Abstract
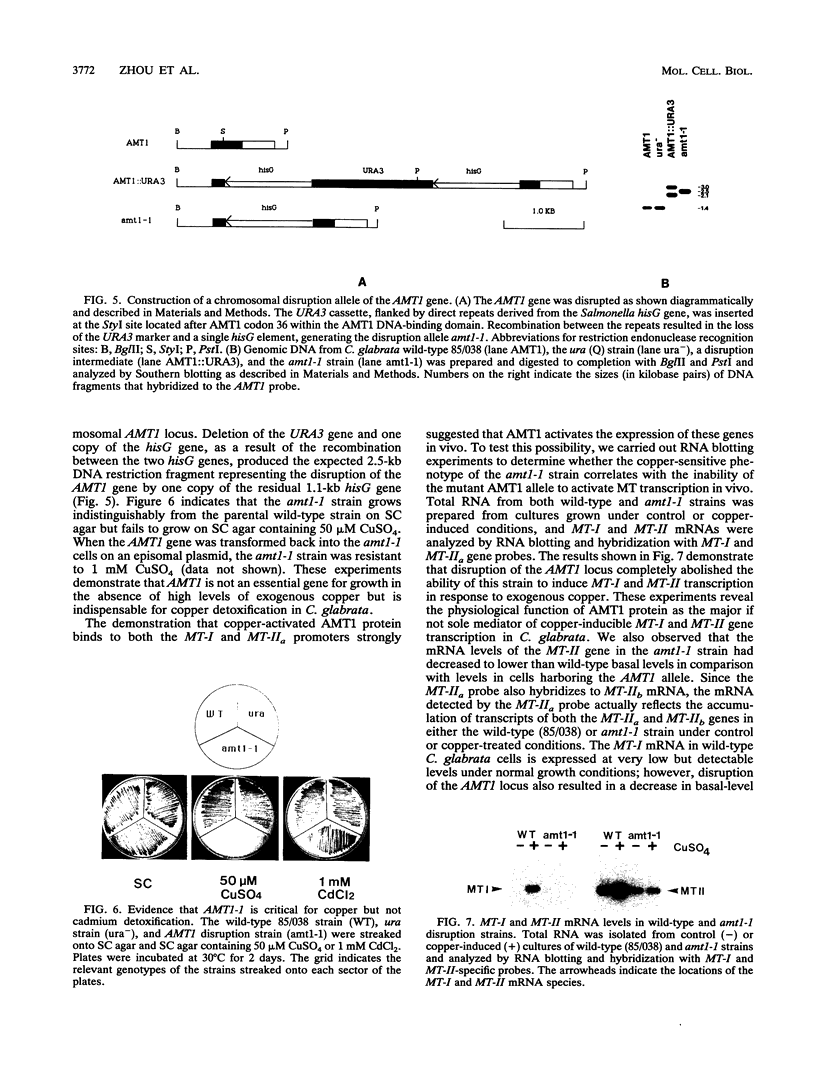
The opportunistic pathogenic yeast Candida glabrata elicits at least two major responses in the presence of high environmental metal levels: transcriptional induction of the metallothionein gene family by copper and the appearance of small (gamma-Glu-Cys)nGly peptides in the presence of cadmium. On the basis of a trans-activation selection scheme in the baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we previously isolated a C. glabrata gene which encodes a copper-activated DNA-binding protein designated AMT1. AMT1 forms multiple specific DNA-protein complexes with both C. glabrata MT-I and MT-IIa promoter DNA fragments. In this report, we localize and define the AMT1-binding sites in the MT-I and MT-IIa promoters and characterize the mode of AMT1 binding. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the AMT1 protein trans activates both the MT-I and MT-IIa genes in vivo in response to copper and that this activation is essential for high-level copper resistance in C. glabrata. Although AMT1-mediated trans activation of the C. glabrata metallothionein genes is essential for copper resistance, AMT1 is completely dispensable for cadmium tolerance. The distinct function that metallothionein genes have in copper but not cadmium detoxification in C. glabrata is in contrast to the role that metallothionein genes play in tolerance to multiple metals in higher organisms.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani E., Cao L., Kleckner N. A method for gene disruption that allows repeated use of URA3 selection in the construction of multiply disrupted yeast strains. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):541–545. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.541.test. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner I., Beattie J. H. Metallothionein and the trace minerals. Annu Rev Nutr. 1990;10:63–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.10.070190.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman C., Skroch P., Dixon W., Tullius T. D., Karin M. A single amino acid change in CUP2 alters its mode of DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4778–4787. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman C., Skroch P., Welch J., Fogel S., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product, regulator of yeast metallothionein expression, is a copper-activated DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4091–4095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler G., Thiele D. J. ACE2, an activator of yeast metallothionein expression which is homologous to SWI5. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):476–485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt T. R., Ecker D. J. Yeast metallothionein and applications in biotechnology. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):351–364. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.351-364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt T. R., Sternberg E. J., Gorman J. A., Clark P., Hamer D., Rosenberg M., Crooke S. T. Copper metallothionein of yeast, structure of the gene, and regulation of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3332–3336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt T. R., Sternberg E., Herd J., Crooke S. T. Cloning and expression of a yeast copper metallothionein gene. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. D., Felber B. K., Walling M. J., Jubier M. F., Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Duplicated heavy metal control sequences of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7392–7396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dameron C. T., Winge D. R., George G. N., Sansone M., Hu S., Hamer D. A copper-thiolate polynuclear cluster in the ACE1 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6127–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. F., Engelke D. R., Thiele D. J. ACE1 transcription factor produced in Escherichia coli binds multiple regions within yeast metallothionein upstream activation sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):426–429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Gedamu L. Functional analyses of promoter elements responsible for the differential expression of the human metallothionein (MT)-IG and MT-IF genes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9866–9875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Jahroudi N., Varshney U., Gedamu L. Structure and expression of the human metallothionein-IG gene. Differential promoter activity of two linked metallothionein-I genes in response to heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11528–11535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hamer D. Cooperative activation of a eukaryotic transcription factor: interaction between Cu(I) and yeast ACE1 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5267–5271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Catalytic RNA: a Nobel Prize for small village science. