Abstract
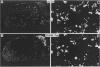
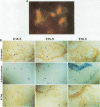
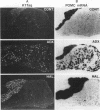
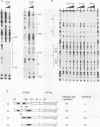
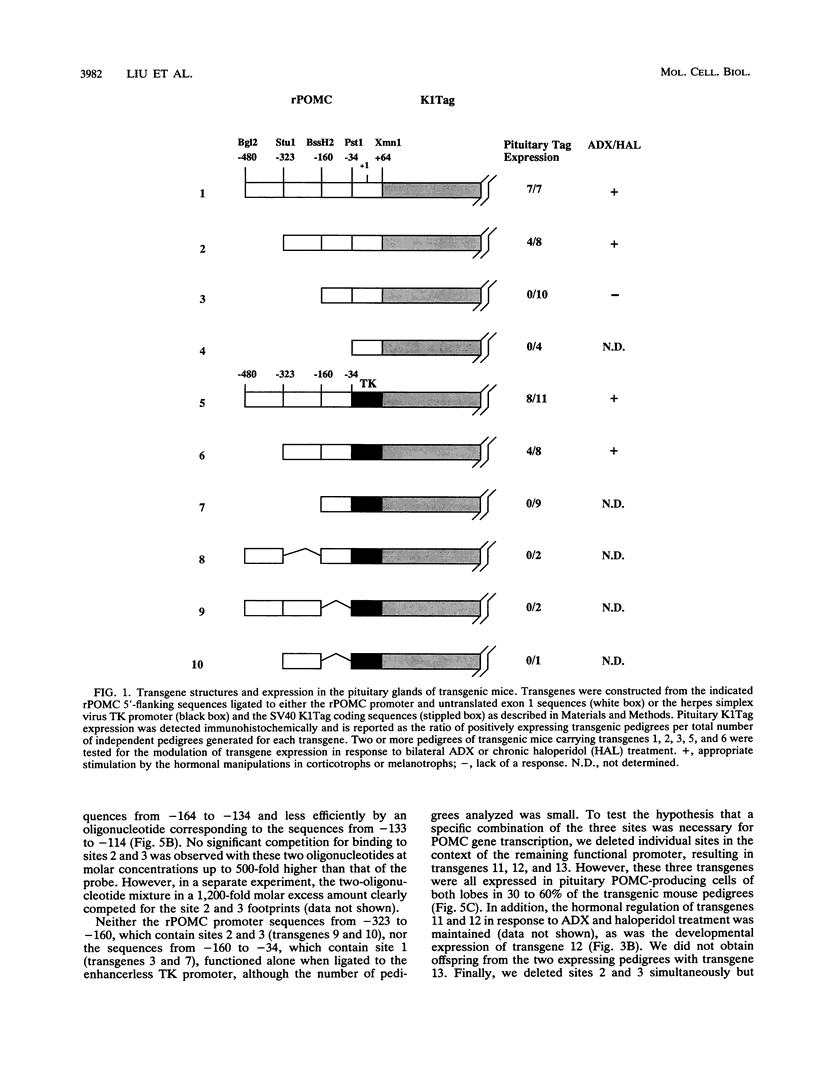
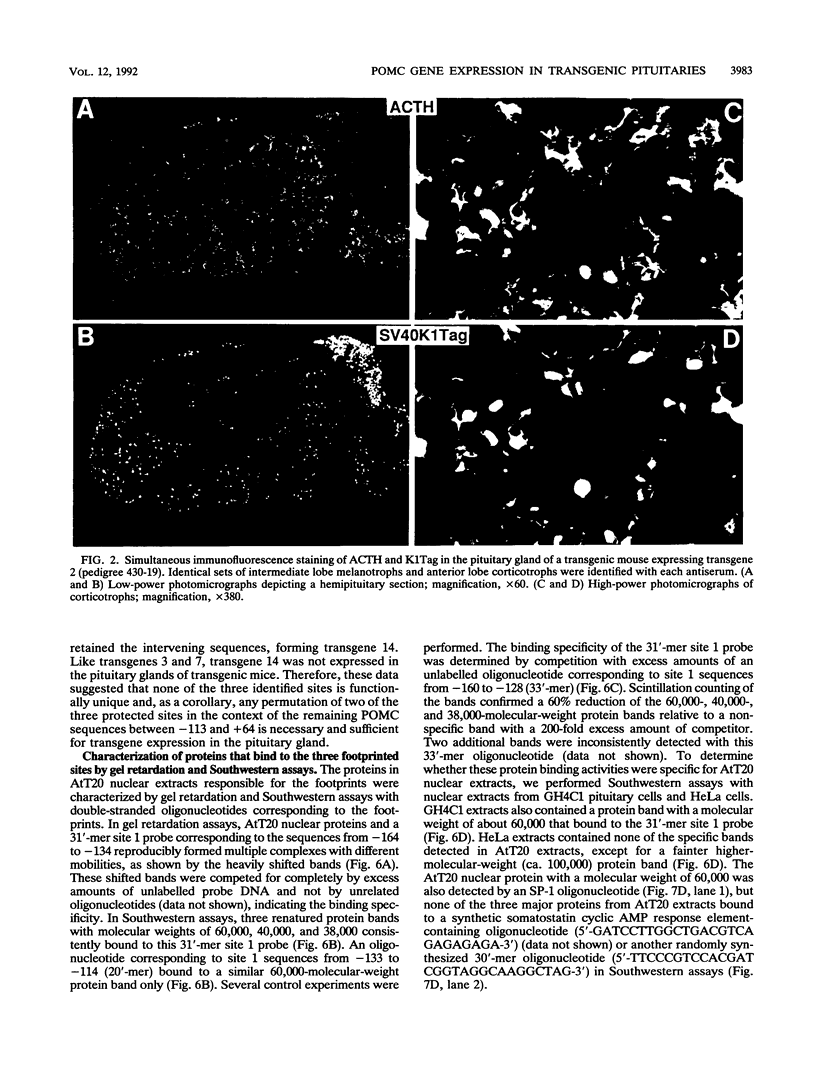
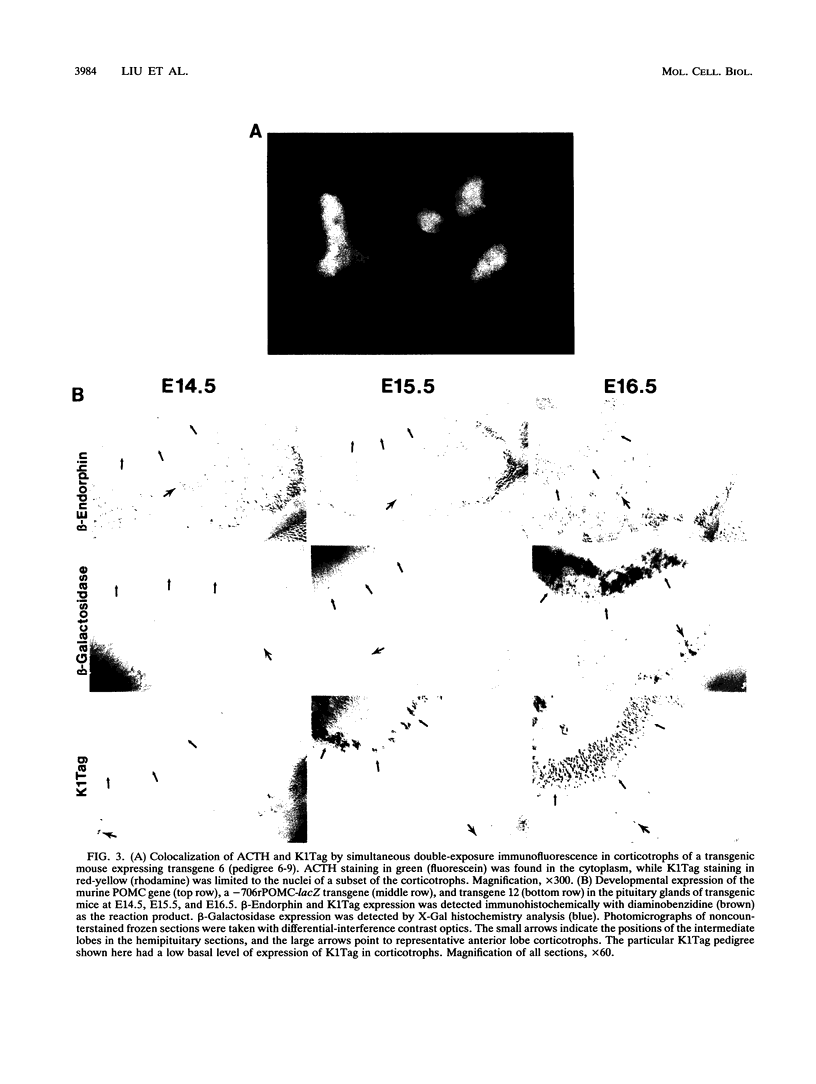
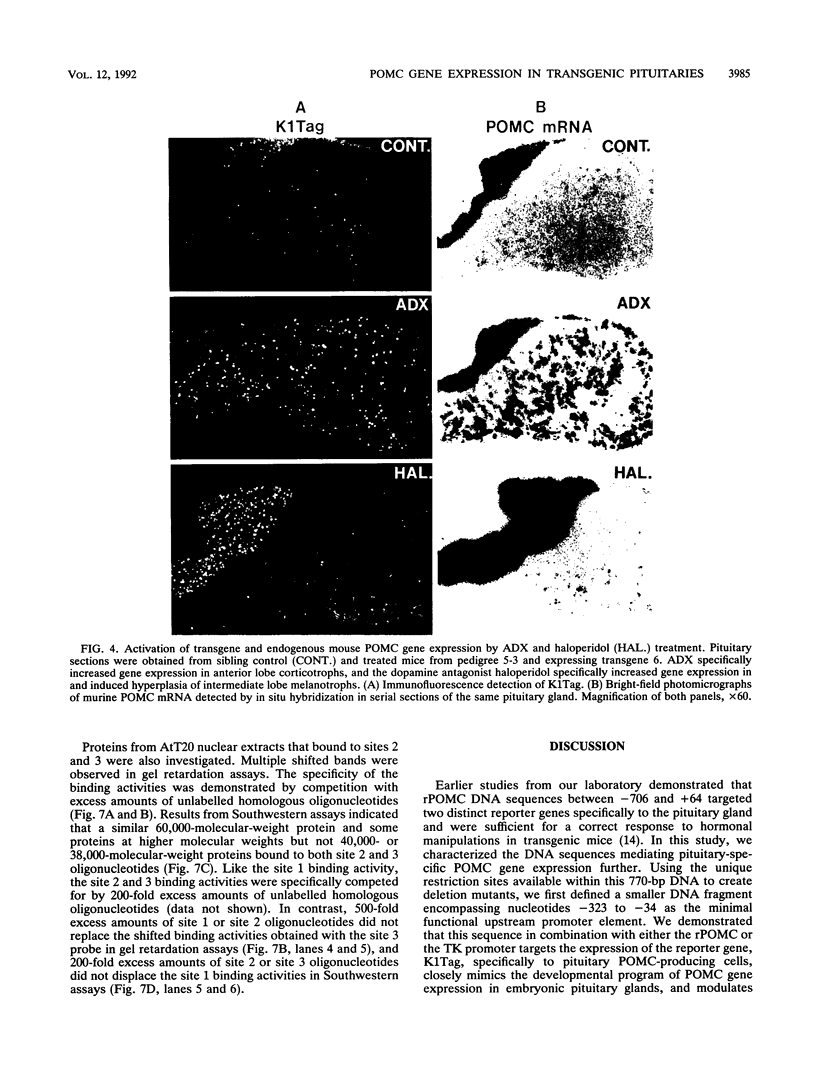
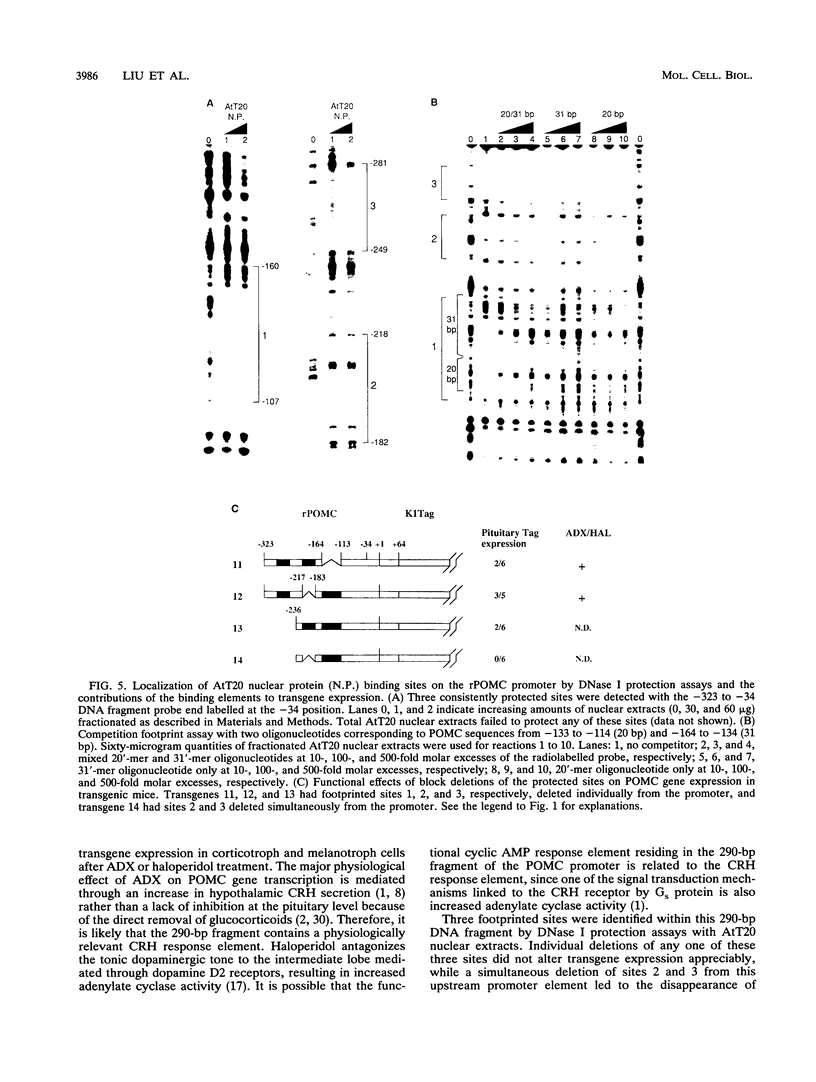
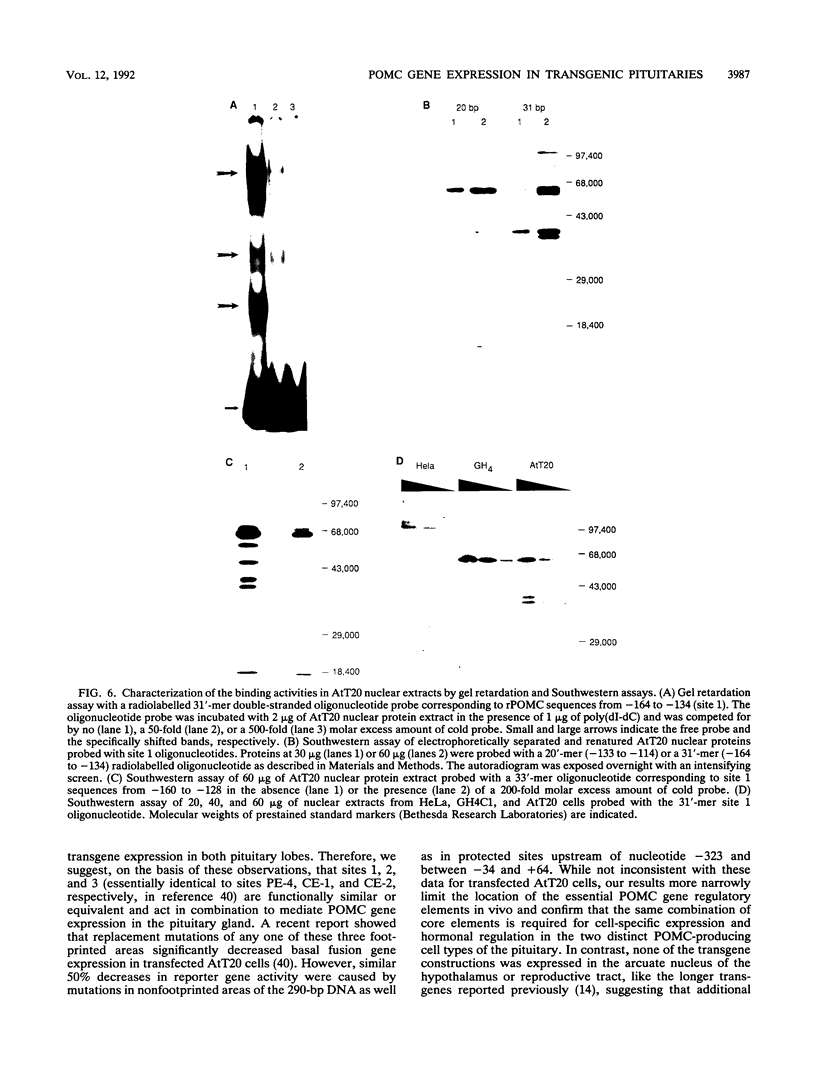
The proopiomelanocortin (POMC) gene is highly expressed in adult mouse pituitary anterior lobe corticotrophs and intermediate lobe melanotrophs. To identify the DNA elements important for this tissue-specific expression, we analyzed a series of POMC reporter genes in transgenic mice. A DNA fragment containing rat POMC 5'-flanking sequences from -323 to -34 recapitulated both basal pituitary cell-specific and hormonally stimulated expression in adult mice when fused to a heterologous thymidine kinase promoter. Developmental onset of the reporter gene expression lagged by 1 day but otherwise closely paralleled the normal ontogeny of murine POMC gene expression, including corticotroph activation at embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) followed by melanotroph activation at E15.5 to E16.5. AtT20 corticotroph nuclear protein extracts interacted with three specific regions of the functional POMC promoter in DNase I protection assays. The positions of these protected sites were -107 to -160 (site 1), -182 to -218 (site 2), and -249 to -281 (site 3). Individual deletions of these footprinted sites did not alter transgene expression; however, the simultaneous deletion of sites 2 and 3 prevented transgene expression in both corticotrophs and melanotrophs. Electrophoretic mobility shift and Southwestern (DNA-protein) assays