Abstract
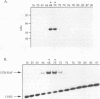
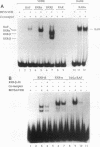
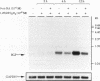
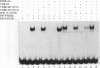
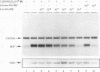
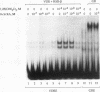
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) binds the vitamin D-responsive element (VDRE) as a heterodimer with an unidentified receptor auxiliary factor (RAF) present in mammalian cell nuclear extracts. VDR also interacts with the retinoid X receptors (RXRs), implying that RAF may be related to the RXRs. Here we demonstrate that highly purified HeLa cell RAF contained RXR beta immunoreactivity and that both activities copurified and precisely coeluted in high-resolution hydroxylapatite chromatography. Furthermore, an RXR beta-specific antibody disrupted VDR-RAF-VDRE complexes in mobility shift assays. These data strongly indicate that HeLa RAF is highly related to or is identical to RXR beta. Consequently, the effect of the 9-cis retinoic acid ligand for RXRs was examined in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3]-activated gene expression systems. Increasing concentrations of 9-cis retinoic acid (1 nM to 1 microM) markedly reduced 1,25(OH)2D3-dependent accumulation of osteocalcin mRNA in osteoblast-like ROS 17/2.8 cells. All-trans retinoic acid also interfered with vitamin D responsiveness, but it was consistently less potent than the 9-cis isomer. Transient transfection studies revealed that attenuation by 9-cis retinoic acid was at the transcriptional level and was mediated through interactions at the osteocalcin VDRE. Furthermore, overexpression of both RXR beta and RXR alpha augmented 1,25(OH)2D3 responsiveness in transient expression studies. Direct analysis of VDRE binding in mobility shift assays demonstrated that heteromeric interactions between VDR and RXR were enhanced by 1,25(OH)2D3 and were not affected appreciably by 9-cis retinoic acid, except that inhibition was observed at high retinoid concentrations. These data suggest a regulatory mechanism for osteocalcin gene expression that involves 1,25(OH)2D3-induced heterodimerization of VDR and unliganded RXR. 9-cis retinoic acid may attenuate 1,25(OH)2D3 responsiveness by diverting RXRs away from VDR-mediated transcription and towards other RXR-dependent transcriptional pathways.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg C., Bendik I., Wyss A., Meier E., Sturzenbecker L. J., Grippo J. F., Hunziker W. Two nuclear signalling pathways for vitamin D. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):657–660. doi: 10.1038/361657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darwish H. M., DeLuca H. F. Identification of a 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-response element in the 5'-flanking region of the rat calbindin D-9k gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):603–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowd D. R., Miesfeld R. L. Evidence that glucocorticoid- and cyclic AMP-induced apoptotic pathways in lymphocytes share distal events. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3600–3608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flink I. L., Morkin E. Interaction of thyroid hormone receptors with strong and weak cis-acting elements in the human alpha-myosin heavy chain gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11233–11237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Gleason S. L., Levi B. Z., Hirschfeld S., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8289–8293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh J. C., Jurutka P. W., Galligan M. A., Terpening C. M., Haussler C. A., Samuels D. S., Shimizu Y., Shimizu N., Haussler M. R. Human vitamin D receptor is selectively phosphorylated by protein kinase C on serine 51, a residue crucial to its trans-activation function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9315–9319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner S. A., Scott R. A., Pike J. W. Sequence elements in the human osteocalcin gene confer basal activation and inducible response to hormonal vitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Allan G. F., Riley D., Rodriguez R., Schrader W. T., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. The progesterone receptor stimulates cell-free transcription by enhancing the formation of a stable preinitiation complex. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90740-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor-COUP-TF interactions modulate retinoic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Noonan D. J., Heyman R. A., Evans R. M. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):771–774. doi: 10.1038/358771a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao J., Ozono K., Sone T., McDonnell D. P., Pike J. W. Vitamin D receptor interaction with specific DNA requires a nuclear protein and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9751–9755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. N., Haussler C. A., Terpening C. M., Galligan M. A., Reeder M. C., Whitfield G. K., Haussler M. R. Baculovirus-mediated expression of the human vitamin D receptor. Functional characterization, vitamin D response element interactions, and evidence for a receptor auxiliary factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18808–18813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. Avian and mammalian receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: in vitro translation to characterize size and hormone-dependent regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):354–358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Segars J. H., Driggers P. H., Hirschfeld S., Nagata T., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP expressed from a baculovirus vector binds to multiple hormone response elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):219–230. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Mangelsdorf D. J., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the avian receptor for vitamin D. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1214–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.3029866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H., Komm B. S., Haussler M. R. Dietary restriction of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D elicits differential regulation of the mRNAs for avian intestinal calbindin-D28k and the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor. J Bone Miner Res. 1992 Apr;7(4):441–448. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650070412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison N. A., Shine J., Fragonas J. C., Verkest V., McMenemy M. L., Eisman J. A. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-responsive element and glucocorticoid repression in the osteocalcin gene. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1158–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2588000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Vogel R. L., Craig A. M., Prahl J., DeLuca H. F., Denhardt D. T. Identification of a DNA sequence responsible for binding of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhancement of mouse secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP-1 or osteopontin) gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9995–9999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozono K., Liao J., Kerner S. A., Scott R. A., Pike J. W. The vitamin D-responsive element in the human osteocalcin gene. Association with a nuclear proto-oncogene enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21881–21888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich P. M., Heersche J. N., Tinker D. O., Jones G. Retinoic acid stimulates 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 binding in rat osteosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8274–8280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. D., O'Donnell A. L., Koenig R. J. Ligand-dependent synergy of thyroid hormone and retinoid X receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22010–22013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. K., Moss V. E., Prahl J. M., DeLuca H. F. A nuclear protein essential for binding of rat 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor to its response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone T., Kerner S., Pike J. W. Vitamin D receptor interaction with specific DNA. Association as a 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-modulated heterodimer. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23296–23305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone T., Ozono K., Pike J. W. A 55-kilodalton accessory factor facilitates vitamin D receptor DNA binding. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1578–1586. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpening C. M., Haussler C. A., Jurutka P. W., Galligan M. A., Komm B. S., Haussler M. R. The vitamin D-responsive element in the rat bone Gla protein gene is an imperfect direct repeat that cooperates with other cis-elements in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3- mediated transcriptional activation. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):373–385. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Eriksson P., Perlmann T. The purified activated glucocorticoid receptor is a homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]