Abstract
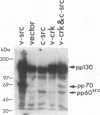
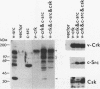
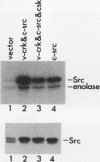
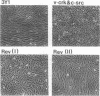
The protein product of the CT10 virus, p47gag-crk (v-Crk), which contains Src homology region 2 (SH2) and 3 (SH3) domains but lacks a kinase domain, is believed to cause an increase in cellular protein tyrosine phosphorylation. A candidate tyrosine kinase, Csk (C-terminal Src kinase), has been implicated in c-Src Tyr-527 phosphorylation, which negatively regulates the protein tyrosine kinase of pp60c-src (c-Src). To investigate how c-Src kinase activity is regulated in vivo, we first looked at whether v-Crk can activate c-Src kinase. We found that cooverexpression of v-Crk and c-Src caused elevation of c-Src kinase activity, resulting in an increase of tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins and morphological transformation of rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. v-Crk and c-Src complexes were not detected, although v-Crk bound to a variety of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in cells overexpressing v-Crk and c-Src. Overexpression of Csk in these transformed cells caused reversion to normal phenotypes and also reduced the level of c-Src kinase activity. However, Csk did not cause reversion of cells transformed by v-Src or c-Src527F, in which Tyr-527 was changed to Phe. These results strongly suggest that Csk acts on Tyr-527 of c-Src and suppresses c-Src kinase activity in vivo. Because Csk can suppress transformation by cooverexpression of v-Crk and c-Src, we suggest that v-Crk causes activation of c-Src in vivo by altering the phosphorylation state of Tyr-527.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagrodia S., Chackalaparampil I., Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Altered tyrosine 527 phosphorylation and mitotic activation of p60c-src. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):172–175. doi: 10.1038/349172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. B., Fajardo J. E., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Tyrosine-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cellular p130 provide high affinity binding substrates to analyze Crk-phosphotyrosine-dependent interactions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10588–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Ledbetter J. A., Barbacid M. Product of vav proto-oncogene defines a new class of tyrosine protein kinase substrates. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):68–71. doi: 10.1038/356068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chackalaparampil I., Shalloway D. Altered phosphorylation and activation of pp60c-src during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90422-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Kornbluth S., Hanafusa H. Enzymatically inactive p60c-src mutant with altered ATP-binding site is fully phosphorylated in its carboxy-terminal regulatory region. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):937–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90520-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Reynolds A. B., Vines R. R., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to individual tyrosine-phosphorylated protein substrates of oncogene-encoded tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3328–3332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Fantl W. J., Williams L. T. The C-terminal SH2 domain of p85 accounts for the high affinity and specificity of the binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Johnson P. J., Shalloway D. Regulation by the autophosphorylation site in overexpressed pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4541–4546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Jove R., Hanafusa H. Characterization of avian and viral p60src proteins expressed in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Hu P., Katzav S., Li W., Oliver J. M., Ullrich A., Weiss A., Schlessinger J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of vav proto-oncogene product containing SH2 domain and transcription factor motifs. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):71–74. doi: 10.1038/356071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Binding of transforming protein, P47gag-crk, to a broad range of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1537–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.1694307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Identification of domains of the v-crk oncogene product sufficient for association with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1607–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Association of the v-crk oncogene product with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Mutagenic analysis of the v-crk oncogene: requirement for SH2 and SH3 domains and correlation between increased cellular phosphotyrosine and transformation. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3581–3589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3581-3589.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Baltimore D. The noncatalytic src homology region 2 segment of abl tyrosine kinase binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with high affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):627–631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Kaplan J. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of p60c-src by p34cdc2-associated protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):775–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nada S., Okada M., MacAuley A., Cooper J. A., Nakagawa H. Cloning of a complementary DNA for a protein-tyrosine kinase that specifically phosphorylates a negative regulatory site of p60c-src. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):69–72. doi: 10.1038/351069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Nada S., Yamanashi Y., Yamamoto T., Nakagawa H. CSK: a protein-tyrosine kinase involved in regulation of src family kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24249–24252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Nakagawa H. A protein tyrosine kinase involved in regulation of pp60c-src function. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20886–20893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. M., Olsen M., Boettiger D., Vogt V. M. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies to gag protein p19 of avian sarcoma and leukaemia viruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3177–3182. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X., van der Geer P., Letwin K., Waterfield M. D., Hunter T., Pawson T. Tyr721 regulates specific binding of the CSF-1 receptor kinase insert to PI 3'-kinase SH2 domains: a model for SH2-mediated receptor-target interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Kanner S. B., Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Stable association of activated pp60src with two tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3951–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Daly R. J., Daum G., Li N., Fischer E. H., Burgess W. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):559–567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabe H., Knudsen B., Okada M., Nada S., Nakagawa H., Hanafusa H. Molecular cloning and expression of chicken C-terminal Src kinase: lack of stable association with c-Src protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabe H., Kuno J., Koromilas A., Saito Y., Kinashi T., Ueda M., Takamatsu T., Hamaguchi M., Kawakami T., Honjo T. Comparison of protein tyrosine phosphorylation and morphological changes induced by IL-2 and IL-3. Int Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1137–1148. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.11.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Coussens P. M., Yaciuk P. Overexpression of the c-src protein does not induce transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7071–7075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Choi J. K., Bagrodia S., Copeland T. D., Maller J. L., Shalloway D. Purified maturation promoting factor phosphorylates pp60c-src at the sites phosphorylated during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. E., Soriano P., Brugge J. S. Phosphorylation of c-Src on tyrosine 527 by another protein tyrosine kinase. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.1719633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]