Abstract
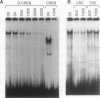
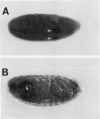
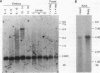
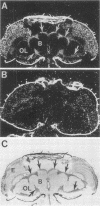
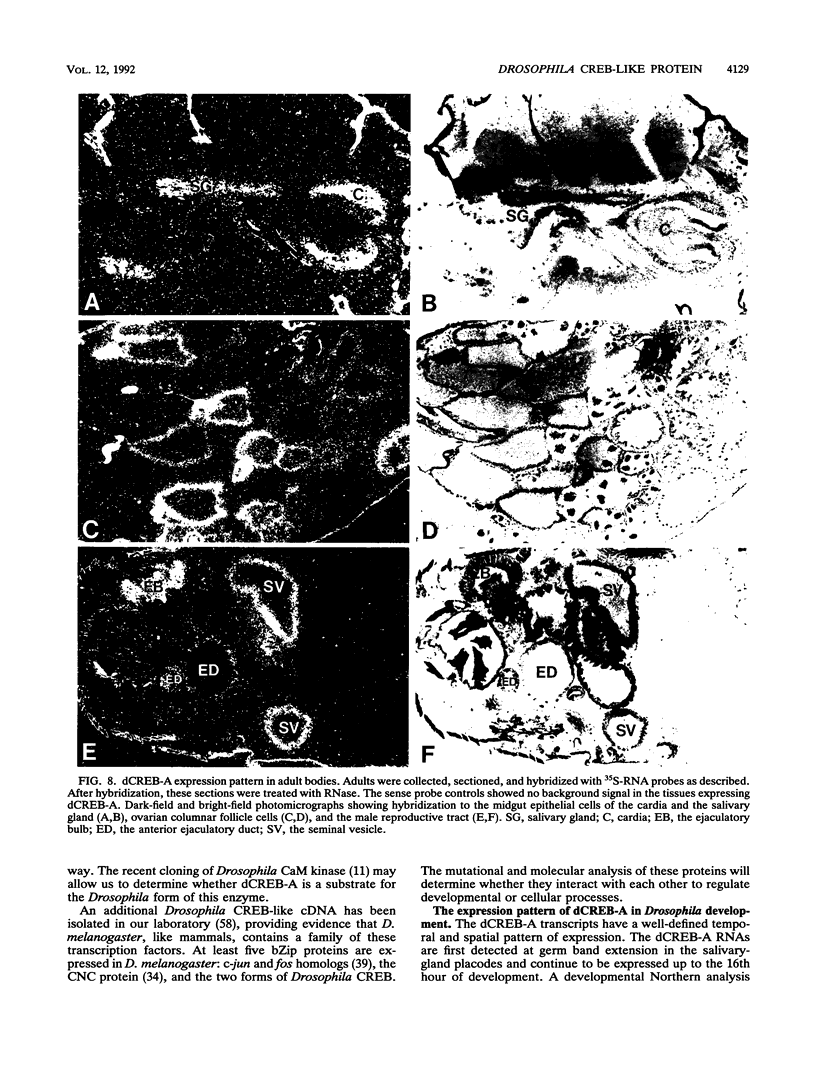
In this report, we describe the isolation and initial characterization of a Drosophila protein, dCREB-A, that can bind the somatostatin cyclic AMP (cAMP)-responsive element and is capable of activating transcription in cell culture. Sequence analysis demonstrates that this protein is a member of the leucine zipper family of transcription factors. dCREB-A is unusual in that it contains six hydrophobic residue iterations in the zipper domain rather than the four or five commonly found in this group of proteins. The DNA-binding domain is more closely related to mammalian CREB than to the AP-1 factors in both sequence homology and specificity of cAMP-responsive element binding. In embryos, dCREB-A is expressed in the developing salivary gland. A more complex pattern of expression is detected in the adult; transcripts are found in the brain and optic lobe cell bodies, salivary gland, and midgut epithelial cells of the cardia. In females, dCREB-A is expressed in the ovarian columnar follicle cells, and in males, dCREB-A RNA is seen in the seminal vesicle, ejaculatory duct, and ejaculatory bulb. These results suggest that the dCREB-A transcription factor may be involved in fertility and neurological functions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel T., Bhatt R., Maniatis T. A Drosophila CREB/ATF transcriptional activator binds to both fat body- and liver-specific regulatory elements. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):466–480. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio L., Mahowald A. P., Perrimon N. Requirement of the Drosophila raf homologue for torso function. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):288–291. doi: 10.1038/342288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Hayes T. E., Roos B., Dixon J. E. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the cell specific expression of the rat somatostatin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5715–5728. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Adler J. E., Dreyfus C. F., Friedman W. F., LaGamma E. F., Roach A. H. Biochemistry of information storage in the nervous system. