Abstract
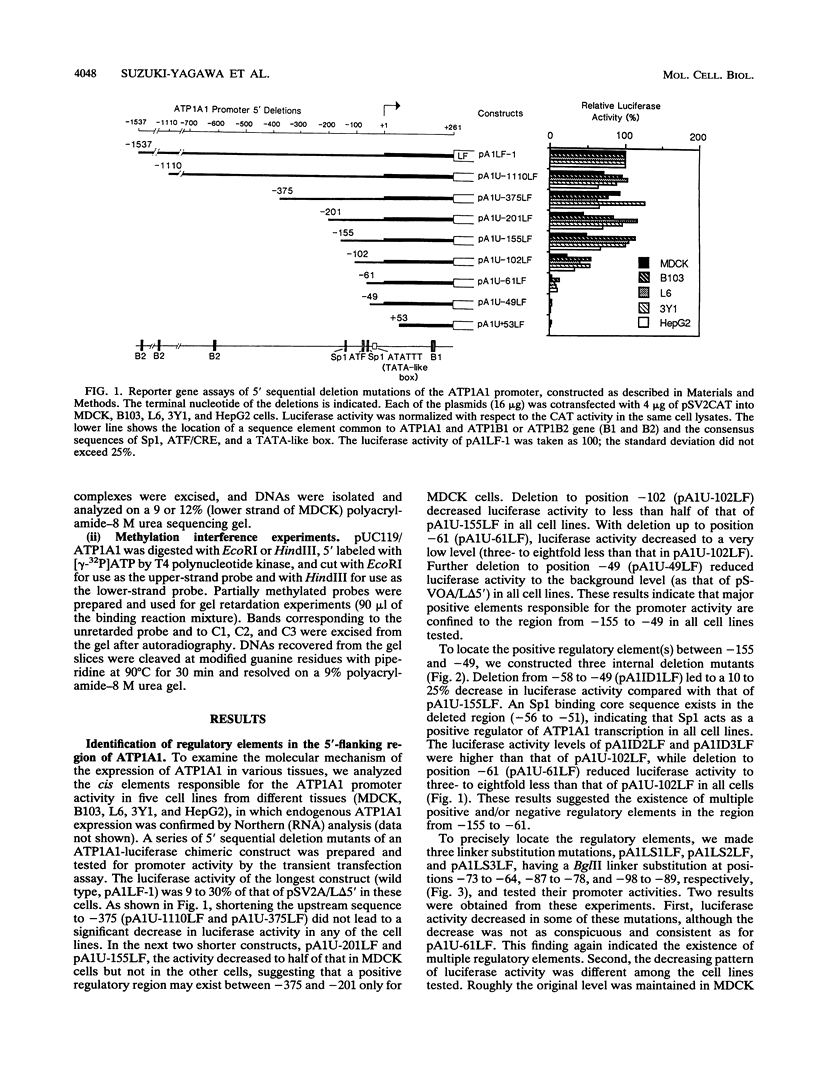
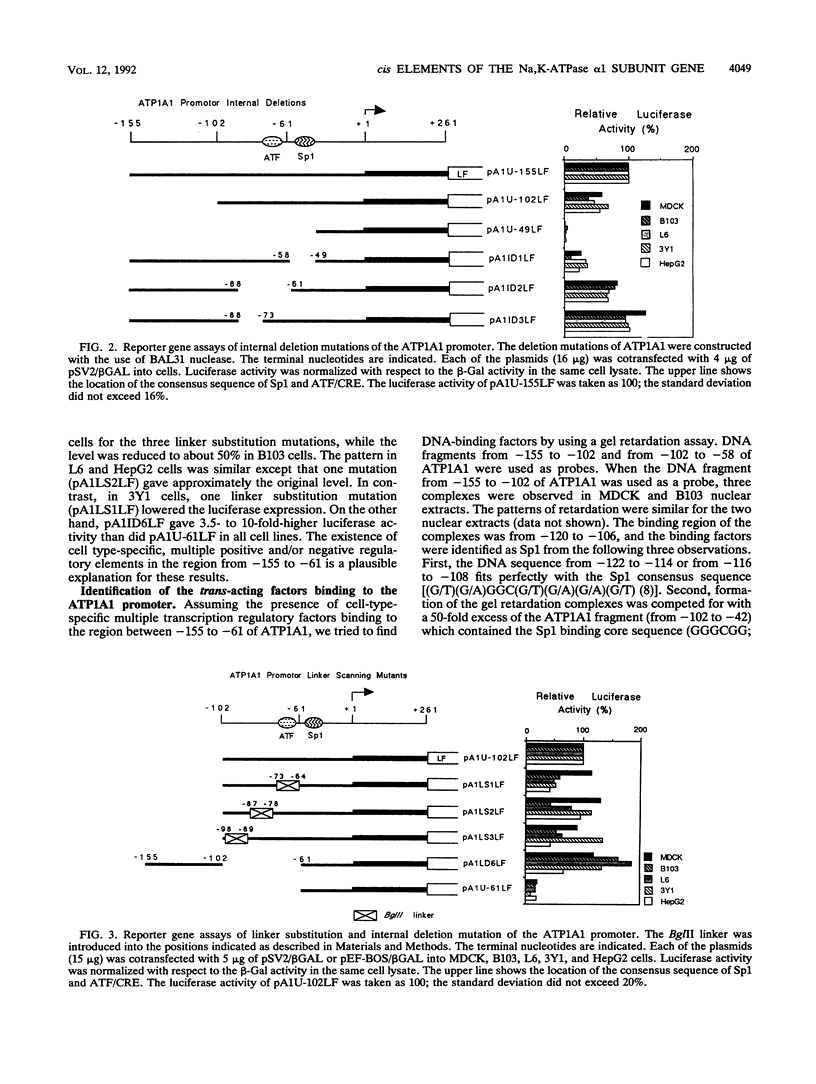
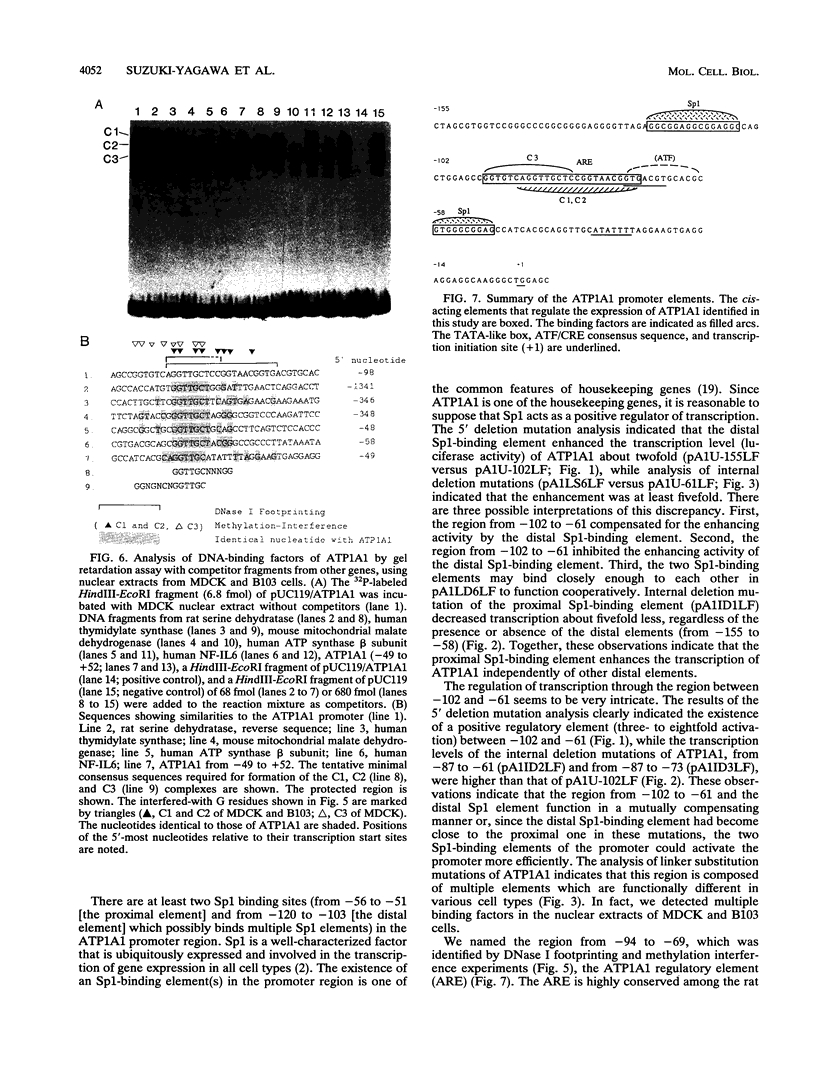
Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 subunit gene (ATP1A1) is one of the housekeeping genes involved in homeostasis of Na+ and K+ in all animal cells. We identified and characterized the cis-acting elements that regulate the expression of ATP1A1. The region between -155 and -49 was determined as a positive regulatory region in five cultured cell lines of different tissue origins (MDCK, B103, L6, 3Y1, and HepG2). The region was divided into three subregions: from -120 to -106 (including the Sp1 binding site), from -102 to -61, and from -58 to -49 (including an Sp1 consensus sequence). Cell type-specific factors binding to the middle subregion (from -102 to -61) were detected by gel retardation analysis, using nuclear extracts prepared from MDCK and B103 cells. Two gel retardation complexes were formed in the B103 nuclear extract, and three were formed in the MDCK nuclear extract. DNA binding regions of these factors were located at -88 to -69 and differed from each other in DNase I footprinting experiments. These factors also showed different binding characteristics in gel retardation competition and methylation interference experiments. The identified cis element was named the ATP1A1 regulatory element. The core sequence of this element is found in several other genes involved in cellular energy metabolism, suggesting that the sequence is a common regulatory element responsive to the state of energy metabolism.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognet M., Lone Y. C., Vaulont S., Kahn A., Marie J. Structure of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good P. J., Richter K., Dawid I. B. A nervous system-specific isotype of the beta subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase expressed during early development of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9088–9092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera V. L., Emanuel J. R., Ruiz-Opazo N., Levenson R., Nadal-Ginard B. Three differentially expressed Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit isoforms: structural and functional implications. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1855–1865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano I., Nagai F., Satoh K., Ushiyama K., Nakao T., Kano K. Structure of the alpha 1 subunit of horse Na,K-ATPase gene. