Abstract
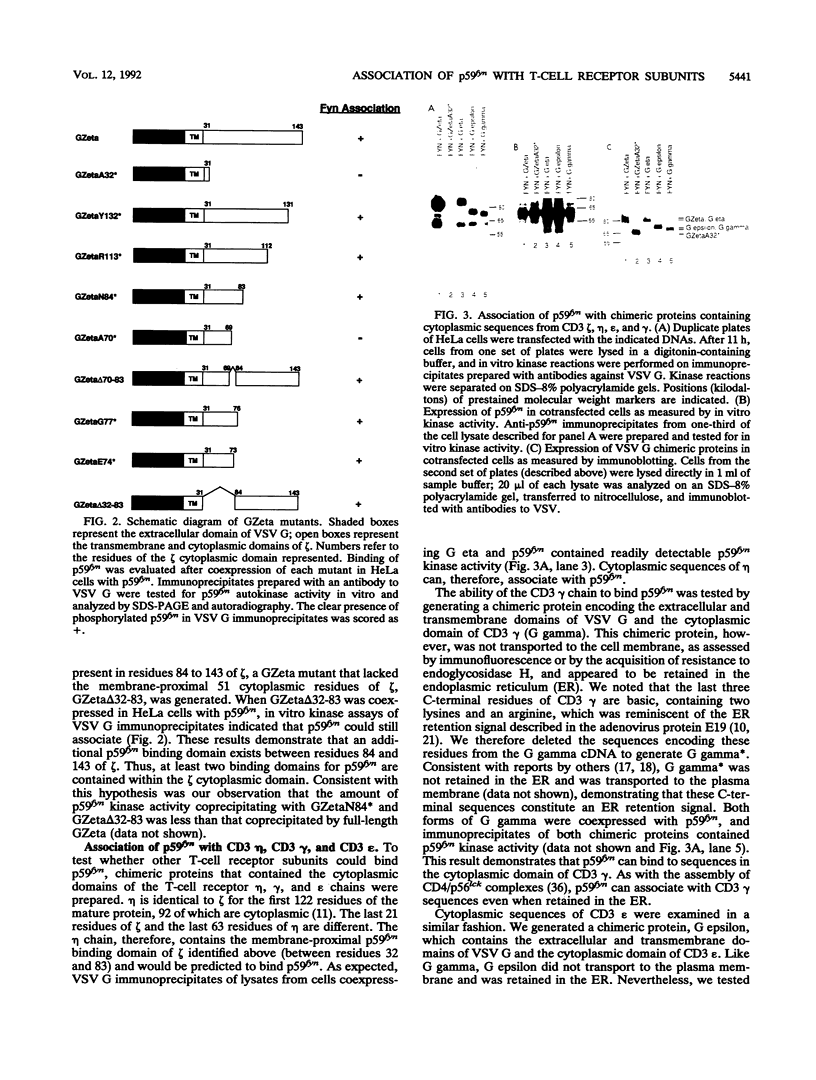
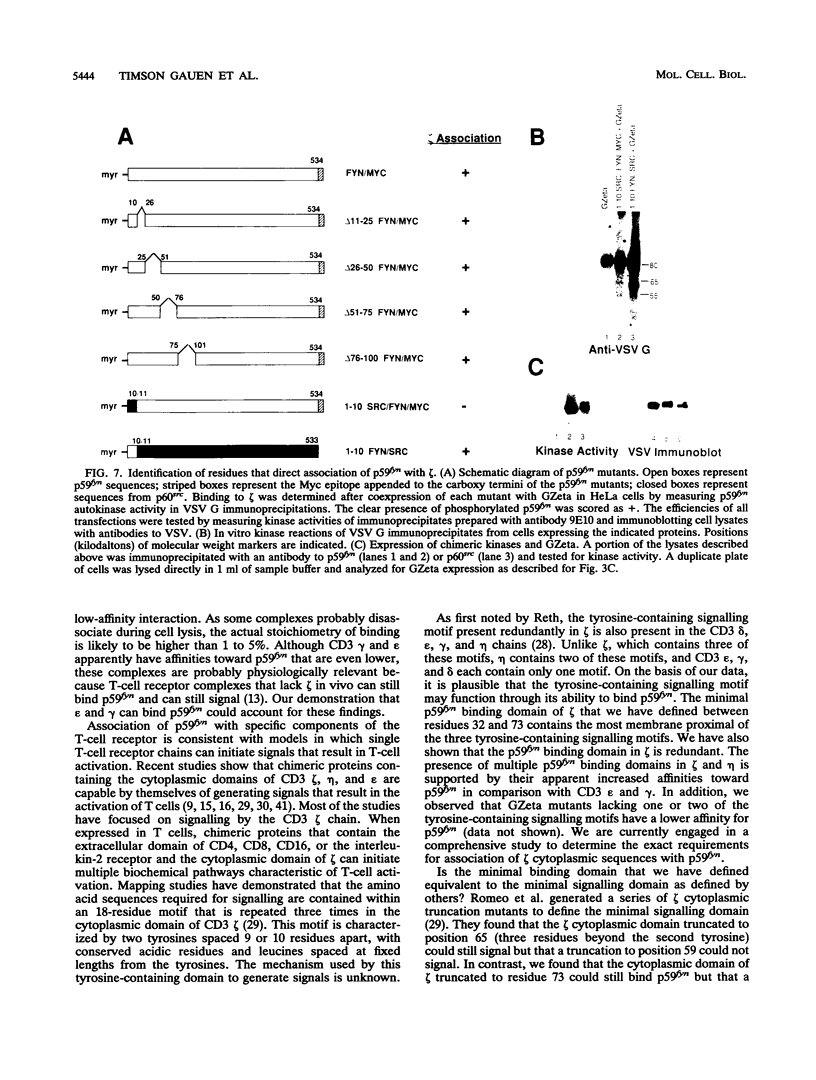
Several lines of evidence link the protein tyrosine kinase p59fyn to the T-cell receptor. The molecular basis of this interaction has not been established. Here we show that the tyrosine kinase p59fyn can associate with chimeric proteins that contain the cytoplasmic domains of CD3 epsilon, gamma, zeta (zeta), and eta. Mutational analysis of the zeta cytoplasmic domain demonstrated that the membrane-proximal 41 residues of zeta are sufficient for p59fyn binding and that at least two p59fyn binding domains are present. The association of p59fyn with the zeta chain was specific, as two closely related Src family protein tyrosine kinases, p60src and p56lck, did not associate with a chimeric protein that contained the cytoplasmic domain of zeta. Mutational analysis of p59fyn revealed that a 10-amino-acid sequence in the unique amino-terminal domain of p59fyn was responsible for the association with zeta. These findings support evidence that p59fyn is functionally and structurally linked to the T-cell receptor. More importantly, these studies support a critical role for the unique amino-terminal domains of Src family kinases in the coupling of tyrosine kinases to the signalling pathways of cell surface receptors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by a src family protein-tyrosine kinase (p59fyn). Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Processing of p60v-src to its myristylated membrane-bound form. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2781–2788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann M., Guttinger M., Amrein K. E., Burn P. Protein tyrosine kinase p59fyn is associated with the T cell receptor-CD3 complex in functional human lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):283–286. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. R., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Identification of a consensus motif for retention of transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3153–3162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y. J., Clayton L. K., Howard F. D., Koyasu S., Sieh M., Steinbrich R., Tarr G. E., Reinherz E. L. Molecular cloning of the CD3 eta subunit identifies a CD3 zeta-related product in thymus-derived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., McConkey D. J., Clayton L. K., Abraham S., Yandava B., Katagiri T., Moingeon P., Yamamoto T., Reinherz E. L. Phosphorylation of multiple CD3 zeta tyrosine residues leads to formation of pp21 in vitro and in vivo. Structural changes upon T cell receptor stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancios L., Lyles D. S. The interactionof antiody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Analysis of neutralizing epitopes with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. T-cell and basophil activation through the cytoplasmic tail of T-cell-receptor zeta family proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallabiabarrena A., Fresno M., Alarcón B. An endoplasmic reticulum retention signal in the CD3 epsilon chain of the T-cell receptor. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):593–596. doi: 10.1038/357593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Jackson M., Peterson P. A. Short cytoplasmic sequences serve as retention signals for transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Carr S. A., Strittmatter P. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase as myristic acid and the complete amino acid sequence of the membrane-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13349–13354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puddington L., Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Cytoplasmic domains of cellular and viral integral membrane proteins substitute for the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in transport to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2147–2157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Ling H. P. Identification of a 32K plasma membrane protein that binds to the myristylated amino-terminal sequence of p60v-src. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):84–86. doi: 10.1038/346084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Reconstitution of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60v-src into phospholipid vesicles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1896–1905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Specific and saturable binding of pp60v-src to plasma membranes: evidence for a myristyl-src receptor. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90842-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):383–384. doi: 10.1038/338383b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Amiot M., Seed B. Sequence requirements for induction of cytolysis by the T cell antigen/Fc receptor zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):889–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Seed B. Cellular immunity to HIV activated by CD4 fused to T cell or Fc receptor polypeptides. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90327-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Chalupny J., Whitney J. A., Hammond C., Amrein K. E., Kavathas P., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. Short related sequences in the cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 mediate binding to the amino-terminal domain of the p56lck tyrosine protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1853–1862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. L., Lee H. M., Rich S., Soriano P. pp59fyn mutant mice display differential signaling in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. L., Lee H. M., Rich S., Soriano P. pp59fyn mutant mice display differential signaling in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. M., Letourneur F., Hoeveler A., Brocker T., Luton F., Malissen B. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex is composed of at least two autonomous transduction modules. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Baniyash M., Hou D., Samelson L. E., Burgess W. H., Klausner R. D. Molecular cloning of the zeta chain of the T cell antigen receptor. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1018–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.3278377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]