Abstract
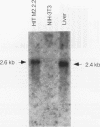
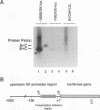
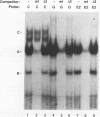
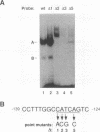
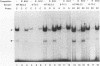
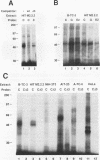
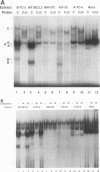
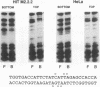
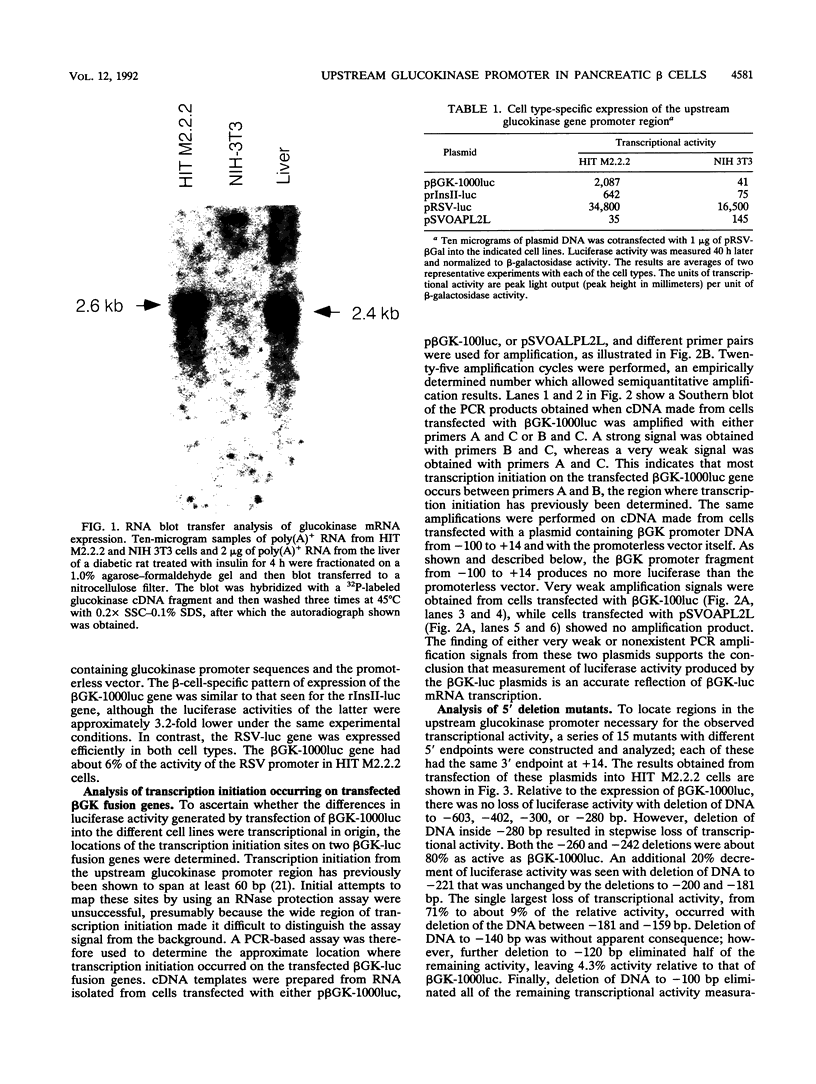
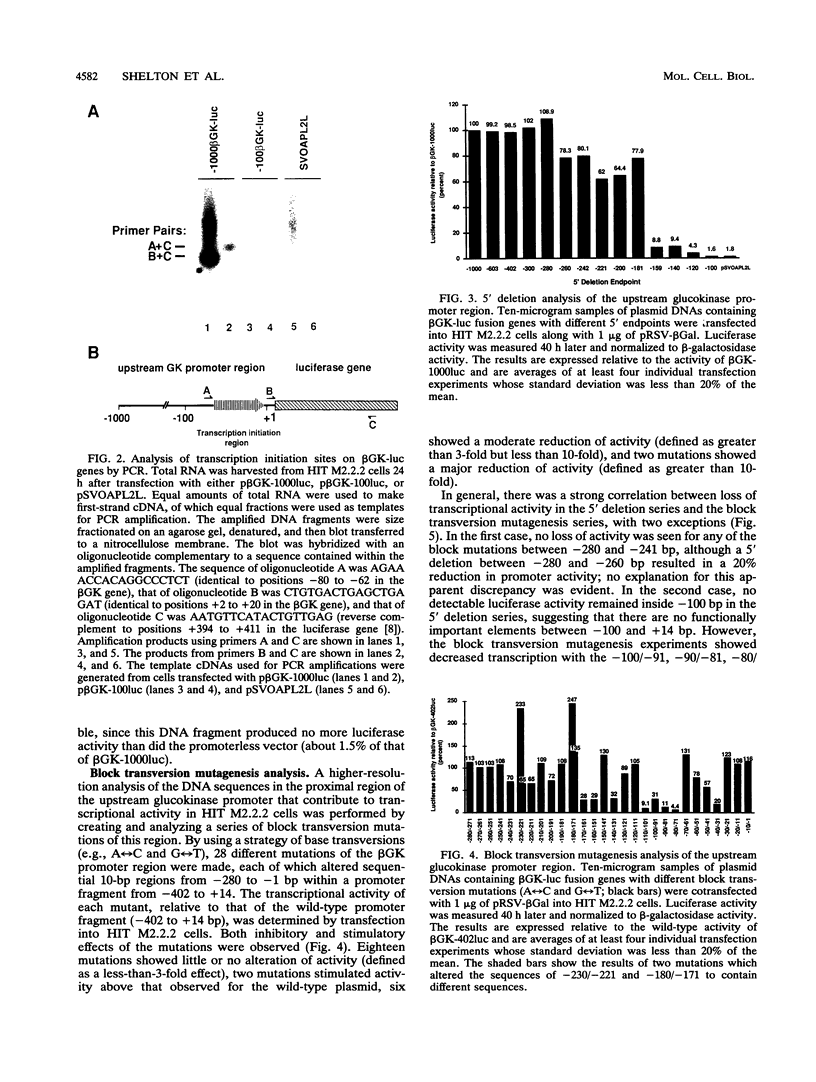
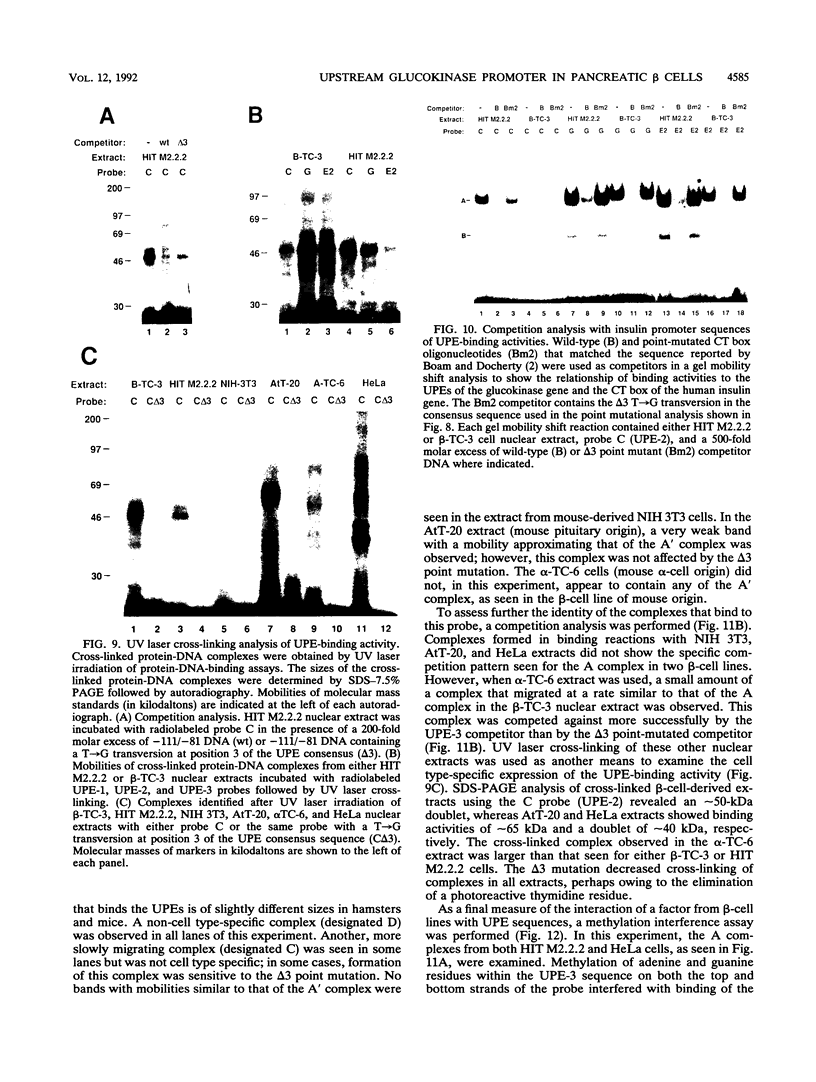
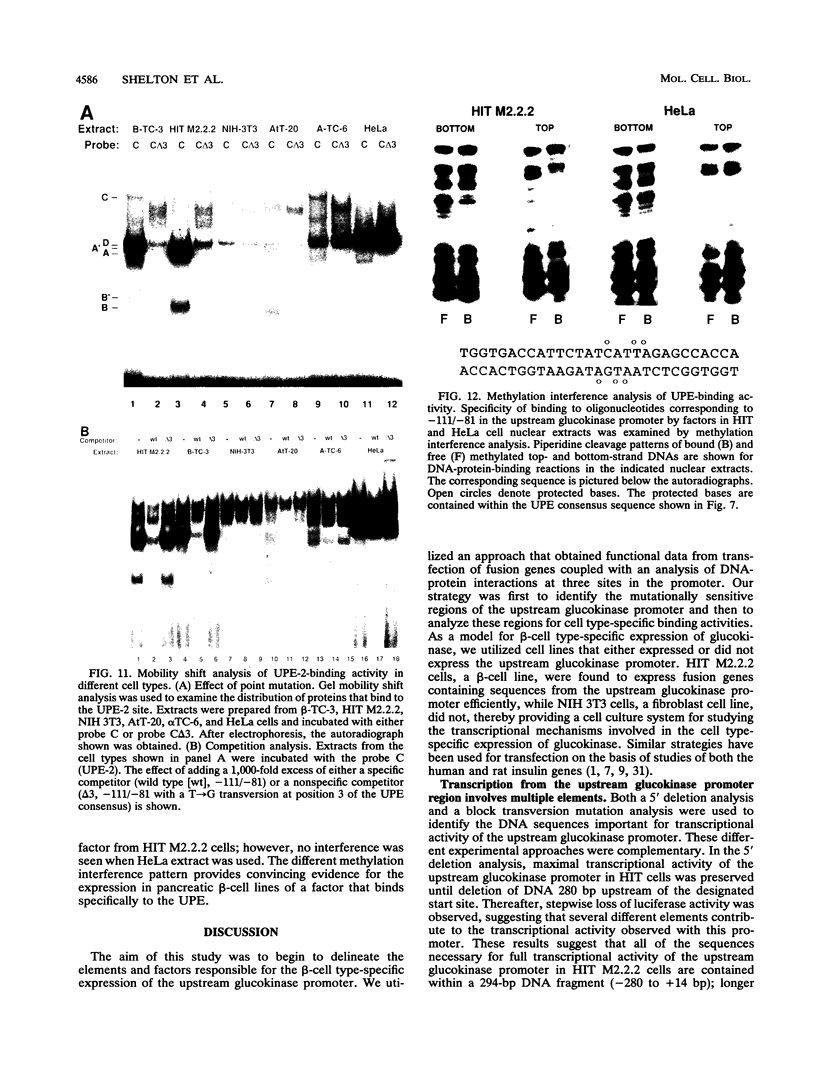
beta-cell type-specific expression of the upstream glucokinase promoter was studied by transfection of fusion genes and analysis of DNA-protein interactions. A construct containing 1,000 bp of 5'-flanking DNA was efficiently expressed in HIT M2.2.2 cells, a beta-cell-derived line that makes both insulin and glucokinase, but not in NIH 3T3 cells, a heterologous cell line. In a series of 5' deletion mutations between bases -1000 and -100 (relative to a base previously designated +1), efficient expression in HIT cells was maintained until -280 bp, after which transcription decreased in a stepwise manner. The sequences between -180 and -1 bp contributing to transcriptional activity in HIT cells were identified by studying 28 block transversion mutants that spanned this region in 10-bp steps. Two mutations reduced transcription 10-fold or more, while six reduced transcription between 3- and 10-fold. Three mutationally sensitive regions of this promoter were found to bind to a factor that was expressed preferentially in pancreatic islet beta cells. The binding sites, designated upstream promoter elements (UPEs), shared a consensus sequence of CAT(T/C)A(C/G). Methylation of adenine and guanine residues within this sequence prevented binding of the beta-cell factor, as did mutations at positions 2, 3, and 5. Analysis of nuclear extracts from different cell lines identified UPE-binding activity in HIT M2.2.2 and beta-TC-3 cells but not in AtT-20, NIH 3T3, or HeLa cells; the possibility of a greatly