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 19;250(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80691-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Nojima H., Ohta T., Nagano K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2833–2844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Okamoto H., Yagawa Y., Nagano K. Regulation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase. II. Cloning and analysis of the 5'-flanking region of the rat NKAB2 gene encoding the beta 2 subunit. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90099-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Suzuki-Yagawa Y., Watanabe Y., Nagano K. Identification and characterization of the cis-elements regulating the rat AMOG (adhesion molecule on glia)/Na,K-ATPase beta 2 subunit gene. J Biochem. 1992 Apr;111(4):515–522. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Yagawa Y., Nagano K. Regulation of Na+,K(+)-ATPases. I. Cloning and analysis of the 5'-flanking region of the rat NKAA2 gene encoding the alpha 2 subunit. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90098-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Moores J. C., David D., Respess J. G., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T. The organization of the human HPRT gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3103–3118. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane L. K., Shull M. M., Whitmer K. R., Lingrel J. B. Characterization of two genes for the human Na,K-ATPase beta subunit. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Vasallo P., Dackowski W., Emanuel J. R., Levenson R. Identification of a putative isoform of the Na,K-ATPase beta subunit. Primary structure and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4613–4618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Fujioka M., Matsuda Y., Su Y., Dunn T., Miller D. A., Pitot H. C. Sequence of the rat serine dehydratase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10921–10923. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta S., Tomura H., Matsuda K., Kagawa Y. Gene structure of the human mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate synthase beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11257–11262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Lingrel J. B. Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rat Na,K-ATPase catalytic alpha isoform and beta subunit mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10436–10442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Gilmore-Hebert M., Utset M. F., Lai C., Greene A., Benz E. J., Jr Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):284–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Ding S. H., Choudhury B. K., Joh T., Takeshima H., Tsuzuki T., Shimada K. Regulatory regions of the mitochondrial and cytosolic isoenzyme genes participating in the malate-aspartate shuttle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1293–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull M. M., Pugh D. G., Lingrel J. B. Characterization of the human Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 gene and identification of intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17532–17543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull M. M., Pugh D. G., Lingrel J. B. The human Na, K-ATPase alpha 1 gene: characterization of the 5'-flanking region and identification of a restriction fragment length polymorphism. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90475-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver B. J., Bokar J. A., Virgin J. B., Vallen E. A., Milsted A., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulation of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is mediated by an 18-base-pair element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Mitchell P. J., Crouse G. F. Analysis of the mouse Dhfr/Rep-3 major promoter region by using linker-scanning and internal deletion mutations and DNase I footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6003–6012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Edelman I. S. The role of sodium transport in thyroid thermogenesis. Fed Proc. 1979 Jul;38(8):2150–2153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somma M. P., Gambino I., Lavia P. Transcription factors binding to the mouse HTF9 housekeeping promoter differ between cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4451–4458. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Kaneda S., Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Gotoh O., Seno T. Human thymidylate synthase gene: isolation of phage clones which cover a functionally active gene and structural analysis of the region upstream from the translation initiation codon. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):575–583. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Vasser M., Powers D. B. Cassette mutagenesis: an efficient method for generation of multiple mutations at defined sites. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagawa Y., Kawakami K., Nagano K. Cloning and analysis of the 5'-flanking region of rat Na+/K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90099-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]