Abstract
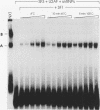
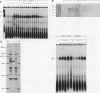
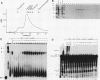
Splicing factor SF1 represents one of the proteins that function early in the splicing of nuclear pre-mRNA in the formation of a presplicing complex. SF1 was purified to homogeneity from HeLa cell nuclear extracts by column chromatography. It consists of a single polypeptide of 75 kDa and is distinct from other protein factors that function early in spliceosome assembly. SF1 activity is completely resistant to temperatures of up to 100 degrees C. The purified protein does not appear to be associated with RNA-binding, RNA-annealing, or ATPase activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ast G., Goldblatt D., Offen D., Sperling J., Sperling R. A novel splicing factor is an integral component of 200S large nuclear ribonucleoprotein (InRNP) particles. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):425–432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe B. J., Sproat B. S., Ryder U., Barabino S., Lamond A. I. Antisense probing of the human U4/U6 snRNP with biotinylated 2'-OMe RNA oligonucleotides. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Ballard D. W., Philbrick W. M., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Bridgett M. M., Jamison S. F., Garcia-Blanco M. A. Murine polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Purification, cloning, and mapping of the RNA binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24657–24663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel F., Alzari P. M., Ferrara P., Zakin M. M. Cloning and sequencing of PYBP, a pyrimidine-rich specific single strand DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5237–5245. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Spliceosome assembly in yeast. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1014–1027. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delannoy P., Caruthers M. H. Detection and characterization of a factor which rescues spliceosome assembly from a heat-inactivated HeLa cell nuclear extract. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3425–3431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles at the 3' splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Jamison S. F., Sharp P. A. Identification and purification of a 62,000-dalton protein that binds specifically to the polypyrimidine tract of introns. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1874–1886. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. E., Manley J. L. A novel protein factor is required for use of distal alternative 5' splice sites in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5945–5953. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Boshart M., Lupp B., Bosserhoff A., Frank R. W., Schütz G. The rat poly pyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) interacts with a single-stranded DNA motif in a liver-specific enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1243–1249. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Smith J., Claude A., Lin R. J. The purified yeast pre-mRNA splicing factor PRP2 is an RNA-dependent NTPase. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2319–2326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in formation of spliceosomes. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Frick M., Keller W. Separation of multiple components of HeLa cell nuclear extracts required for pre-messenger RNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17630–17640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A. Presplicing complex formation requires two proteins and U2 snRNP. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1155–1167. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Utans U. Three protein factors (SF1, SF3 and U2AF) function in pre-splicing complex formation in addition to snRNPs. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1503–1509. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud S., Reed R. An ATP-independent complex commits pre-mRNA to the mammalian spliceosome assembly pathway. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2534–2546. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. G., Mayer S. A., Tempst P., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization and molecular cloning of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein: a component of a complex necessary for pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1237–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rymond B. C., Rosbash M. Electrophoresis of ribonucleoproteins reveals an ordered assembly pathway of yeast splicing complexes. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):341–345. doi: 10.1038/324341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. An early hierarchic role of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in spliceosome assembly. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1028–1035. doi: 10.1126/science.2973660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Guthrie C. PRP16 is an RNA-dependent ATPase that interacts transiently with the spliceosome. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):494–499. doi: 10.1038/349494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seraphin B., Rosbash M. Identification of functional U1 snRNA-pre-mRNA complexes committed to spliceosome assembly and splicing. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Szer W., Furdon P. J., Kole R. Antibodies to hnRNP core proteins inhibit in vitro splicing of human beta-globin pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5241–5254. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA binding specificity of hnRNP proteins: a subset bind to the 3' end of introns. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3519–3529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utans U., Behrens S. E., Lührmann R., Kole R., Krämer A. A splicing factor that is inactivated during in vivo heat shock is functionally equivalent to the [U4/U6.U5] triple snRNP-specific proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):631–641. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Nishiyama K., Araki K., Kitamura D., Watanabe T. Purification of an octamer sequence (ATGCAAAT)-binding protein from human B cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10105–10116. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Biochemical characterization of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor: an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor with a novel intranuclear distribution. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Identification, purification, and biochemical characterization of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9243–9247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]