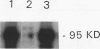
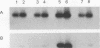
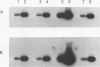
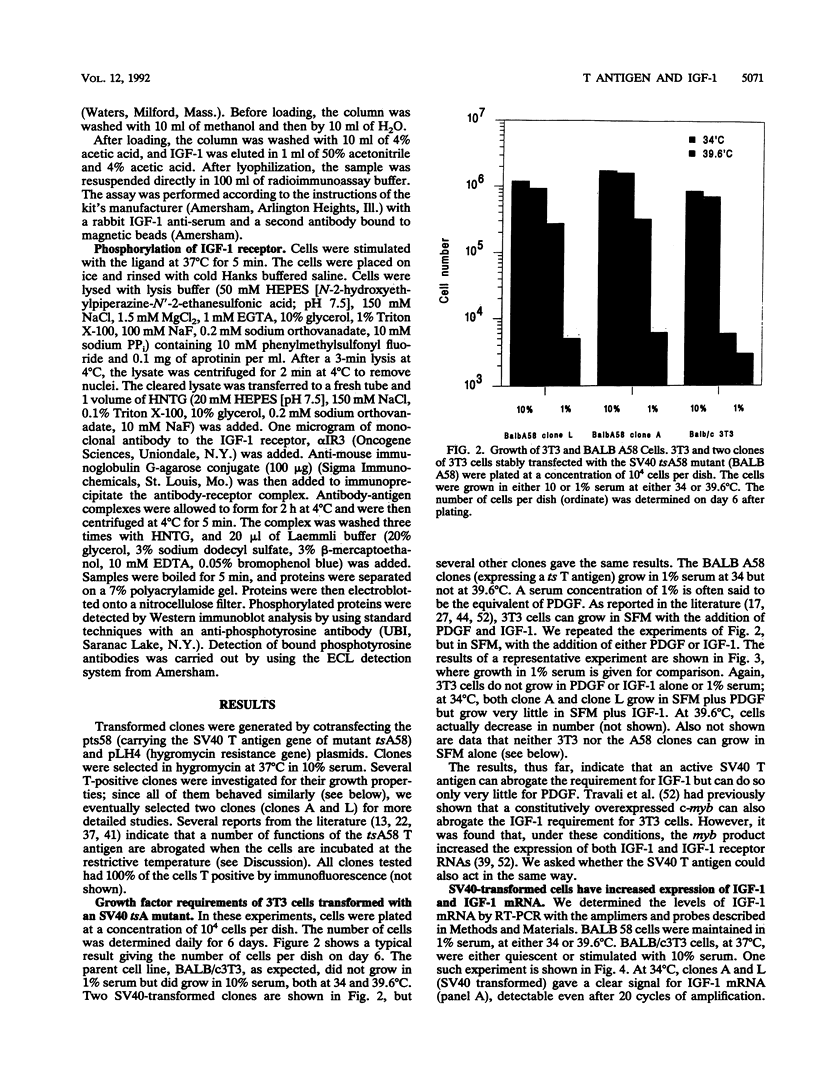
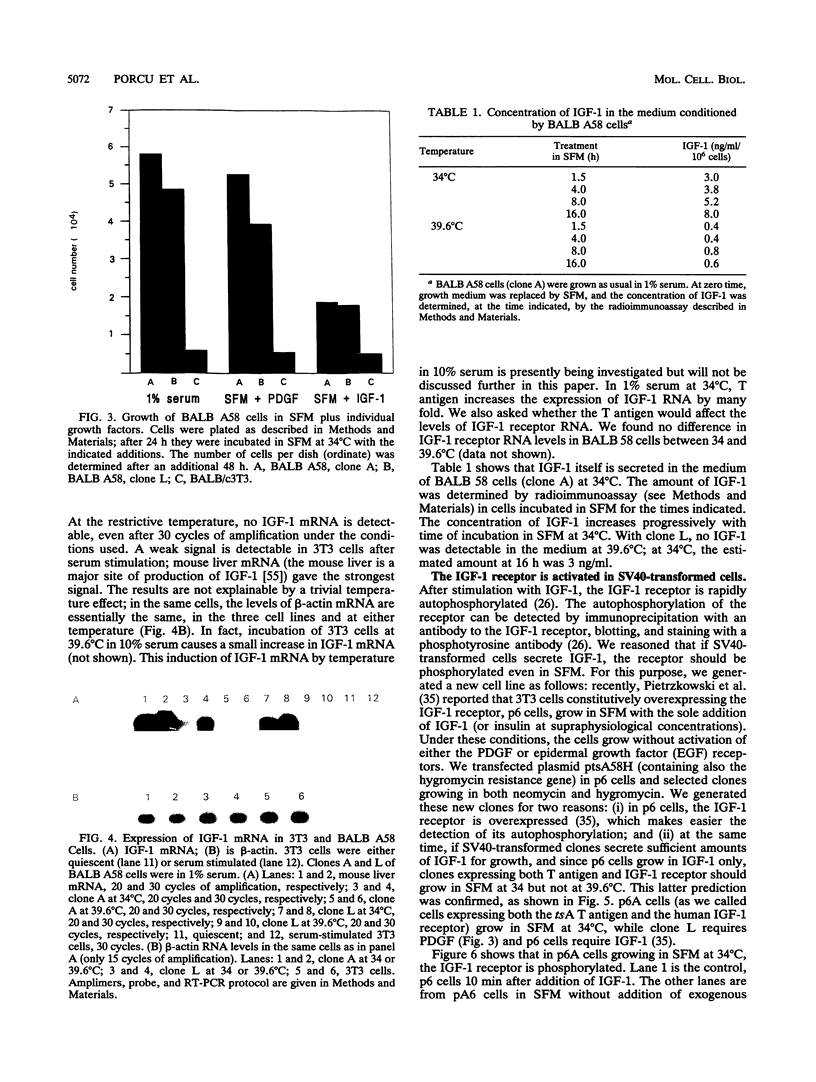
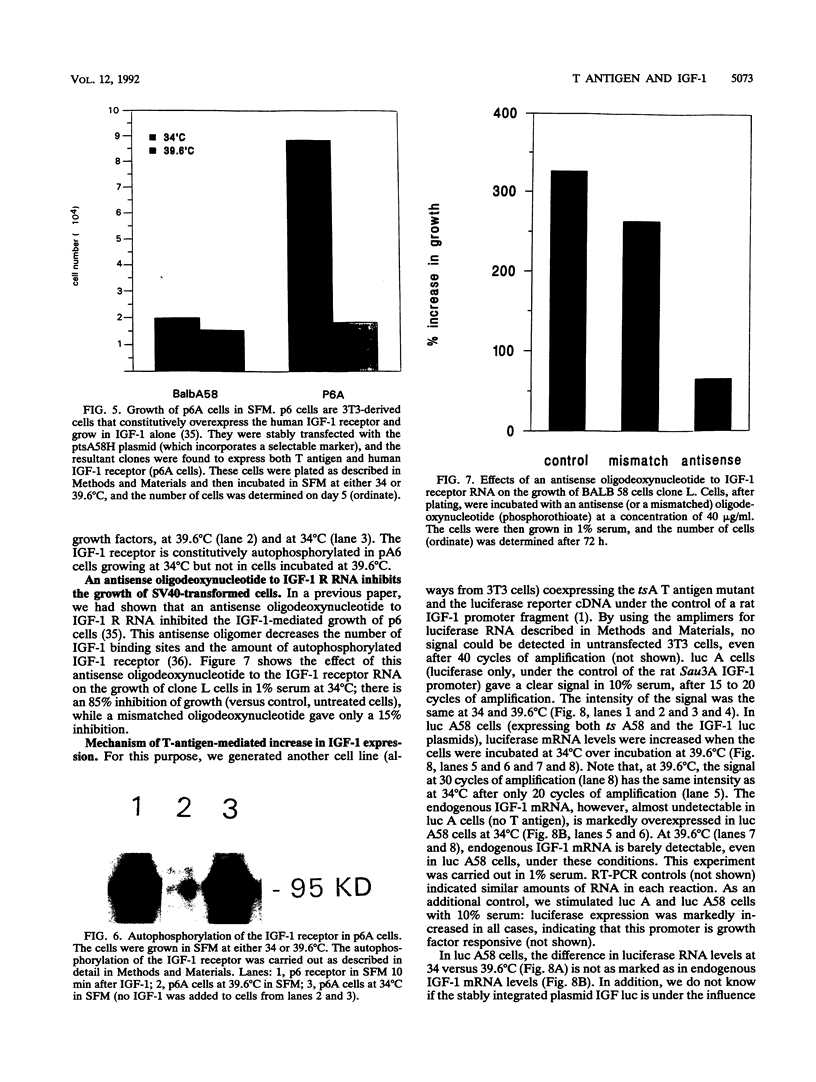
Abstract
We have used a plasmid expressing a temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen, stably transfected into 3T3 cells, to study the role of insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and its receptor in T-antigen-mediated growth. While 3T3 cells do not grow in serum-free medium, in 1% serum, or with the sole addition of either platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) or IGF-1, cells expressing the tsA T antigen (BALB 58 cells) grow at 34 degrees C in either PDGF or 1% serum but not in IGF-1. At the restrictive temperature (39.6 degrees C), these cells can only grow in 10% serum. We show that BALB 58 cells, at 34 degrees C, have a markedly increased expression of IGF-1 and IGF-1 mRNA and that their growth in 1% serum (at 34 degrees C) is inhibited by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to the IGF-1 receptor RNA. When this tsA plasmid is stably transfected into cells constitutively overexpressing the human IGF-1 receptor cDNA, the resulting cell lines show a constitutively phosphorylated IGF-1 receptor and grow in serum-free medium at 34 degrees C (but not at 39.6 degrees C). A functional SV40 T antigen also increases the expression of a plasmid in which the reporter luciferase gene is under the control of a rat IGF-1 promoter. We conclude (i) that the SV40 T antigen induces the expression of IGF-1 and IGF-1 mRNA, at least in part by a transcriptional mechanism, thus altering the growth factors requirements, and (ii) that, in BALB/c3t3 cells, the SV40 T antigen necessitates a functional IGF-1 receptor for its growth-stimulating effect in low serum (or PDGF).
Full text
PDF
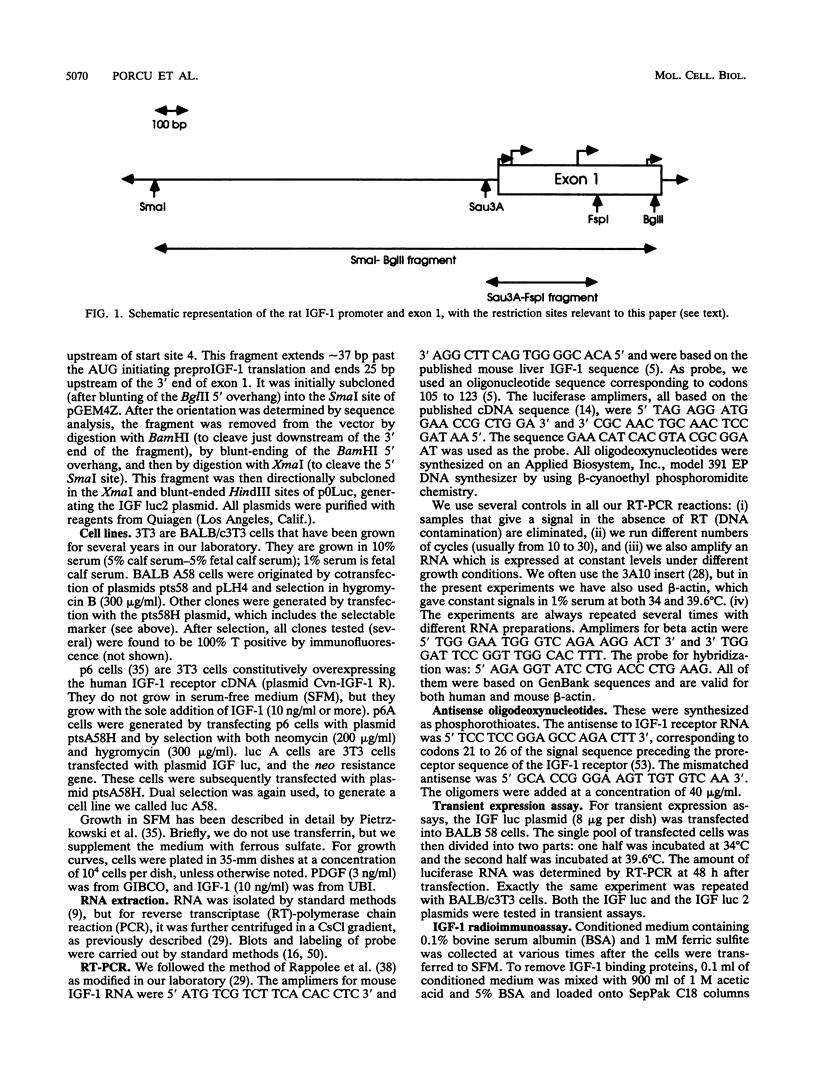




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M. L., Ben-Hur H., LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Transcription initiation in the two leader exons of the rat IGF-I gene occurs from disperse versus localized sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):887–893. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamo M. L., Ben-Hur H., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Regulation of start site usage in the leader exons of the rat insulin-like growth factor-I gene by development, fasting, and diabetes. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1677–1686. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Offord E., Paduwat N., Bruggmann H. SV40 activates transcription from the transferrin receptor promoter by inducing a factor which binds to the CRE/AP-1 recognition sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec;19(25):7117–7123. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.25.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Stempien M. M., Fong N. M., Rall L. B. Sequences of liver cDNAs encoding two different mouse insulin-like growth factor I precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7873–7882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourre F., Sarasin A. Targeted mutagenesis of SV40 DNA induced by UV light. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):68–70. doi: 10.1038/305068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci C., Mallucci P., Roberts C. T., Frunzio R., Bruni C. B. Nucleotide sequence of a genomic fragment of the rat IGF-I gene spanning an alternate 5' non coding exon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3596–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Pardee A. B. Post-transcriptional control of the onset of DNA synthesis by an insulin-like growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1807–1814. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Multiple hormones stimulate the production of somatomedin by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):850–856. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Shaw D. S. Variables controlling somatomedin production by cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):137–142. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Kurth M., Graessmann M., Graessmann A., Knippschild U. Altered phosphorylation at specific sites confers a mutant phenotype to SV40 wild-type large T antigen in a flat revertant of SV40-transformed cells. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1931–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrov Z., Meir R., Barak Y., Zaizov R., Zadik Z. Human growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 enhance the proliferation of human leukemic blasts. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Mar;9(3):394–399. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.3.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gai X. X., Rizzo M. G., Lee J., Ullrich A., Baserga R. Abrogation of the requirements for added growth factors in 3T3 cells constitutively expressing the p53 and IGF-1 genes. