Abstract
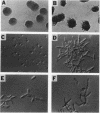
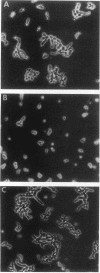
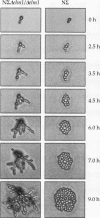
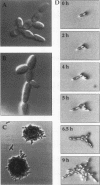
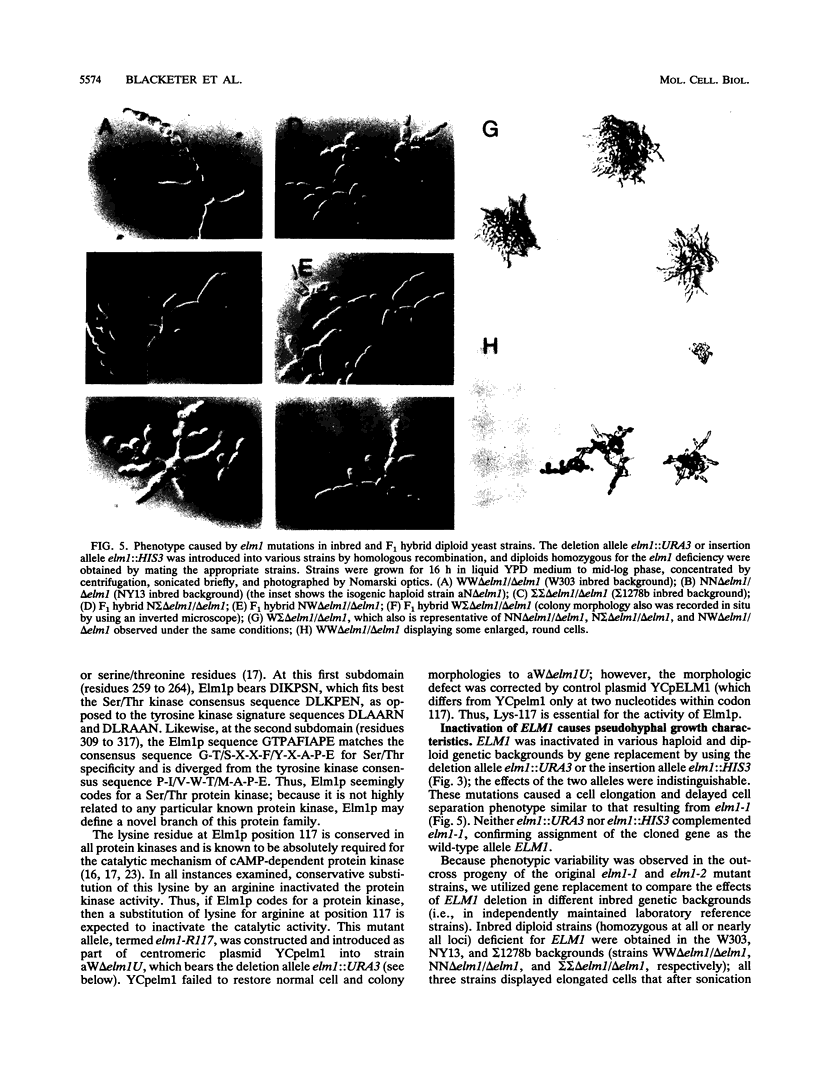
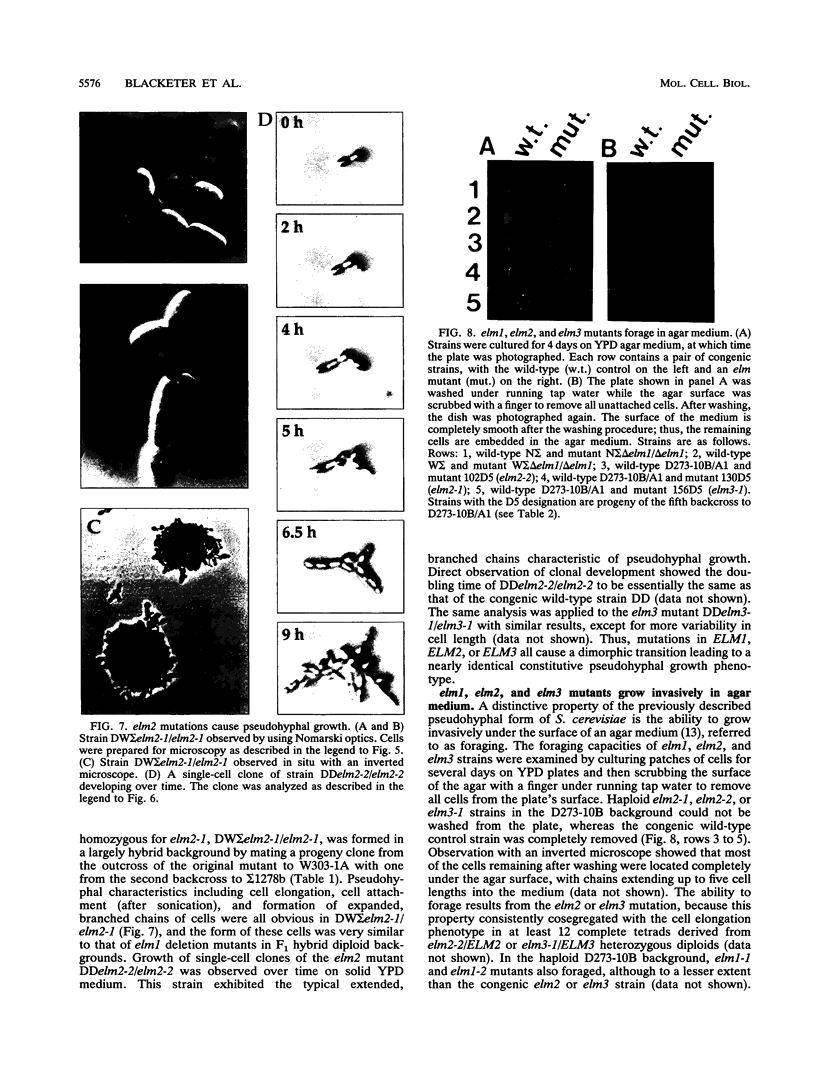
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes ELM1, ELM2, and ELM3 were identified on the basis of the phenotype of constitutive cell elongation. Mutations in any of these genes cause a dimorphic transition to a pseudohyphal growth state characterized by formation of expanded, branched chains of elongated cells. Furthermore, elm1, elm2, and elm3 mutations cause cells to grow invasively under the surface of agar medium. S. cerevisiae is known to be a dimorphic organism that grows either as a unicellular yeast or as filamentous cells termed pseudohyphae; although the yeast-like form usually prevails, pseudohyphal growth may occur during conditions of nitrogen starvation. The morphologic and physiological properties caused by elm1, elm2, and elm3 mutations closely mimic pseudohyphal growth occurring in conditions of nitrogen starvation. Therefore, we propose that absence of ELM1, ELM2, or ELM3 function causes constitutive execution of the pseudohyphal differentiation pathway that occurs normally in conditions of nitrogen starvation. Supporting this hypothesis, heterozygosity at the ELM2 or ELM3 locus significantly stimulated the ability to form pseudohyphae in response to nitrogen starvation. ELM1 was isolated and shown to code for a novel protein kinase homolog. Gene dosage experiments also showed that pseudohyphal differentiation in response to nitrogen starvation is dependent on the product of CDC55, a putative B regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, and a synthetic phenotype was observed in elm1 cdc55 double mutants. Thus, protein phosphorylation is likely to regulate differentiation into the pseudohyphal state.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F. Ustilago maydis, the delightful blight. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Hough J. S. Elongation of yeast cells in continuous culture. Nature. 1965 May 15;206(985):676–678. doi: 10.1038/206676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J., Herskowitz I. Genetic control of bud site selection in yeast by a set of gene products that constitute a morphogenetic pathway. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1203–1212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90015-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Boquet P., Madaule P., Popoff M. R., Rubin E. J., Gill D. M. The mammalian G protein rhoC is ADP-ribosylated by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 and affects actin microfilaments in Vero cells. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIFELDER D. Bud position in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:567–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.567-568.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. K., Pringle J. R. Cellular morphogenesis in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle: localization of the CDC11 gene product and the timing of events at the budding site. Dev Genet. 1991;12(4):281–292. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno C. J., Ljungdahl P. O., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Unipolar cell divisions in the yeast S. cerevisiae lead to filamentous growth: regulation by starvation and RAS. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1077–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90079-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarer B. K., Pringle J. R. Immunofluorescence localization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC12 gene product to the vicinity of the 10-nm filaments in the mother-bud neck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3678–3687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. IV. Genes controlling bud emergence and cytokinesis. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Dec;69(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Zolnierowicz S., Stapleton A. E., Goebl M., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Pringle J. R. CDC55, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in cellular morphogenesis: identification, characterization, and homology to the B subunit of mammalian type 2A protein phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5767–5780. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. B., Haarer B. K., Pringle J. R. Cellular morphogenesis in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle: localization of the CDC3 gene product and the timing of events at the budding site. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):535–544. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl P. O., Gimeno C. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. SHR3: a novel component of the secretory pathway specifically required for localization of amino acid permeases in yeast. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):463–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90515-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R., Myers A. M. Characterization of two members of the rho gene family from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):779–783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Z. Y., Wang W., Wilson S. E., Schlender K. K., Trumbly R. J., Reimann E. M. Identification of a glycogen synthase phosphatase from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as protein phosphatase 2A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10925–10932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Preston R. A., Adams A. E., Stearns T., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K., Jones E. W. Fluorescence microscopy methods for yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:357–435. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Carlberg M., Hu G. Z., Nehlin J. O. Protein phosphatase 2A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on cell growth and bud morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4876–4884. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene: expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Magee P. T. Genetics of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):226–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.226-241.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A. H., Brandriss M. C. A regulatory region responsible for proline-specific induction of the yeast PUT2 gene is adjacent to its TATA box. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4634–4641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon A. A., Cohen P. T., Stark M. J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A performs an essential cellular function and is encoded by two genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4339–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R. High-frequency switching in Candida albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992 Apr;5(2):183–203. doi: 10.1128/cmr.5.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Hirota M., Nakayasu M., Ojika M., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Sugimura T. Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWNSEND G. F., LINDEGREN C. C. Characteristic growth patterns of the different members of a polyploid series of Saccharomyces. J Bacteriol. 1954 Apr;67(4):480–483. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.4.480-483.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Akai A., Foury F. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system XVI. Modified form of the ATPase proteolipid in oligomycin-resistant mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 15;65(3):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. I., Lickteig R. L., Estes R., Rundell K., Walter G., Mumby M. C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1988–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zyl W., Huang W., Sneddon A. A., Stark M., Camier S., Werner M., Marck C., Sentenac A., Broach J. R. Inactivation of the protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit A results in morphological and transcriptional defects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4946–4959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]