Abstract
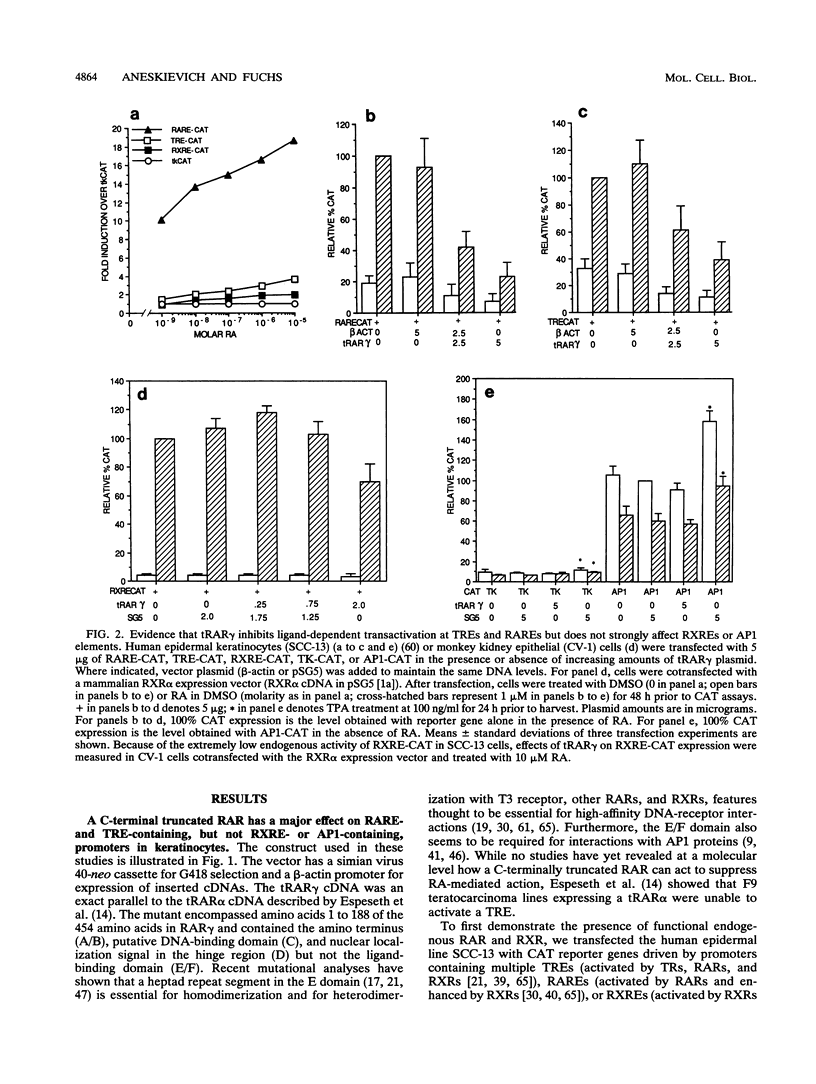
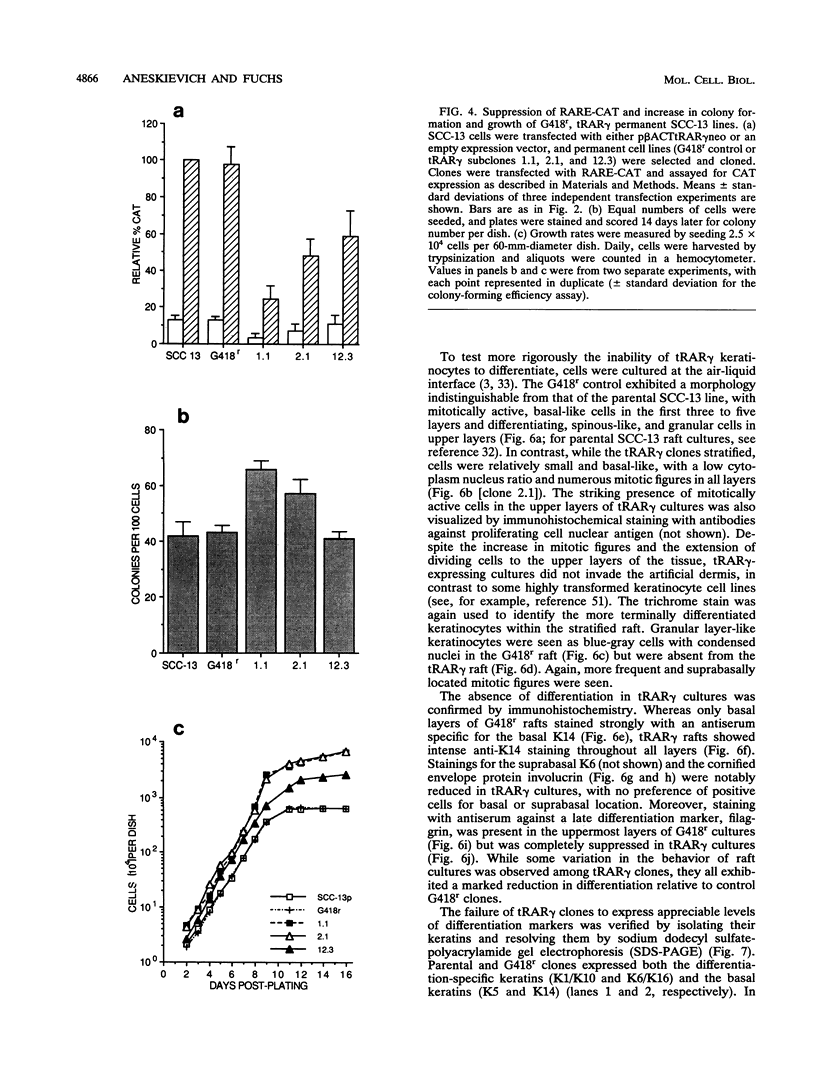
Terminal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes is inhibited by 1 microM retinoic acid, a concentration which induces differentiation in a number of cell types, including F9 teratocarcinoma cells. The molecular basis for these opposing retinoid responses is unknown, although retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and retinoid X receptors (RXRs) have been detected in both cell types. When F9 cells are stably transfected with a truncated RAR alpha lacking the E/F domain necessary for ligand binding and RAR/RXR dimerization, action at retinoid response elements is suppressed and cells produce a retinoic acid-resistant phenotype; i.e., they are blocked in differentiation (A. S. Espeseth, S. P. Murphy, and E. Linney, Genes Dev. 3:1647-1656, 1989). If retinoid receptors influence epidermal differentiation only in a negative fashion, then suppression of transactivation at retinoid response elements would be expected to enhance, rather than block, keratinocyte differentiation. In this study, we show that surprisingly, even though constitutive expression of an analogous truncated RAR gamma in keratinocytes specifically suppressed transactivation at retinoid response elements, keratinocytes were blocked, rather than enhanced, in their ability to undergo morphological and biochemical features of differentiation. These findings demonstrate a direct and hitherto unrecognized role for RARs and RXRs in positively as well as negatively regulating epidermal differentiation. Additionally, our studies extend those of Espeseth et al. (Genes Dev. 3:1647-1656, 1989), indicating a novel RAR function independent of the E/F domain.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYOUB P., SHKLAR G. A modification of the Mallory connective tissue stain as a stain for keratin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963 May;16:580–581. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(63)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcalay M., Zangrilli D., Pandolfi P. P., Longo L., Mencarelli A., Giacomucci A., Rocchi M., Biondi A., Rambaldi A., Lo Coco F. Translocation breakpoint of acute promyelocytic leukemia lies within the retinoic acid receptor alpha locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselineau D., Bernard B. A., Bailly C., Darmon M., Pruniéras M. Human epidermis reconstructed by culture: is it "normal"? J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Feb;86(2):181–186. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12284237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselineau D., Bernard B. A., Bailly C., Darmon M. Retinoic acid improves epidermal morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1989 Jun;133(2):322–335. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselineau D., Dale B. A., Bernard B. A. Filaggrin production by cultured human epidermal keratinocytes and its regulation by retinoic acid. Differentiation. 1990 Dec;45(3):221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Pfahl M. A novel thyroid hormone receptor encoded by a cDNA clone from a human testis library. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):788–791. doi: 10.1126/science.3672126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Bućan M., Francke U., Colberg-Poley A. M., Gruss P. Sequential expression of murine homeo box genes during F9 EC cell differentiation. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2209–2215. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca L., Yuspa S. H. Altered glycoprotein synthesis in mouse epidermal cells treated with retinyl acetate in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):106–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichele G. Retinoic acid induces a pattern of digits in anterior half wing buds that lack the zone of polarizing activity. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):863–867. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Fisher G. J., Zhang Q. Y., Eisen D., Krust A., Kastner P., Chambon P., Voorhees J. J. Retinoic acid receptor gene expression in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Apr;96(4):425–433. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espeseth A. S., Murphy S. P., Linney E. Retinoic acid receptor expression vector inhibits differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1647–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELL H. B., MELLANBY E. Metaplasia produced in cultures of chick ectoderm by high vitamin A. J Physiol. 1953 Mar;119(4):470–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C., Byers M. R., Iadarola M. J., Powers E. A. Patterns of epithelial expression of Fos protein suggest important role in the transition from viable to cornified cell during keratinization. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):253–258. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Yang C. R., Au M., Casanova J., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. A domain containing leucine-zipper-like motifs mediate novel in vivo interactions between the thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1610–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes by vitamin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Franco R., Weinberger C., Albert V. R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. A c-erb-A binding site in rat growth hormone gene mediates trans-activation by thyroid hormone. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):738–741. doi: 10.1038/329738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Watt F. M. Regulation by vitamin A of envelope cross-linking in cultured keratinocytes derived from different human epithelia. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1115–1117. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Crowe D. L., Rheinwald J. G., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. Abnormal expression of retinoic acid receptors and keratin 19 by human oral and epidermal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):3972–3981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. G., Santon J. B., Glass C. K., Gill G. N. Ligand-activated thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors inhibit growth factor receptor promoter expression. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1165–1175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90393-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husmann M., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Hermann T., Tzukerman M., Pfahl M. Antagonism between retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4097–4103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Jetten M. E., Sherman M. I. Stimulation of differentiation of several murine embryonal carcinoma cell lines by retinoic acid. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Dec;124(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Brent G. A., Warne R. L., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D. Thyroid hormone receptor binds to a site in the rat growth hormone promoter required for induction by thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5670–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopan R., Fuchs E. The use of retinoic acid to probe the relation between hyperproliferation-associated keratins and cell proliferation in normal and malignant epidermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):295–307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopan R., Traska G., Fuchs E. Retinoids as important regulators of terminal differentiation: examining keratin expression in individual epidermal cells at various stages of keratinization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):427–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leask A., Rosenberg M., Vassar R., Fuchs E. Regulation of a human epidermal keratin gene: sequences and nuclear factors involved in keratinocyte-specific transcription. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1985–1998. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noji S., Yamaai T., Koyama E., Nohno T., Fujimoto W., Arata J., Taniguchi S. Expression of retinoic acid receptor genes in keratinizing front of skin. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt M. A., Kralova J., McBurney M. W. A dominant negative mutation of the alpha retinoic acid receptor gene in a retinoic acid-nonresponsive embryonal carcinoma cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6445–6453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Lutz Y., Saunders M., Scheuer I., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptor gamma: specific immunodetection and phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):535–545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Krust A., Zelent A., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Specific spatial and temporal distribution of retinoic acid receptor gamma transcripts during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):213–222. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif M., Privalsky M. L. v-erbA oncogene function in neoplasia correlates with its ability to repress retinoic acid receptor action. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Schilling K., Robertson L., Luk D., Oberdick J., Curran T., Morgan J. I. fos-lacZ transgenic mice: mapping sites of gene induction in the central nervous system. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90105-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. B. Early effects of vitamin A on protein synthesis in the epidermis of embryonic chick skin cultured in serum-containing medium. Dev Biol. 1973 Feb;30(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Role of retinoids in differentiation and carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3034–3040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellmach V., Leask A., Fuchs E. Retinoid-mediated transcriptional regulation of keratin genes in human epidermal and squamous cell carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4582–4586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler A., Kopan R., Duvic M., Fuchs E. Use of monospecific antisera and cRNA probes to localize the major changes in keratin expression during normal and abnormal epidermal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):427–446. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomic M., Jiang C. K., Epstein H. S., Freedberg I. M., Samuels H. H., Blumenberg M. Nuclear receptors for retinoic acid and thyroid hormone regulate transcription of keratin genes. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):965–973. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Molecular cloning of gene sequences transcriptionally regulated by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cyclic AMP in cultured mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;107(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolbach S. B., Howe P. R. TISSUE CHANGES FOLLOWING DEPRIVATION OF FAT-SOLUBLE A VITAMIN. J Exp Med. 1925 Nov 30;42(6):753–777. doi: 10.1084/jem.42.6.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Rheinwald J. G. A new small (40 kd) keratin filament protein made by some cultured human squamous cell carcinomas. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Harris C. C. Altered differentiation of mouse epidermal cells treated with retinyl acetate in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Wills K. N., Graupner G., Tzukerman M., Hermann T., Pfahl M. Ligand-binding domain of thyroid hormone receptors modulates DNA binding and determines their bifunctional roles. New Biol. 1991 Feb;3(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Pals C., Kruijer W. Transcriptional control of c-jun by retinoic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1585–1591. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]