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1263–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.2884727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers D., Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Defect in cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase due to the dunce mutation of learning in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):79–81. doi: 10.1038/289079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Struhl G. Localized surface activity of torso, a receptor tyrosine kinase, specifies terminal body pattern in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2025–2038. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. O., Wall J. B., Pugh P. C., Ito M., Mueller S. A., Kennedy M. B. The alpha subunit of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase is highly conserved in Drosophila. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):439–450. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90296-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. S., Verhave M., Kasper S., Tsukada T., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. The CGTCA sequence motif is essential for biological activity of the vasoactive intestinal peptide gene cAMP-regulated enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming R. J., Scottgale T. N., Diederich R. J., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The gene Serrate encodes a putative EGF-like transmembrane protein essential for proper ectodermal development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2188–2201. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP response element binding proteins: a cornucopia of transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori K., Angel P., Le Beau M. M., Karin M. Structure and chromosomal localization of the functional intronless human JUN protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9148–9152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Waeber G., Habener J. F. Multiple adenosine 3',5'-cyclic [corrected] monophosphate response element DNA-binding proteins generated by gene diversification and alternative exon splicing. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):920–930. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., O'Shea E. K., Kim P. S., Sauer R. T. Sequence requirements for coiled-coils: analysis with lambda repressor-GCN4 leucine zipper fusions. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1400–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.2147779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Rubin G. M. Isolation and characterization of Drosophila cAMP-dependent protein kinase genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1539–1556. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Sziber P. P., Quinn W. G. Loss of calcium/calmodulin responsiveness in adenylate cyclase of rutabaga, a Drosophila learning mutant. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J., Vani K., Leung S., Epstein A. Segmentally restricted, cephalic expression of a leucine zipper gene during Drosophila embryogenesis. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;34(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90086-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
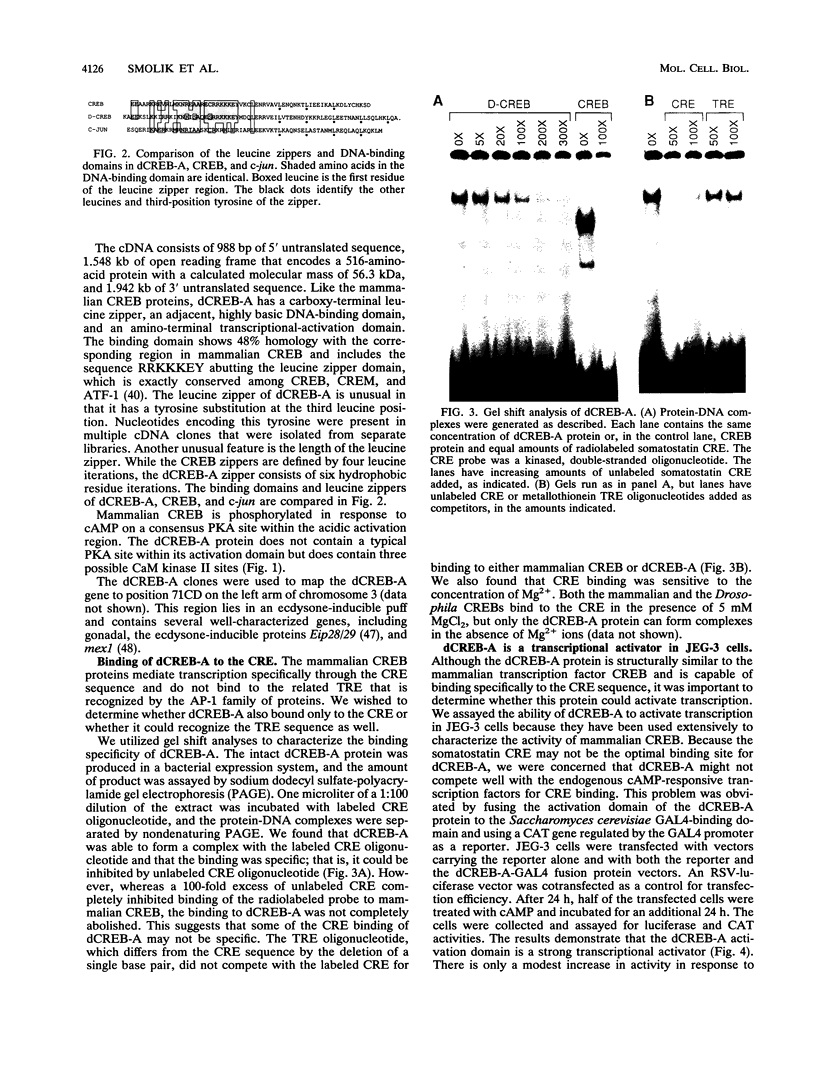
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Role of ion flux in the control of c-fos expression. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):552–555. doi: 10.1038/322552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Admon A., Patel N., Tjian R. The Drosophila Fos-related AP-1 protein is a developmentally regulated transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):822–834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu W. T., Struhl K. Highly conserved residues in the bZIP domain of yeast GCN4 are not essential for DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4918–4926. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. G., Wong T. W., Magnuson M. A., Shabb J. B., Granner D. K. Identification of basal and cyclic AMP regulatory elements in the promoter of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3467–3475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfuss R. P., Walton K. M., Loriaux M. M., Goodman R. H. The cAMP-regulated enhancer-binding protein ATF-1 activates transcription in response to cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18431–18434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
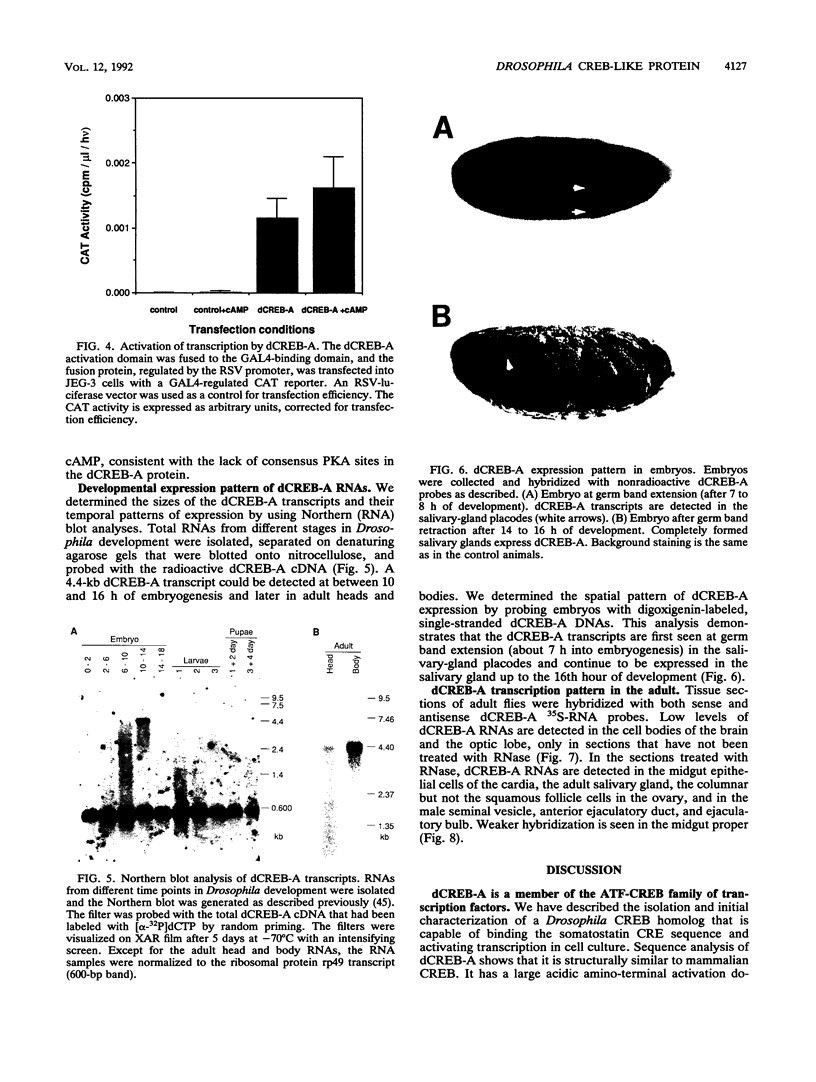
