Abstract
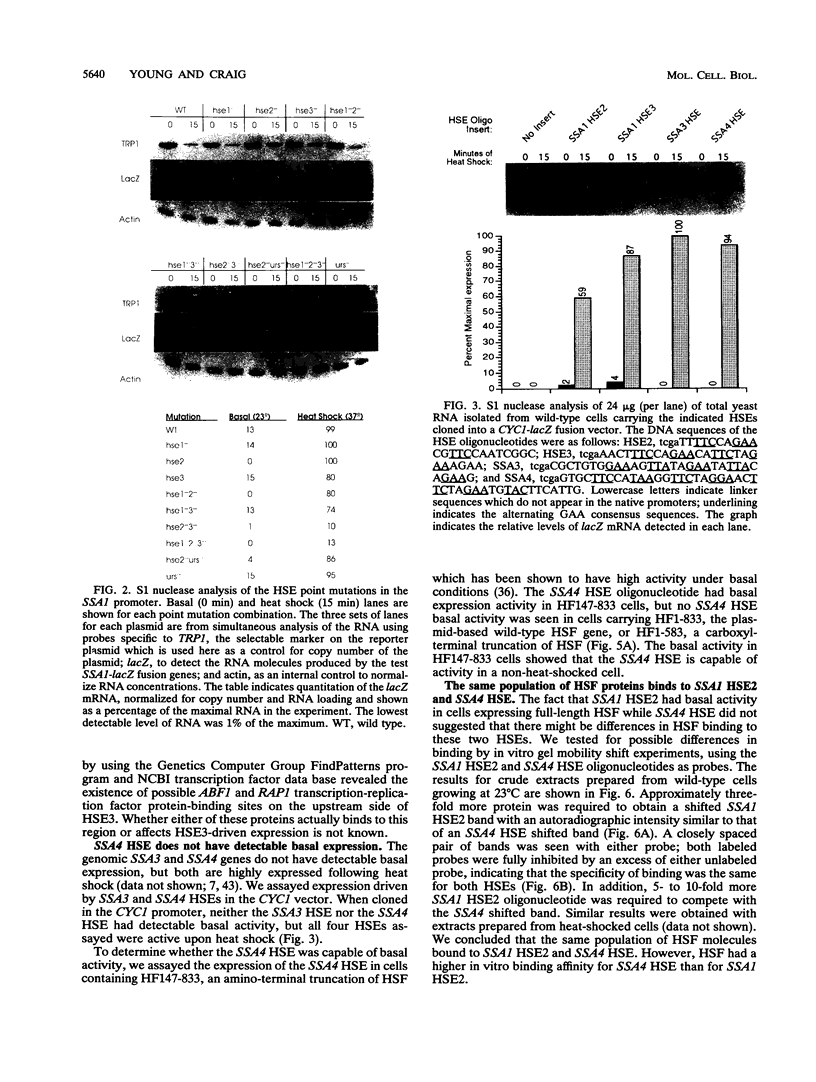
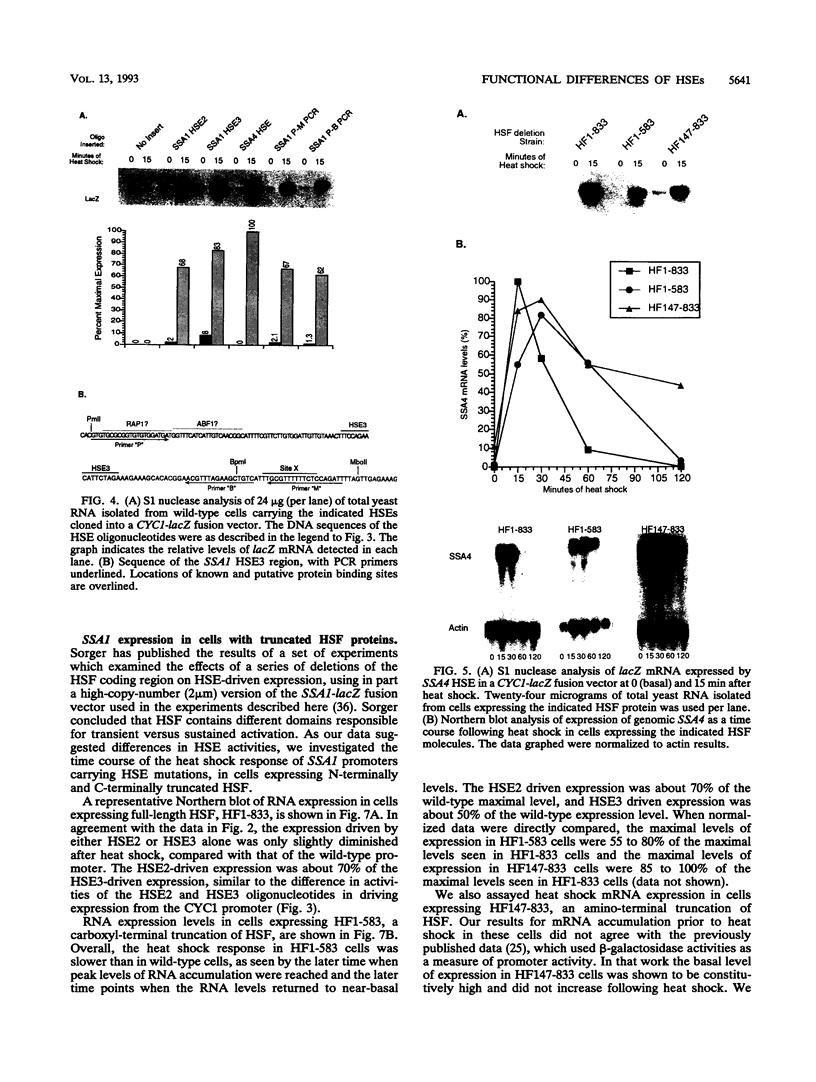
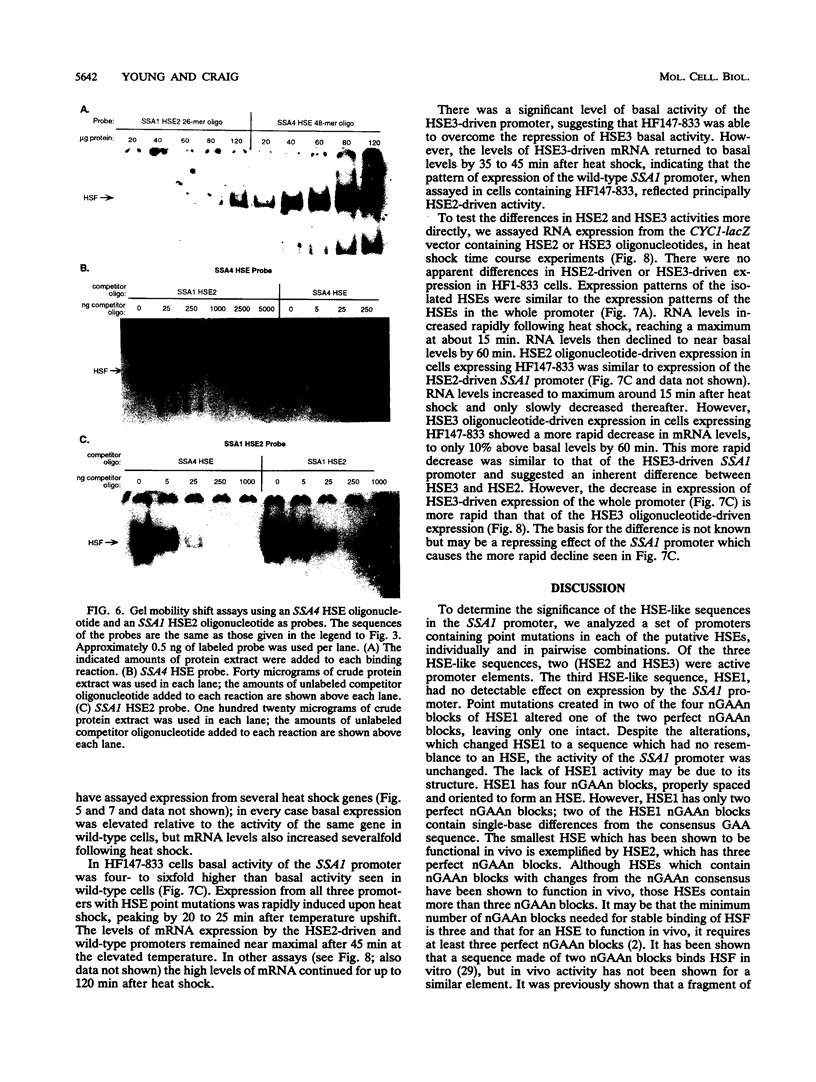
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae HSP70 gene SSA1 has multiple heat shock elements (HSEs). To determine the significance of each of these sequences for expression of SSA1, we analyzed expression from a set of promoters containing point mutations in each of the HSEs, individually and in pairwise combinations. Of the three HSE-like sequences, two (HSE2 and HSE3) were active promoter elements; only one, HSE2, was active under basal growth conditions. Either HSE2 or HSE3 alone was able to drive SSA1 transcription at near-normal rates after heat shock. Both HSE2 and HSE3 were capable of driving basal transcription when placed in the context of the CYC1 promoter. Previous analysis had identified an upstream repressing sequence overlapping HSE2 that repressed basal transcription driven by HSE2. Our analysis showed that basal transcription driven by HSE3 was repressed both by the distant upstream repressing sequence and by closer flanking sequences. The ability to drive basal transcription is not inherent in all natural HSEs, since the HSEs from the heat-inducible SSA3 and SSA4 genes showed no basal activity when placed in the CYC1 vector. Gel mobility shift experiments showed that the same population of heat shock transcription factor molecules bound to HSEs capable of driving basal activity and to HSEs having very low or undetectable basal activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. C., Gross D. S. The yeast heat shock response is induced by conversion of cells to spheroplasts and by potent transcriptional inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7429–7435. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7429-7435.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Mechanisms of heat-shock gene activation in higher eukaryotes. Adv Genet. 1987;24:31–72. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Heyward S., Fackenthal D. L. Temperature-dependent regulation of a heterologous transcriptional activation domain fused to yeast heat shock transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boorstein W. R., Craig E. A. Structure and regulation of the SSA4 HSP70 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18912–18921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boorstein W. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of SSA3, an HSP70 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3262–3267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Westwood J. T., Becker P. B., Wilson S., Lambert K., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90511-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. Essential roles of 70kDa heat inducible proteins. Bioessays. 1989 Aug-Sep;11(2-3):48–52. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Gross C. A. Is hsp70 the cellular thermometer? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Jacobsen K. Mutations of the heat inducible 70 kilodalton genes of yeast confer temperature sensitive growth. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):841–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. J., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Regulation of heat shock factor in Schizosaccharomyces pombe more closely resembles regulation in mammals than in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Yeast TATA-binding protein TFIID binds to TATA elements with both consensus and nonconsensus DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5718–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Yamamoto T., Ohkuma Y., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Analysis of structure-function relationships of yeast TATA box binding factor TFIID. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1171–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. Constitutive binding of yeast heat shock factor to DNA in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5040–5042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Schuetz T. J., Larin Z. Heat-inducible human factor that binds to a human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neves A. M., Barahona I., Galego L., Rodrigues-Pousada C. Ubiquitin genes in Tetrahymena pyriformis and their expression during heat shock. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sotelo J., Wiederrecht G., Okuda A., Parker C. S. The yeast heat shock transcription factor contains a transcriptional activation domain whose activity is repressed under nonshock conditions. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. O., Craig E. A. Positive and negative regulation of basal expression of a yeast HSP70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2025–2033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. O., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of a yeast HSP70 gene by heat shock factor and an upstream repression site-binding factor. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1299–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Bienz M. A synthetic heat-shock promoter element confers heat-inducibility on the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Giorgi G., Clos J., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a human heat shock factor, HSF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6906–6910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarge K. D., Zimarino V., Holm K., Wu C., Morimoto R. I. Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock factors with distinct inducible and constitutive DNA-binding ability. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1902–1911. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Rose S., Zott W., Schöffl F., Nover L., Schöff F. Three tomato genes code for heat stress transcription factors with a region of remarkable homology to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast HSF. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4495–4501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz T. J., Gallo G. J., Sheldon L., Tempst P., Kingston R. E. Isolation of a cDNA for HSF2: evidence for two heat shock factor genes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6911–6915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of an hsp70 heat shock gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1906–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Nelson H. C. Trimerization of a yeast transcriptional activator via a coiled-coil motif. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Yeast heat shock factor contains separable transient and sustained response transcriptional activators. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90123-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. E., Craig E. A. Self-regulation of 70-kilodalton heat shock proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1622–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Becker J., Kosic-Smithers J., Craig E. A. Yeast Hsp70 RNA levels vary in response to the physiological status of the cell. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2680–2688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2680-2688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Seto D., Parker C. S. Isolation of the gene encoding the S. cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