reduced amount in alpha-TC-6 cells could not be excluded. UV laser cross-linking experiments supported the beta-cell type expression of this factor and showed it to be approximately 50 kDa in size. Gel mobility shift competition experiments showed that this beta-cell factor is the same that binds to similar elements, termed CT boxes, in the insulin promoter. Thus, a role for these elements (UPEs or CT boxes), and the beta-cell factor that binds to them, in determining the expression of genes in the beta cells of pancreatic islets is suggested.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boam D. S., Clark A. R., Docherty K. Positive and negative regulation of the human insulin gene by multiple trans-acting factors. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8285–8296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boam D. S., Docherty K. A tissue-specific nuclear factor binds to multiple sites in the human insulin-gene enhancer. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):233–239. doi: 10.1042/bj2640233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrapkiewicz N. B., Davis C. M., Chu D. T., Caldwell C. M., Granner D. K. Rat gene 33: analysis of its structure, messenger RNA and basal promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6651–6667. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Masuoka H., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific transcription of the insulin gene is mediated by basic helix-loop-helix DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe D. T., Tsai M. J. Mutagenesis of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region defines sequences important for expression in HIT cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1784–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber M., Sealy L. Rous sarcoma virus enhancer factor I is a ubiquitous CCAAT transcription factor highly related to CBF and NF-Y. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22243–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockensmith J. W., Kubasek W. L., Vorachek W. R., Evertsz E. M., von Hippel P. H. Laser cross-linking of protein-nucleic acid complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:211–236. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08015-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. D., Quaade C., Milburn J. L., Cassidy L., Newgard C. B. Expression of normal and novel glucokinase mRNAs in anterior pituitary and islet cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4521–4530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Möbius G., Seitz H. J., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Tissue-specific expression of glucokinase: identification of the gene product in liver and pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):1998–2001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetton T. L., Magnuson M. A. Heterogeneous expression of glucokinase among pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2619–2623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Edlund T., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J., Walker M. D. A mutational analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: expression in beta cells is dependent on two related sequences within the enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Thor S., Norberg T., Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Insulin gene enhancer binding protein Isl-1 is a member of a novel class of proteins containing both a homeo- and a Cys-His domain. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):879–882. doi: 10.1038/344879a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang Y., Jetton T. L., Zimmerman E. C., Najafi H., Matschinsky F. M., Magnuson M. A. Effects of alternate RNA splicing on glucokinase isoform activities in the pancreatic islet, liver, and pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6999–7007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A., Shelton K. D. An alternate promoter in the glucokinase gene is active in the pancreatic beta cell. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15936–15942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A. Tissue-specific regulation of glucokinase gene expression. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Feb;48(2):115–121. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240480202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M. Glucokinase as glucose sensor and metabolic signal generator in pancreatic beta-cells and hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):647–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Thor S., Edlund T. Novel insulin promoter- and enhancer-binding proteins that discriminate between pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):897–904. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Cook R. A., Crisel R. M., Sharp J. D., Schmidt R. J., Williams D. C., Wilson C. P. Insulin synthesis in a clonal cell line of simian virus 40-transformed hamster pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4339–4343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott V., Clark A. R., Hutton J. C., Docherty K. Two proteins act as the IUF1 insulin gene enhancer binding factor. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81217-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Weil P. A., Stein R. Identification of a pancreatic beta-cell insulin gene transcription factor that binds to and appears to activate cell-type-specific expression: its possible relationship to other cellular factors that bind to a common insulin gene sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1564–1572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Poon D., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific expression of the rat insulin II gene is controlled by positive and negative cellular transcriptional elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3253–3259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]