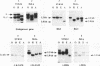
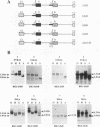
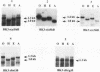
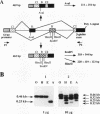
Abstract
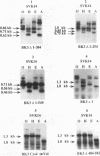
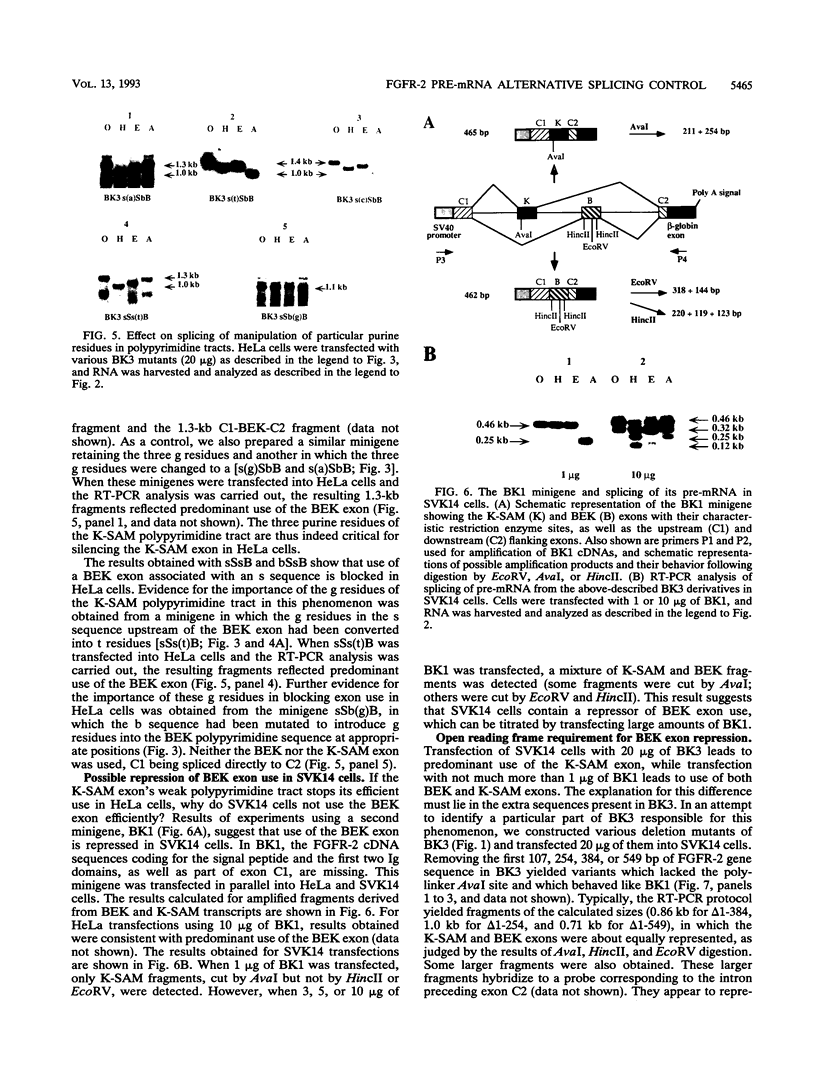
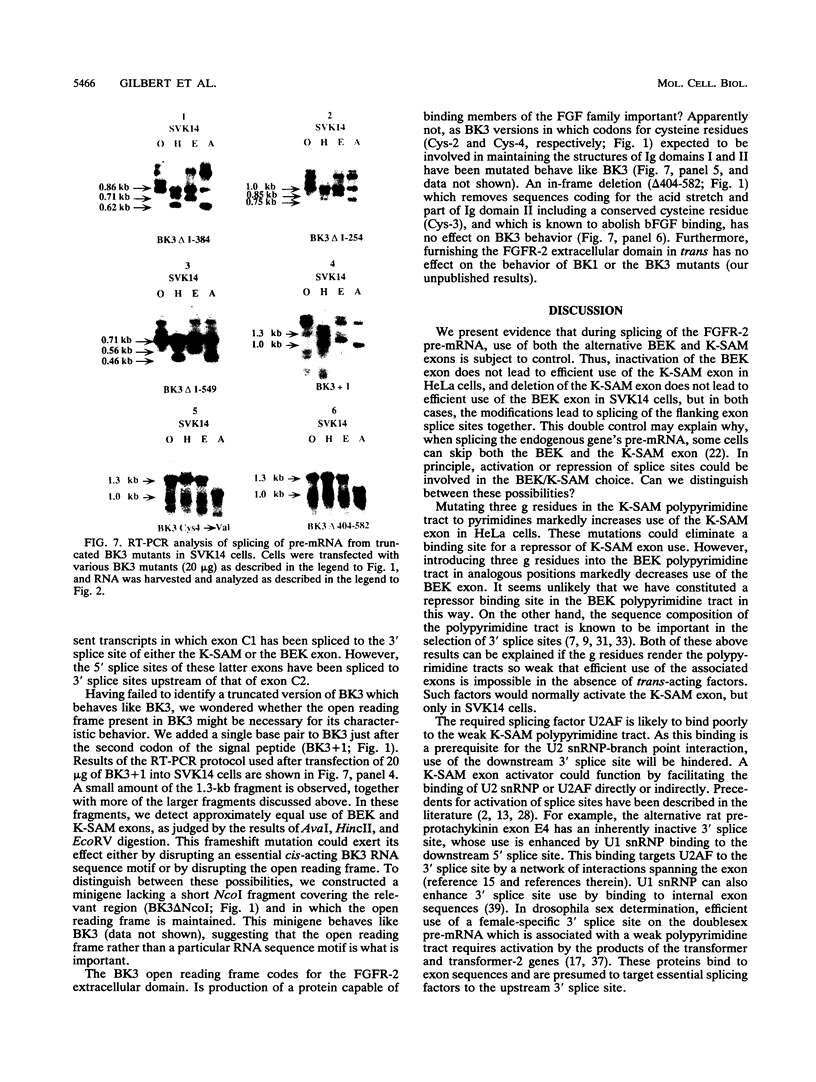
The fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 gene pre-mRNA can be spliced by using either the K-SAM exon or the BEK exon. The exon chosen has a profound influence on the ligand-binding specificity of the receptor obtained. Cells make a choice between the two alternative exons by controlling use of both exons. Using fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 minigenes, we have shown that in cells normally using the K-SAM exon, the BEK exon is not used efficiently even in the absence of the K-SAM exon. This is because these cells apparently express a titratable repressor of BEK exon use. In cells normally using the BEK exon, the K-SAM exon is not used efficiently even in the absence of a functional BEK exon. Three purines in the K-SAM polypyrimidine tract are at least in part responsible for this, as their mutation to pyrimidines leads to efficient use of the K-SAM exon, while mutating the BEK polypyrimidine tract to include these purines stops BEK exon use.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black D. L. Activation of c-src neuron-specific splicing by an unusual RNA element in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):795–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90291-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion-Arnaud P., Ronsin C., Gilbert E., Gesnel M. C., Houssaint E., Breathnach R. Multiple mRNAs code for proteins related to the BEK fibroblast growth factor receptor. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):979–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouet d'Orval B., d'Aubenton Carafa Y., Sirand-Pugnet P., Gallego M., Brody E., Marie J. RNA secondary structure repression of a muscle-specific exon in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1823–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.2063195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Valle D., Francomano C. A., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):680–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8430317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominski Z., Kole R. Selection of splice sites in pre-mRNAs with short internal exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6075–6083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Ge H., Manley J. L. The role of the polypyrimidine stretch at the SV40 early pre-mRNA 3' splice site in alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):809–817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. S. Statistical analysis of mammalian pre-mRNA splicing sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6369–6382. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W., Mulligan G. J., Wormsley S., Helfman D. M. Alternative splicing of beta-tropomyosin pre-mRNA: cis-acting elements and cellular factors that block the use of a skeletal muscle exon in nonmuscle cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2096–2107. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. E., Grabowski P. J. U1 snRNP targets an essential splicing factor, U2AF65, to the 3' splice site by a network of interactions spanning the exon. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2554–2568. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssaint E., Blanquet P. R., Champion-Arnaud P., Gesnel M. C., Torriglia A., Courtois Y., Breathnach R. Related fibroblast growth factor receptor genes exist in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8180–8184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Hoshijima K., Higuchi I., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Binding of the Drosophila transformer and transformer-2 proteins to the regulatory elements of doublesex primary transcript for sex-specific RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8092–8096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Hoshijima K., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Binding of the Drosophila sex-lethal gene product to the alternative splice site of transformer primary transcript. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):461–463. doi: 10.1038/344461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Schlessinger J., Dionne C. A. Fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases: molecular analysis and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 10;1135(2):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90136-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lu J., Chen H., Werner S., Williams L. T. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor genes: a common structural arrangement underlies the mechanisms for generating receptor forms that differ in their third immunoglobulin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4627–4634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh M., Hattori Y., Sasaki H., Tanaka M., Sugano K., Yazaki Y., Sugimura T., Terada M. K-sam gene encodes secreted as well as transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Piseri A., Fiszman M. Y. Tissue-specific splicing in vivo of the beta-tropomyosin gene: dependence on an RNA secondary structure. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1842–1845. doi: 10.1126/science.2063196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T., Krieg P., Fürstenberger G., Briand J. P., Leroy P., Breathnach R. The mRNA coding for the secreted protease transin is expressed more abundantly in malignant than in benign tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9413–9417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Ryner L., Baker B. S. Autoregulation and multifunctionality among trans-acting factors that regulate alternative pre-mRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19023–19026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Helfman D. M., Krainer A. R. Modulation of exon skipping and inclusion by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 and pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2/ASF. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2993–3001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M. Alternative mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:133–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Smith C. L., Burgess W. H., Chan A. M., Aaronson S. A. Determination of ligand-binding specificity by alternative splicing: two distinct growth factor receptors encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen M. P., Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alpha-tropomyosin mutually exclusive exon selection: competition between branchpoint/polypyrimidine tracts determines default exon choice. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):642–655. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeger L. K., Schoborg R. V., Zhao Q., Tullis G. E., Pintel D. J. Nonsense mutations inhibit splicing of MVM RNA in cis when they interrupt the reading frame of either exon of the final spliced product. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1107–1119. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. The organization of 3' splice-site sequences in mammalian introns. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2113–2123. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Kitazawa T., Katsumata A., Mukamoto M., Okada T., Takeya T. Tissue-specific expression of two isoforms of chicken fibroblast growth factor receptor, bek and Cek3. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jun;3(6):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski B. A., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Sex-specific alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene results from sequence-dependent splice site blockage. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Purkis P., Lane E. B., McKay I. A., Chang S. E. Effects of SV40 transformation on the cytoskeleton and behavioural properties of human keratinocytes. Cell Differ. 1982 May;11(3):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(82)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. Positive control of pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):237–240. doi: 10.1126/science.1566072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Ciudad C. J., Chasin L. A. Nonsense mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene affect RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2868–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watakabe A., Tanaka K., Shimura Y. The role of exon sequences in splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):407–418. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Zimmer Y., Shen G. H., Avivi A., Yarden Y., Givol D. A confined variable region confers ligand specificity on fibroblast growth factor receptors: implications for the origin of the immunoglobulin fold. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1885–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y. A., Goldstein A. M., Weiner A. M. UACUAAC is the preferred branch site for mammalian mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]