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla E. B., Thiele D. J., Silar P., Valentine J. S. ACE1, a copper-dependent transcription factor, activates expression of the yeast copper, zinc superoxide dismutase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8558–8562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–951. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Thiele D. J., Lemontt J. E. Function and autoregulation of yeast copperthionein. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):685–690. doi: 10.1126/science.3887570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heguy A., West A., Richards R. I., Karin M. Structure and tissue-specific expression of the human metallothionein IB gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2149–2157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R., Thiele D. J. Copper-induced binding of cellular factors to yeast metallothionein upstream activation sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert J., Culotta V., Fürst P., Gedamu L., Hamer D. Regulation of metallothionein gene transcription by metals. Adv Inorg Biochem. 1990;8:139–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahroudi N., Foster R., Price-Haughey J., Beitel G., Gedamu L. Cell-type specific and differential regulation of the human metallothionein genes. Correlation with DNA methylation and chromatin structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6506–6511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Metallothioneins: proteins in search of function. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Kojima Y. Chemistry and biochemistry of metallothionein. Experientia Suppl. 1987;52:25–61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6784-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra R. K., Garey J. R., Butt T. R., Gray W. R., Winge D. R. Candida glabrata metallothioneins. Cloning and sequence of the genes and characterization of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19747–19753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra R. K., Garey J. R., Winge D. R. Selective and tandem amplification of a member of the metallothionein gene family in Candida glabrata. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6369–6375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra R. K., Tarbet E. B., Gray W. R., Winge D. R. Metal-specific synthesis of two metallothioneins and gamma-glutamyl peptides in Candida glabrata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8815–8819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra R. K., Thorvaldsen J. L., Macreadie I. G., Winge D. R. Disruption analysis of metallothionein-encoding genes in Candida glabrata. Gene. 1992 May 1;114(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra R. K., Winge D. R. Metal ion resistance in fungi: molecular mechanisms and their regulated expression. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Jan;45(1):30–40. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silar P., Butler G., Thiele D. J. Heat shock transcription factor activates transcription of the yeast metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Misra T. K., Laddaga R. A. DNA sequence analysis of bacterial toxic heavy metal resistances. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1989 Jul-Sep;21:145–163. doi: 10.1007/BF02917247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Misra T. K. Plasmid-mediated heavy metal resistances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:717–743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Nucifora G., Chu L., Misra T. K. Bacterial resistance ATPases: primary pumps for exporting toxic cations and anions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczypka M. S., Thiele D. J. A cysteine-rich nuclear protein activates yeast metallothionein gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):421–429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J. ACE1 regulates expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J., Hamer D. H. Tandemly duplicated upstream control sequences mediate copper-induced transcription of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae copper-metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J. Metal-regulated transcription in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J., Fogel S., Buchman C., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product regulates the expression of the CUP1 gene, coding for yeast metallothionein. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):255–260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou P. B., Thiele D. J. Isolation of a metal-activated transcription factor gene from Candida glabrata by complementation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]