demonstrated that multiple AtT20 nuclear proteins bound to these footprinted sites. We conclude that the sequences between -323 and -34 of the rat POMC gene promoter are both necessary and sufficient for correct spatial, temporal, and hormonally regulated expression in the pituitary gland. Our data suggest that the three footprinted sites within the promoter are functionally interchangeable and act in combination with promoter elements between -114 and -34. The inability of any reporter gene construction to dissociate basal and hormonally stimulated expression suggests that these DNA elements are involved in both of these two characteristics of POMC gene expression in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilera G., Harwood J. P., Wilson J. X., Morell J., Brown J. H., Catt K. J. Mechanisms of action of corticotropin-releasing factor and other regulators of corticotropin release in rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8039–8045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autelitano D. J., Lundblad J. R., Blum M., Roberts J. L. Hormonal regulation of POMC gene expression. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:715–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Karin M. Function of the homeodomain protein GHF1 in pituitary cell proliferation. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):197–199. doi: 10.1126/science.1677216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civelli O., Birnberg N., Herbert E. Detection and quantitation of pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA in pituitary and brain tissues from different species. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6783–6787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Kalla K., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Cell-specific expression of the prolactin gene in transgenic mice is controlled by synergistic interactions between promoter and enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):959–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. F., Makara G. B., Roberts J. L., Levin N., Blum M. Corticotrope response to removal of releasing factors and corticosteroids in vivo. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2190–2197. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drolet D. W., Scully K. M., Simmons D. M., Wegner M., Chu K. T., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. TEF, a transcription factor expressed specifically in the anterior pituitary during embryogenesis, defines a new class of leucine zipper proteins. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1739–1753. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., Trifiro M. A., Plante R. K., Nemer M., Eriksson P., Wrange O. Glucocorticoid receptor binding to a specific DNA sequence is required for hormone-dependent repression of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5305–5314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkabes S., Loh Y. P., Nieburgs A., Wray S. Prenatal ontogenesis of pro-opiomelanocortin in the mouse central nervous system and pituitary gland: an in situ hybridization and immunocytochemical study. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 Mar 1;46(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield J. M., Daikh D. I., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., Bond C. T., Allen R. G. In situ hybridization detection of marked differences in pre-proopiomelanocortin messenger ribonucleic acid content of individual corticotropes and melanotropes. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1359–1364. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höllt V., Haarmann I., Seizinger B. R., Herz A. Chronic haloperidol treatment increases the level of in vitro translatable messenger ribonucleic acid coding for the beta-endorphin/adrenocorticotropin precursor proopiomelanocortin in the pars intermedia of the rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):1885–1891. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeannotte L., Trifiro M. A., Plante R. K., Chamberland M., Drouin J. Tissue-specific activity of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4058–4064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E. Growth hormone gene regulation: a paradigm for cell-type-specific gene activation. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar T. R., Fairchild-Huntress V., Low M. J. Gonadotrope-specific expression of the human follicle-stimulating hormone beta-subunit gene in pituitaries of transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–90. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.1.1738375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M., Ptashne M., Green M. R. How different eukaryotic transcriptional activators can cooperate promiscuously. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):359–361. doi: 10.1038/345359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira S. A., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Glass C. K., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of rat growth hormone genomic sequences targeting pituitary expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4755–4759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. J., Goodman R. H., Ebert K. M. Cryptic human growth hormone gene sequences direct gonadotroph-specific expression in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):2028–2033. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-2028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad J. R., Roberts J. L. Regulation of proopiomelanocortin gene expression in pituitary. Endocr Rev. 1988 Feb;9(1):135–158. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Albert V. R., Elsholtz H. P., Lu L. I., Rosenfeld M. G. Activation of cell-specific expression of rat growth hormone and prolactin genes by a common transcription factor. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1400–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2831625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Lugo D. I. Proopiomelanocortin gene expression, prohormone processing, and secretion during rat pituitary development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;512:318–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb24970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegel A. T., Lu Y., Remenick J., Wolford R. G., Berard D. S., Hager G. L. Proopiomelanocortin gene promoter elements required for constitutive and glucocorticoid-repressed transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1973–1982. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegel A. T., Remenick J., Wolford R. G., Berard D. S., Hager G. L. A novel transcriptional activator (PO-B) binds between the TATA box and cap site of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4513–4521. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Rosenzweig B. A., Friend K. E., Mason M. E. Thyrotropin (TSH)-releasing hormone-responsive elements in the rat TSH beta gene have distinct biological and nuclear protein-binding properties. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.1.1738370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. I., Funder J. W. Proopiomelanocortin processing in the pituitary, central nervous system, and peripheral tissues. Endocr Rev. 1988 Feb;9(1):159–179. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien M., Drouin J. Pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin gene expression requires synergistic interactions of several regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3492–3503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. M., Rehfuss R. P., Chrivia J. C., Lochner J. E., Goodman R. H. A dominant repressor of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP)-regulated enhancer-binding protein activity inhibits the cAMP-mediated induction of the somatostatin promoter in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;6(4):647–655. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1350057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y. G., Daikoku S. An immunohistochemical study on the cytogenesis of adenohypophysial cells in fetal rats. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellstein A., Dobrenski A. F., Radonovich M. N., Brady J. F., Riegel A. T. Purification of PO-B, a protein that has increased affinity for the pro-opiomelanocortin gene promoter after dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12234–12241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Rice P. W., Chamberlain M., Cole C. N. Mapping the transcriptional transactivation function of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2778–2790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2778-2790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]