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(4):377–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B., Goldring S. R. Cytokines and cell growth control. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(4):301–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Davies J. Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizuka N., Sukegawa I., Takano K., Asakawa K., Horikawa R., Tsushima T., Shizume K. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor I receptors on human erythroleukemia cell line (K-562 cells). Endocrinol Jpn. 1987 Feb;34(1):81–88. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.34.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicot M., Flores-Riveros J. R., Lane M. D. The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor is responsible for mediating the effects of insulin, IGF-1, and IGF-2 in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9382–9391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Cell lines established by a temperature-sensitive simian virus 40 large-T-antigen gene are growth restricted at the nonpermissive temperature. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1672–1681. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Hyland J. K., Watt R., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Microinjected c-myc as a competence factor. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1313–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.4001943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaleko M., Rutter W. J., Miller A. D. Overexpression of the human insulinlike growth factor I receptor promotes ligand-dependent neoplastic transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):464–473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koniecki J., Nugent P., Kordowska J., Baserga R. Effect of the SV40 T antigen on the posttranscriptional regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and DNA polymerase-alpha genes. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 1;51(5):1465–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Gray A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential signalling potential of insulin- and IGF-1-receptor cytoplasmic domains. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1369–1375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Y., Lee A. S. Induction of two genes by glucose starvation in hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):988–992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson K. E., Baserga R. Transcriptional activity of the human thymidine kinase gene determined by a method using the polymerase