Abstract
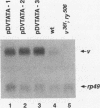
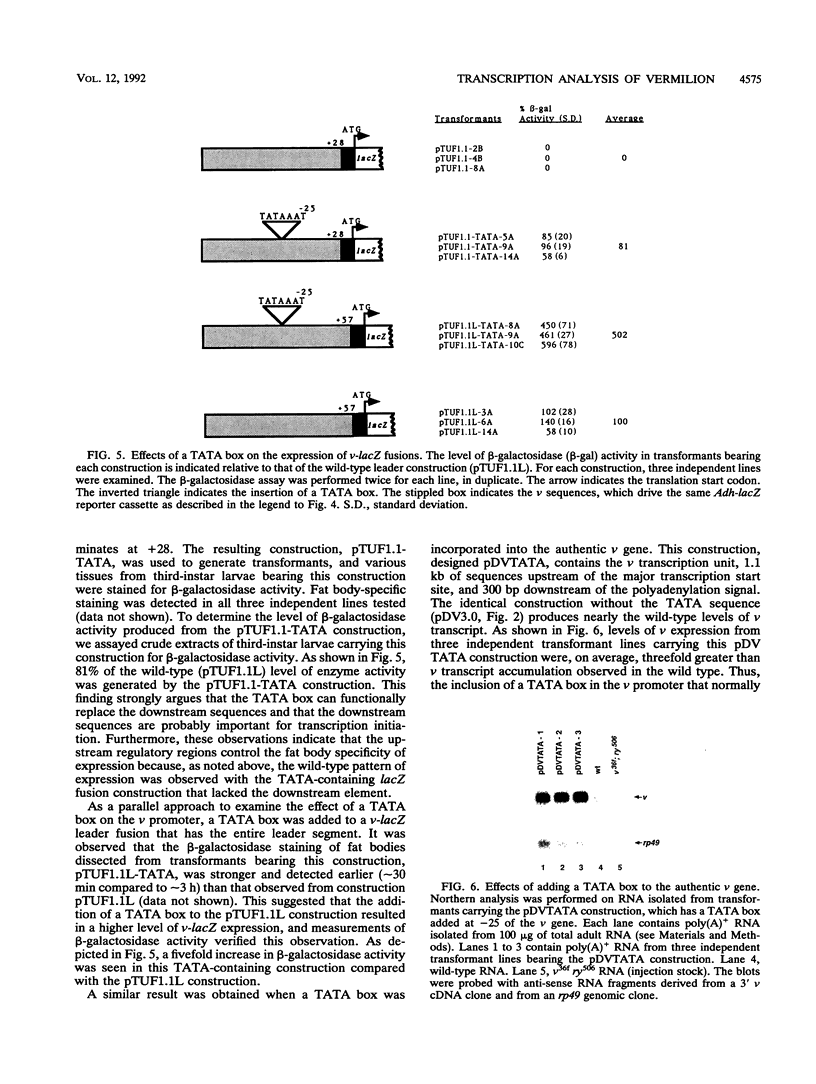
Transcriptional regulation of the TATA-less promoter of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion (v) gene was investigated. Developmental Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed that v transcripts accumulate during late embryo, larval, and adult stages. Sequences that control expression in adults were delineated by analyzing a series of 5' and 3' deletion constructions after germ line transformation. These studies defined two regions, -300 to -600 and -60 to -160, relative to the major transcription start site, as important for maximal levels of expression. Analysis of transformants bearing v-lacZ promoter fusions showed that larval expression is fat body specific and that expression depends on sequences located between +19 and +36 downstream of transcription start site. This downstream element can be functionally replaced by a TATA box in vivo. Furthermore, when added to the wild-type v promoter, a TATA element augments the level of v transcription by three- to fivefold.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkhipova I. R., Ilyin Y. V. Properties of promoter regions of mdg1 Drosophila retrotransposon indicate that it belongs to a specific class of promoters. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1169–1177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Lobos S., Merino A., Buckbinder L., Weinmann R., Natarajan V., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Role of factors IID and MLTF in transcription from the adenovirus major late and IVa2 promoters. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7704–7714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Drosophila Adh: a promoter element expands the tissue specificity of an enhancer. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R. L., Wolfner M. F., Lis J. T. Spatial and temporal pattern of hsp26 expression during normal development. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):747–754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Yamamoto T., Ohkuma Y., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Analysis of structure-function relationships of yeast TATA box binding factor TFIID. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1171–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Meselson M. Drosophila retrotransposon promoter includes an essential sequence at the initiation site and requires a downstream sequence for full activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):102–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mismer D., Rubin G. M. Analysis of the promoter of the ninaE opsin gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):565–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. In vitro analysis of the Antennapedia P2 promoter: identification of a new Drosophila transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1615–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puissant C., Houdebine L. M. An improvement of the single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):148–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Ruth R. S., Pret A. M., Fridell R. A., Ali A. J. Structure and transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene and several mutant alleles. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1423–1431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Voelker R. A. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila vermilion locus and its suppressible alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):404–408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Lis J. T. A germline transformation analysis reveals flexibility in the organization of heat shock consensus elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2971–2988. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeller W. C., Poole S. J., Kornberg T. In vitro transcription of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):68–81. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S. The Drosophila E74 promoter contains essential sequences downstream from the start site of transcription. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):782–792. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]