Abstract
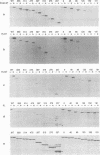
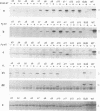
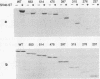
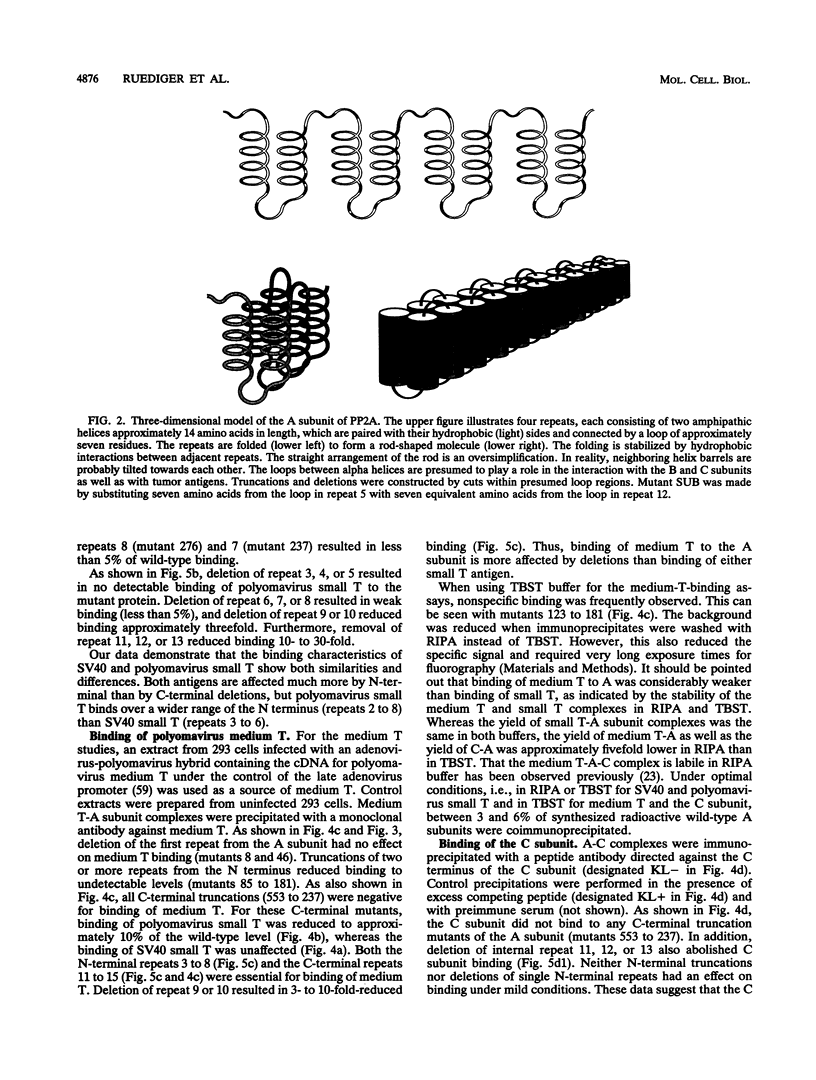
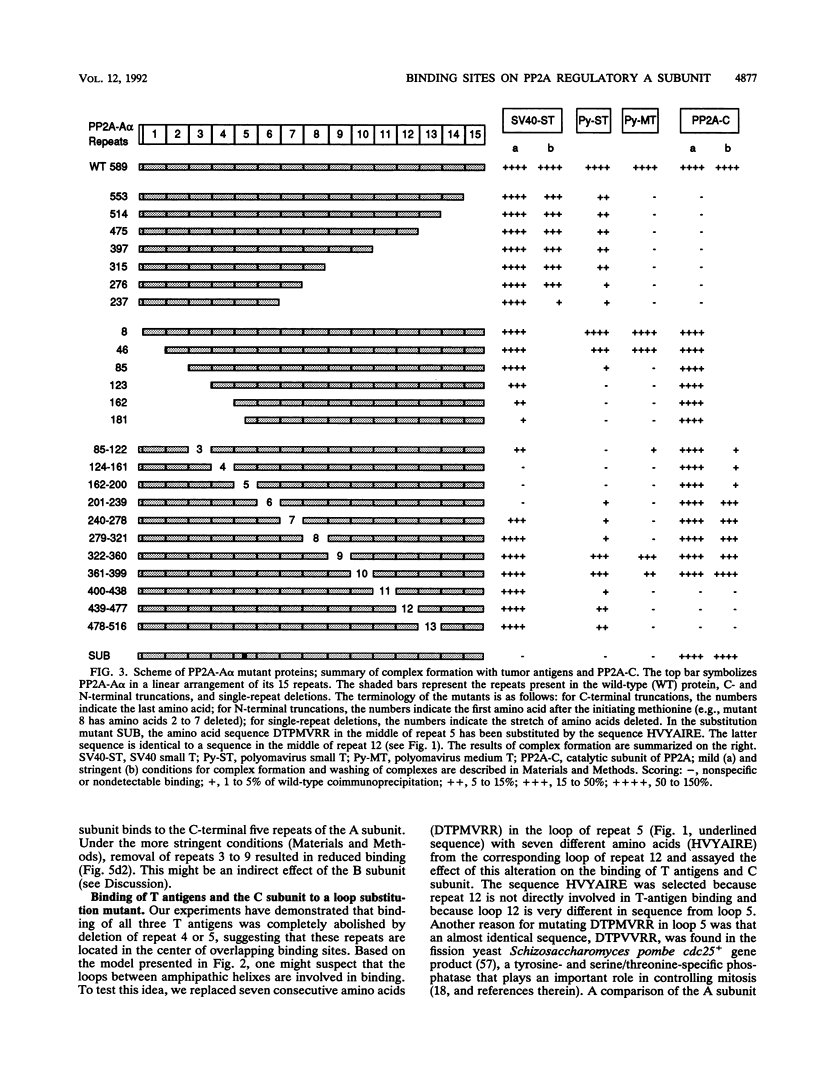
Protein phosphatase 2A is composed of three subunits: the catalytic subunit C and two regulatory subunits, A and B. The A subunit consists of 15 nonidentical repeats and has a rodlike shape. It is associated with the B and C subunits as well as with the simian virus 40 small T, polyomavirus small T, and polyomavirus medium T tumor antigens. We determined the binding sites on subunit A for subunit C and tumor antigens by site-directed mutagenesis of A. Twenty-four N- and C-terminal truncations and internal deletions of A were assayed by coimmunoprecipitation for their ability to bind C and tumor antigens. It was found that C binds to repeats 11 to 15 at the C terminus of A, whereas T antigens bind to overlapping but distinct regions of the N terminus. Simian virus 40 small T binds to repeats 3 to 6, and polyomavirus small T and medium T bind to repeats 2 to 8. The data suggest cooperativity between C and T antigens in binding to A. This is most apparent for medium T antigen, which can only bind to those A subunit molecules that provide the entire binding region for the C subunit. We infer from our results that B also binds to N-terminal repeats. A model of the small T/medium T/B-A-C complexes is presented.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone M., Hauser J., Carty M. P., Rundell K., Dixon K., Levine A. S. Simian virus 40 (SV40) small t antigen inhibits SV40 DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1804–1808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1804-1808.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., Benjamin T. L. Identification of DNA sequence changes leading to loss of transforming ability in polyoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Isolation and partial characterization of an Mr 60,000 subunit of a type 2A phosphatase from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7267–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Harvey R., Espino P. C., Semba K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Smith A. E. Peptide antibodies to the human c-fyn gene product demonstrate pp59c-fyn is capable of complex formation with the middle-T antigen of polyomavirus. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3845–3855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Hermann J., Hendrix P., Ozon R., Merlevede W. Okadaic acid, a specific protein phosphatase inhibitor, induces maturation and MPF formation in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami R., Turk B., Enderle K., Howe A., Rundell K. Effect of zinc ions on the biochemical behavior of simian virus 40 small-t antigen expressed in bacteria. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1746–1751. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1746-1751.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. D., Yang S. I., Mumby M. C. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the catalytic subunit of bovine type 2A protein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4880–4884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer T., Carbone-Wiley A., Scheidtmann K. H., Walter G. Interactions between polyomavirus medium T antigen and three cellular proteins of 88, 61, and 37 kilodaltons. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3902–3909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3902-3909.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer T., Scheidtmann K. H., Hutchinson M. A., Eckhart W., Walter G. Complexes of polyoma virus medium T antigen and cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7952–7954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Zolnierowicz S., Stapleton A. E., Goebl M., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Pringle J. R. CDC55, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in cellular morphogenesis: identification, characterization, and homology to the B subunit of mammalian type 2A protein phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5767–5780. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Adams-Pearson C., Maurer F., Müller P., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. alpha- and beta-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3166–3173. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Imazu M., Usui H., Kinohara N., Takeda M. Resolution and reassociation of three distinct components from pig heart phosphoprotein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1526–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jog P., Joshi B., Dhamankar V., Imperiale M. J., Rutila J., Rundell K. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 small-t antigen. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2895–2900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2895-2900.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi B., Rundell K. Association of simian virus 40 small-t antigen with the 61-kilodalton component of a cellular protein complex. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5649–5651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5649-5651.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamibayashi C., Estes R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. C. Subunit interactions control protein phosphatase 2A. Effects of limited proteolysis, N-ethylmaleimide, and heparin on the interaction of the B subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13251–13260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Sakai R., Tahira T., Tsuda H., Ito N., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Molecular cloning of rat phosphoprotein phosphatase 2A beta cDNA and increased expressions of phosphatase 2A alpha and 2A beta in rat liver tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):821–827. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80323-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Carbone A., Walter G. Purified polyoma virus medium T antigen has tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity but no significant phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1866–1874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Sudol M., Hanafusa H. Association of the polyomavirus middle-T antigen with c-yes protein. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):171–173. doi: 10.1038/325171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Hemming A., Courtneidge S. A. Identification and characterization of p59fyn (a src-like protein tyrosine kinase) in normal and polyoma virus transformed cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3837–3844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens I., Nilsson S. A., Linder S., Magnusson G. Mutational analysis of polyomavirus small-T-antigen functions in productive infection and in transformation. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2126–2133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2126-2133.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. E., Hendrix P., Cron P., Matthies R., Stone S. R., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Hemmings B. A. Structure of the 55-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A: evidence for a neuronal-specific isoform. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3589–3597. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Walter G. Protein phosphatases and DNA tumor viruses: transformation through the back door? Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):589–598. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. V., Magnusson G. T-antigen expression by polyoma mutants with modified RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2095–2101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogris E., Mudrak I., Wintersberger E. Polyomavirus large and small T antigens cooperate in induction of the S phase in serum-starved 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):53–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.53-61.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Cherington V., Morgan W., DeAnda J., Kaplan D., Schaffhausen B., Roberts T. M. Cellular proteins that associate with the middle and small T antigens of polyomavirus. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3934–3940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3934-3940.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Weller W., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Lane W. S., Roberts T. M. The third subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), a 55-kilodalton protein which is apparently substituted for by T antigens in complexes with the 36- and 63-kilodalton PP2A subunits, bears little resemblance to T antigens. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.886-893.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. D., Kerc E. Limited proteolytic digestion and dissociation of smooth muscle phosphatase-I modifies its substrate specificity. Preparation and properties of different forms of smooth muscle phosphatase-I. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3770–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pen J., Welling G. W., Welling-Wester S. An efficient procedure for the isolation of recombinant baculovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):451–451. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruediger R., Van Wart Hood J. E., Mumby M., Walter G. Constant expression and activity of protein phosphatase 2A in synchronized cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4282–4285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K. Complete interaction of cellular 56,000- and 32,000-Mr proteins with simian virus 40 small-t antigen in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1240–1243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1240-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Major E. O., Lampert M. Association of cellular 56,000- and 32,000-molecular-weight protein with BK virus and polyoma virus t-antigens. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1090–1093. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1090-1093.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai R., Ikeda I., Kitani H., Fujiki H., Takaku F., Rapp U., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Flat reversion by okadaic acid of raf and ret-II transformants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9946–9950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Bockus B. J., Berkner K. L., Kaplan D., Roberts T. M. Characterization of middle T antigen expressed by using an adenovirus expression system. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1221–1225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1221-1225.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Mumby M. C., Rundell K., Walter G. Dephosphorylation of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and p53 protein by protein phosphatase 2A: inhibition by small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1996–2003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylates simian virus 40 large T antigen specifically at residues involved in regulation of DNA-binding activity. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2098–2101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2098-2101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Nairn A. C. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:1–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. Tumor antigens induced by nontransforming mutants of polyoma virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola M. M., Langan T., Cohen P. p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites in histone H1 are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 3;1094(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90011-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J., Hemmings B. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7215–7220. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Hirota M., Nakayasu M., Ojika M., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Sugimura T. Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virshup D. M., Kauffman M. G., Kelly T. J. Activation of SV40 DNA replication in vitro by cellular protein phosphatase 2A. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3891–3898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Carbone-Wiley A., Joshi B., Rundell K. Homologous cellular proteins associated with simian virus 40 small T antigen and polyomavirus medium T antigen. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4760–4762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4760-4762.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Carbone A., Welch W. J. Medium tumor antigen of polyomavirus transformation-defective mutant NG59 is associated with 73-kilodalton heat shock protein. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):405–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.405-410.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ferre F., Espiritu O., Carbone-Wiley A. Molecular cloning and sequence of cDNA encoding polyoma medium tumor antigen-associated 61-kDa protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8669–8672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G. Production and use of antibodies against synthetic peptides. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 17;88(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ruediger R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. Association of protein phosphatase 2A with polyoma virus medium tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Yasuda H., Pines J., Yasumoto K., Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Hunter T., Sugimura T., Nishimoto T. Okadaic acid, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases, activates cdc2/H1 kinase and transiently induces a premature mitosis-like state in BHK21 cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4331–4338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. I., Lickteig R. L., Estes R., Rundell K., Walter G., Mumby M. C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1988–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Hearing P., Rundell K. Cellular proteins associated with simian virus 40 early gene products in newly infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):147–154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.147-154.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z. Y., Veldman G. M., Cowie A., Carr A., Schaffhausen B., Kamen R. Construction and functional characterization of polyomavirus genomes that separately encode the three early proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):170–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.170-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cruz e Silva O. B., Alemany S., Campbell D. G., Cohen P. T. Isolation and sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding the entire catalytic subunit of a type-2A protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80966-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]