Abstract
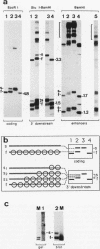
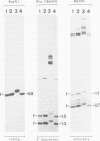
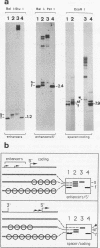
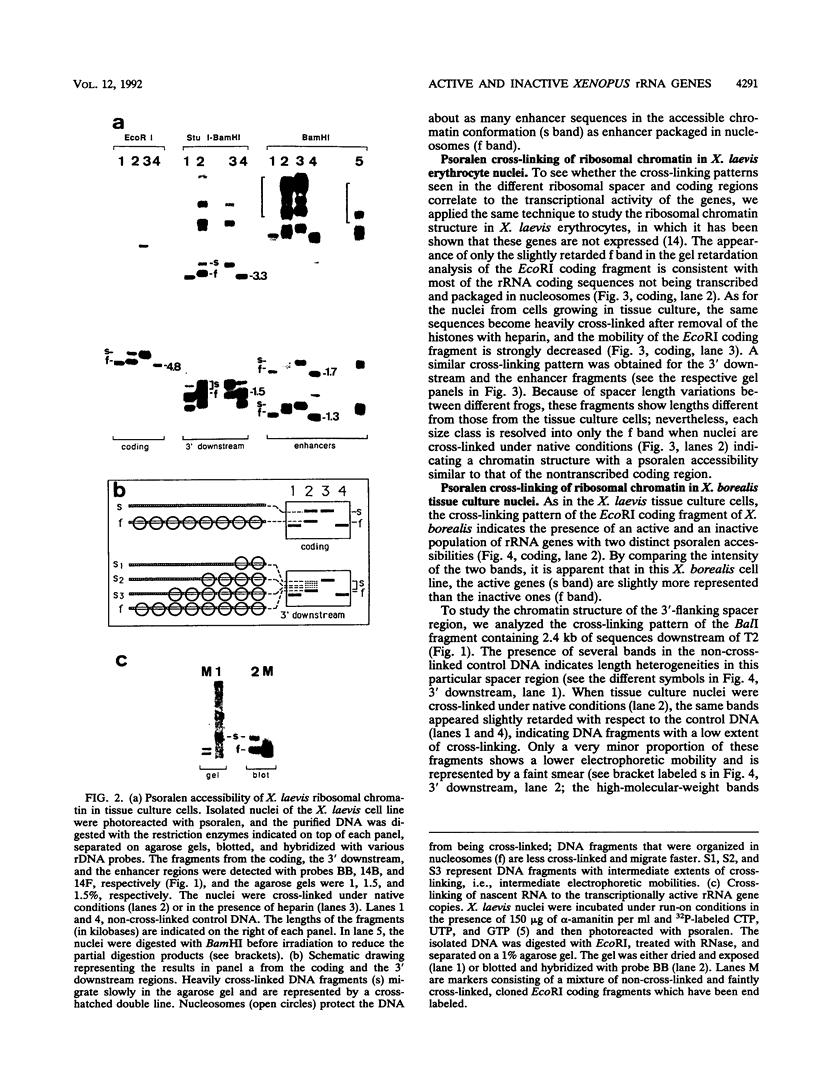
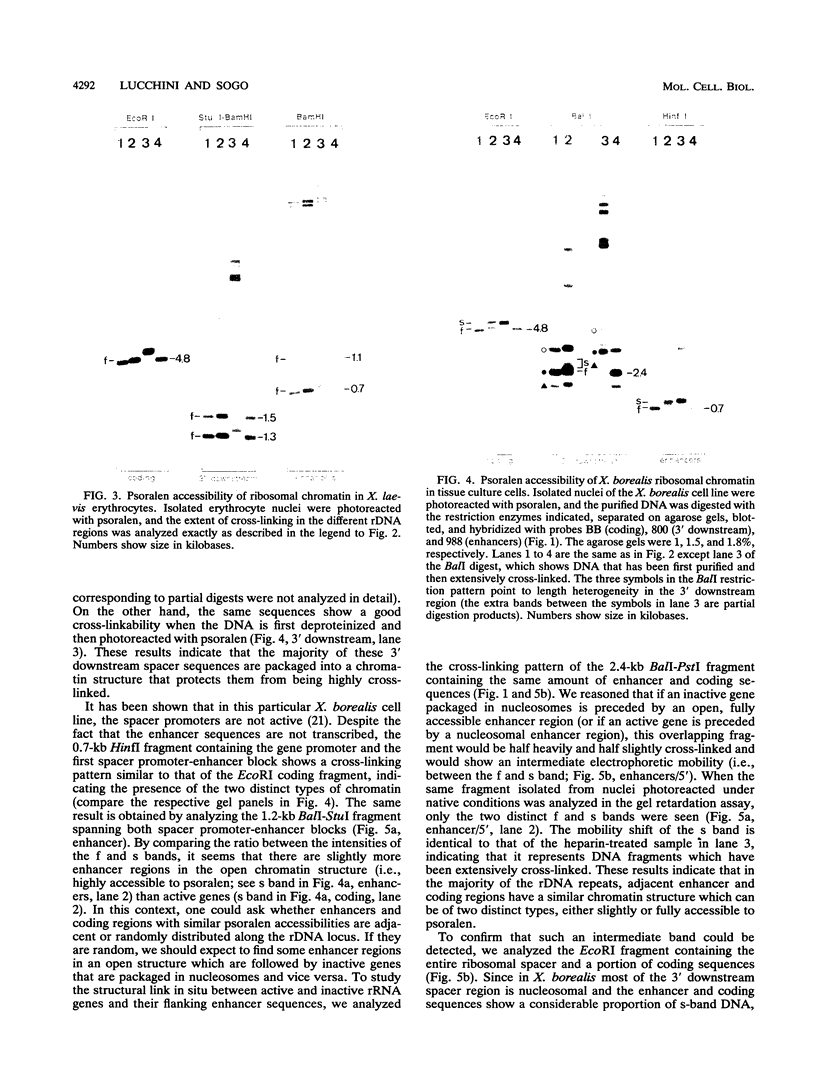
The accessibility of DNA in chromatin to psoralen was assayed to compare the chromatin structure of the rRNA coding and spacer regions of the two related frog species Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis. Isolated nuclei from tissue culture cells were photoreacted with psoralen, and the extent of cross-linking in the different rDNA regions was analyzed by using a gel retardation assay. In both species, restriction fragments from the coding regions showed two distinct extents of cross-linking, indicating the presence of two types of chromatin, one that contains nucleosomes and represents the inactive gene copies, and the other one which is more cross-linked and corresponds to the transcribed genes. A similar cross-linking pattern was obtained with restriction fragments from the enhancer region. Analysis of fragments including these sequences and the upstream portions of the genes suggests that active genes are preceded by nonnucleosomal enhancer regions. The spacer regions flanking the 3' end of the genes gave different results in the two frog species. In X. borealis, all these sequences are packaged in nucleosomes, whereas in X. laevis a distinct fraction, presumably those flanking the active genes, show a heterogeneous chromatin structure. This disturbed nucleosomal organization correlates with the presence of a weaker terminator at the 3' end of the X. laevis genes compared with those of X. borealis, which allows polymerases to transcribe into the downstream spacer.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botchan P., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B. Restriction analysis of the nontranscribed spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. O., Pfenninger O., Sinden R. R., Lehman J. M., Pettijohn D. E. New procedure using a psoralen derivative for analysis of nucleosome associated DNA sequences in chromatin of living cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2043–2063. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T., Pardue M. L. Cross-linking of DNA with trimethylpsoralen is a probe for chromatin structure. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):631–640. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi A., Losa R., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Psoralen-crosslinking of soluble and of H1-depleted soluble rat liver chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):920–928. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi A., Widmer R. M., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Two different chromatin structures coexist in ribosomal RNA genes throughout the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90790-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coveney J., Woodland H. R. The DNase I sensitivity of Xenopus laevis genes transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):578–580. doi: 10.1038/298578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampton J. M., Woodland H. R. A cell-free assay system for the analysis of changes in RNA synthesis during the development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V., Sollner-Webb B. Sites of topoisomerase I action on X. laevis ribosomal chromatin: transcriptionally active rDNA has an approximately 200 bp repeating structure. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. The ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis is transcribed as part of the primary ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6041–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov S. I., Stefanovsky VYu, Karagyozov L., Angelov D., Pashev I. G. The enhancers and promoters of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal spacer are associated with histones upon active transcription of the ribosomal genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6393–6397. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M. A transcription factor, TFIS, interacts with both the promoter and enhancer of the Xenopus rRNA genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1768–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Hayman D. L., Schmid M. Quantitative determination of rDNA transcription units in vertebrate cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Mar;193(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90540-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. V., Shen C. K., Hearst J. E. Cross-linking of DNA in situ as a probe for chromatin structure. Science. 1976 Jul 2;193(4247):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.935855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Tata J. R. Template-engaged and free RNA polymerases during Xenopus erythroid cell maturation. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):496–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Volpe A., Taggart M., McStay B., Bird A. DNaseI-hypersensitive sites at promoter-like sequences in the spacer of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5361–5380. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Banz E., Ness P. J., Parish R. W., Koller T. A structural concept for nucleoli of Dictyostelium discoideum deduced from dissociation studies. Chromosoma. 1984;89(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00292894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Koller T. Structure of the active nucleolar chromatin of Xenopus laevis Oocytes. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A point mutation uncouples RNA 3'-end formation and termination during ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):269–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. DNA sequences for typical ribosomal gene spacers from Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3623–3624. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Functional difference between the sites of ribosomal 40S precursor 3' end formation in Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5271–5277. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Heat shock stabilizes highly unstable transcripts of the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini R., Pauli U., Braun R., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Structure of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA chromatin of Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):829–843. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod D., Bird A. DNAase I sensitivity and methylation of active versus inactive rRNA genes in xenopus species hybrids. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Hu C. H., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. xUBF and Rib 1 are both required for formation of a stable polymerase I promoter complex in X. laevis. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A DNA-binding protein is required for termination of transcription by RNA polymerase I in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2793–2800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner B., Hofmann A., Steinbeisser H., Spring H., Miller O. L., Jr, Trendelenburg M. F. Faithful in vivo transcription termination of Xenopus laevis rDNA. Correlation of electron microscopic spread preparations with S1 transcript analysis. Chromosoma. 1991 Dec;101(4):222–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00365154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscarella D. E., Vogt V. M., Bloom S. E. Characterization of ribosomal RNA synthesis in a gene dosage mutant: the relationship of topoisomerase I and chromatin structure to transcriptional activity. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1501–1513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Mougey E. B., Sollner-Webb B. The Xenopus ribosomal DNA 60- and 81-base-pair repeats are position-dependent enhancers that function at the establishment of the preinitiation complex: analysis in vivo and in an enhancer-responsive in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5093–5104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Grainger R. M. A mosaicism in the higher order structure of Xenopus oocyte nucleolar chromatin prior to and during ribosomal gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Labhart P., McStay B. Processing and termination of RNA polymerase I transcripts. Bioessays. 1987 Mar;6(3):108–112. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Regulatory elements of the generic ribosomal gene. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):466–474. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. rRNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90298-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Jones A. Genomic transcriptional activity and the structure of chromatin. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):495–500. doi: 10.1038/260495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Ribosomal genes of Xenopus laevis: evidence of nucleosomes in transcriptionally active chromatin. Science. 1976 Oct 29;194(4264):529–532. doi: 10.1126/science.973136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Hügle B., Hazan R., Rose K. M. Drug-induced dispersal of transcribed rRNA genes and transcriptional products: immunolocalization and silver staining of different nucleolar components in rat cells treated with 5,6-dichloro-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):672–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U. Structural organization of spacer chromatin between transcribed ribosomal RNA genes in amphibian oocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;23(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Ness P. J., Widmer R. M., Parish R. W., Koller T. Psoralen-crosslinking of DNA as a probe for the structure of active nucleolar chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):897–919. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Mougey E. B. News from the nucleolus: rRNA gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Feb;16(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90025-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadafora C., Crippa M. Compact structure of ribosomal chromatin in Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2691–2704. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer R. M., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Analysis of the psoralen-crosslinking pattern in chromatin DNA by exonuclease digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7013–7024. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]