chain reaction and an intron-specific probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9774–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Adenovirus type 2 activates cell cycle-dependent genes that are a subset of those activated by serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2936–2942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J. A., Steelman L. S., Mayo M. W., Algate P. A., Dellow R. A., Kaleko M. Growth-promoting effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) on hematopoietic cells: overexpression of introduced IGF-1 receptor abrogates interleukin-3 dependency of murine factor-dependent cells by a ligand-dependent mechanism. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):921–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen F., Partanen S., Mäkinen T., Rutanen E. M. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I and their relation to steroid receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1343–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe M. G., Ginzton N. H., Lee P. D., Hintz R. L., Greenberg P. L. Receptor binding and mitogenic effects of insulin and insulinlike growth factors I and II for human myeloid leukemic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Nov;133(2):219–227. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyrat J. P., Bonneterre J., Beuscart R., Djiane J., Demaille A. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer and their relation to estradiol and progesterone receptors. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6429–6433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrzkowski Z., Lammers R., Carpenter G., Soderquist A. M., Limardo M., Phillips P. D., Ullrich A., Baserga R. Constitutive expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor abrogates all requirements for exogenous growth factors. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Apr;3(4):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radna R. L., Caton Y., Jha K. K., Kaplan P., Li G., Traganos F., Ozer H. L. Growth of immortal simian virus 40 tsA-transformed human fibroblasts is temperature dependent. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3093–3096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss K., Ferber A., Travali S., Porcu P., Phillips P. D., Baserga R. The protooncogene c-myb increases the expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor messenger RNAs by a transcriptional mechanism. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 1;51(21):5997–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick-Silverman L., Pang Z., Li G., Jha K. K., Ozer H. L. Retinoblastoma protein and simian virus 40-dependent immortalization of human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2845–2852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2845-2852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. E., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Inhibition of the mitogenic effects of plasma by a monoclonal antibody to somatomedin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2389–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Shepard R. C., Antoniades H. N., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and the regulation of the mammalian fibroblast cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 10;560(2):217–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Scher C. D., Todaro G. J. Induction of cell division in medium lacking serum growth factor by SV40. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. J., Johnson M. D., May F. E., Westley B. R. Role of insulin-like growth factors and the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor in the estrogen-stimulated proliferation of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21172–21178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Capone G. T., Scher C. D., Antoniades H. N., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Dual control of cell growth by somatomedins and platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surmacz E., Nugent P., Pietrzkowski Z., Baserga R. The role of the IGF1 receptor in the regulation of cdc2 mRNA levels in fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Apr;199(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90435-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Reiss K., Ferber A., Petralia S., Mercer W. E., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Constitutively expressed c-myb abrogates the requirement for insulinlike growth factor 1 in 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):731–736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Woloschak M., Adamo M., Shen-Orr Z., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Developmental regulation of the rat insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7451–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumstein P., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences that are regulated by insulin-like growth factor I. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11252–11260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]