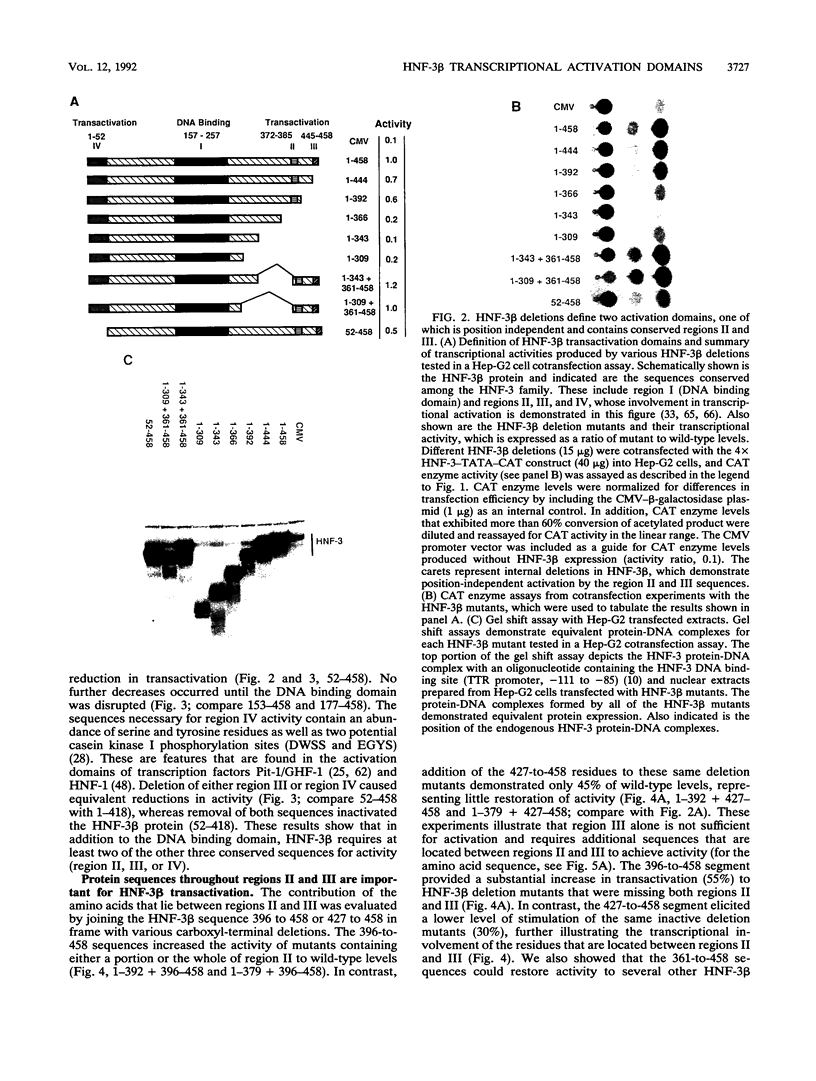
Abstract
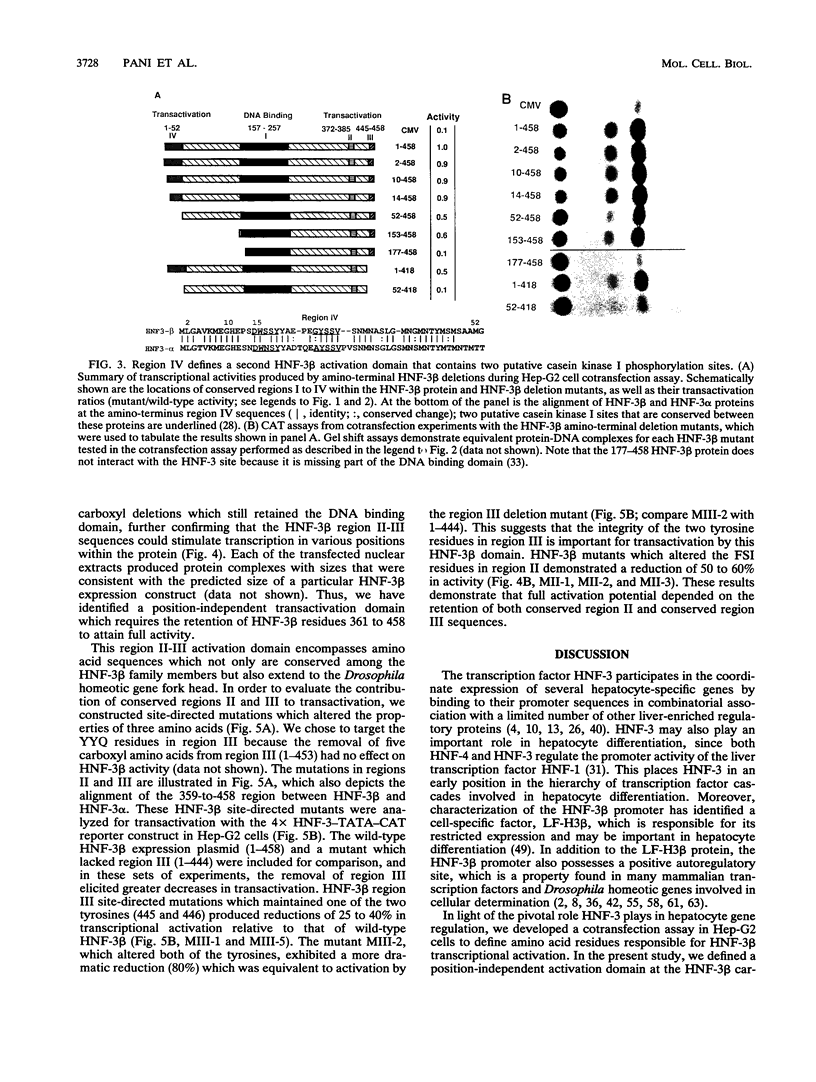
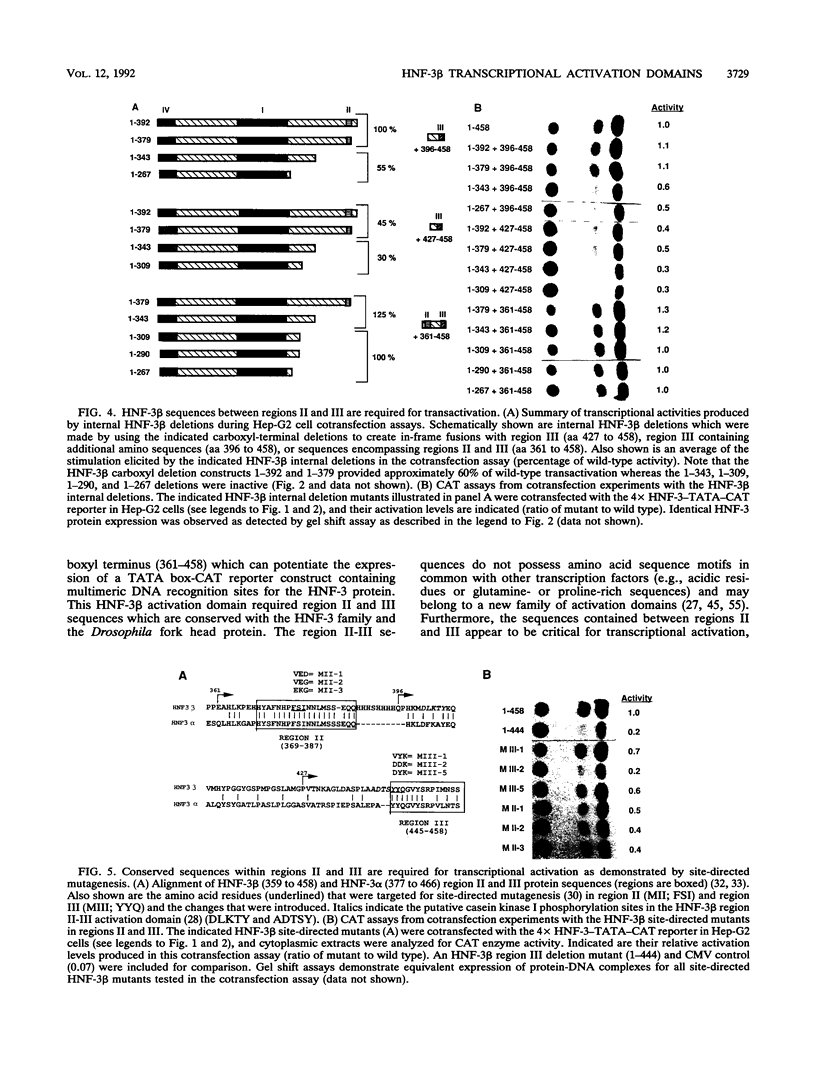
The hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (HNF-3) gene family is composed of three proteins (alpha, beta, and gamma) that are transcription factors involved in the coordinate expression of several liver genes. All three proteins share strong homology in their DNA binding domains (region I) and are able to recognize the same DNA sequence. They also possess two similar stretches of amino acids at the carboxyl terminus (regions II and III) and a fourth segment of homology at the amino terminus (region IV). Furthermore, the HNF-3 proteins demonstrate homology with the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head in regions I, II, and III, suggesting that HNF-3 may be its mammalian homolog. In order to define HNF-3 beta protein domains involved in transcriptional activation, we have used a reporter gene, whose transcription is dependent on HNF-3 binding, for hepatoma cell cotransfection assays with expression vectors that produced different truncated HNF-3 beta proteins. A position-independent activation domain which contained conserved regions II and III was identified at the carboxyl terminus of the HNF-3 beta protein (amino acids 361 to 458). Moreover, site-directed mutations that altered the sequences within regions II and III demonstrated their importance to transactivation. The region II-III domain does not possess amino acid sequences in common with other transcription factors and may define a novel activation motif. HNF-3 beta amino-terminal sequences defined by conserved region IV also contributed to transactivation, but region IV activity required the participation of the region II-III domain. Region IV is abundant in serine amino acids and contains two putative casein kinase I phosphorylation sites, a feature similar to protein motifs described for the transcription factors Pit-1/GHF-1 and HNF-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergson C., McGinnis W. An autoregulatory enhancer element of the Drosophila homeotic gene Deformed. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4287–4297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. R., Blackhart B. D., Haubold K., Levy-Wilson B. Characterization of tissue-specific enhancer elements in the second intron of the human apolipoprotein B gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7848–7859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. P., Ingraham H. A., Treacy M. N., Albert V. R., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. Autoregulation of pit-1 gene expression mediated by two cis-active promoter elements. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):583–586. doi: 10.1038/346583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) binding sites in the mouse transthyretin (TTR) promoter reveal synergistic interactions with its enhancer region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4139–4145. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio C. M., Jackson D. A., Zaret K. S. The extracellular matrix coordinately modulates liver transcription factors and hepatocyte morphology. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4405–4414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. Identification of two polypeptide segments of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein required for transcriptional activation of the serum albumin gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1416–1426. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Fine-structure mapping of the three mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson D. R., Costa R. H., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E. One factor recognizes the liver-specific enhancers in alpha 1-antitrypsin and transthyretin genes. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):786–788. doi: 10.1126/science.3257586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Friedman N., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the mouse albumin enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Multiple and cooperative trans-activation domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Poon D., Stone D., Granner D. K., Chalkley R. Interaction of a liver-specific factor with an enhancer 4.8 kilobases upstream of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3770–3781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Chen L., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Crabtree G. R. A transcriptional hierarchy involved in mammalian cell-type specification. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):457–461. doi: 10.1038/355457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. K., DiPersio C. M., Zaret K. S. Extracellular signals that regulate liver transcription factors during hepatic differentiation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):773–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Brady H., Fukushima J., Karin M. The pituitary-specific regulatory gene GHF1 contains a minimal cell type-specific promoter centered around its TATA box. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1490–1503. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Brady H., Theill L. E., Karin M. Regulation of the pituitary-specific homeobox gene GHF1 by cell-autonomous and environmental cues. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):829–832. doi: 10.1038/345829a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Monaci P., Tomei L., De Francesco R., Nuzzo M., Stunnenberg H., Cortese R. A myosin-like dimerization helix and an extra-large homeodomain are essential elements of the tripartite DNA binding structure of LFB1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1225–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90687-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pani L., Quian X. B., Clevidence D., Costa R. H. The restricted promoter activity of the liver transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 beta involves a cell-specific factor and positive autoactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):552–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D. Q., Shih C. H. An "attenuator domain" is sandwiched by two distinct transactivation domains in the transcription factor C/EBP. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1480–1487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein CIII gene expression is regulated by positive and negative cis-acting elements and tissue-specific protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6857–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain transcription factors: pou-er-ful developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):897–907. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2212–2224. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Strauss E., Orkin S. H. Functional analysis and in vivo footprinting implicate the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 as a positive regulator of its own promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):919–931. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jäckle H. The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors? Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):455–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Menzel P., Rivier J., Montminy M. R. Characterization of a bipartite activator domain in transcription factor CREB. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90664-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]