- Sassone-Corsi P. Cyclic AMP induction of early adenovirus promoters involves sequences required for E1A trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7192–7196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R. A., Butler B. A. Overlapping genes of Drosophila melanogaster: organization of the z600-gonadal-Eip28/29 gene cluster. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):232–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R. A., Xie X., Andres A. J., Galewsky S. Endoderm-specific expression of the Drosophila mex1 gene. Dev Biol. 1991 Jan;143(1):206–211. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90068-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., McFadden G., Greenberg M. E. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):571–582. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90115-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried E., Perkins L. A., Capaci T. M., Perrimon N. Putative protein kinase product of the Drosophila segment-polarity gene zeste-white3. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):825–829. doi: 10.1038/345825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
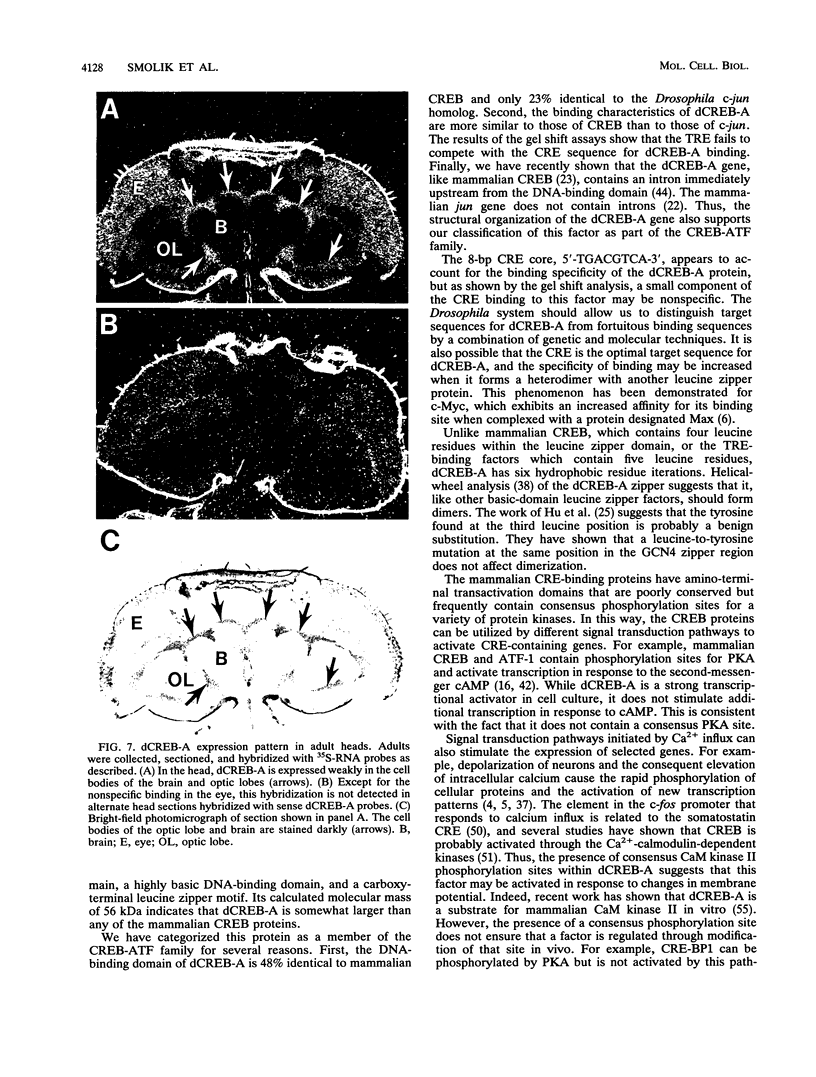
- Sprenger F., Stevens L. M., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The Drosophila gene torso encodes a putative receptor tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):478–483. doi: 10.1038/338478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. M., Rehfuss R. P. Molecular mechanisms of cAMP-regulated gene expression. Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Fall-Winter;4(3-4):197–210. doi: 10.1007/BF02780341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Chaillet J. R., Perkins L. A., Halazonetis T. D., Perrimon N. Drosophila homolog of the mammalian jun oncogene is expressed during embryonic development and activates transcription in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6281–6285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. J., Giam C. Z. Interaction of the human T-cell lymphotrophic virus type I (HTLV-I) transcriptional activator Tax with cellular factors that bind specifically to the 21-base-pair repeats in the HTLV-I enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11445–11449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]