Abstract
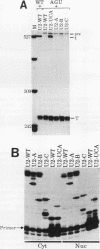
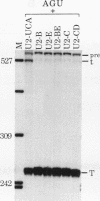
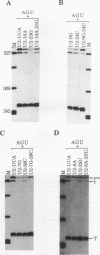
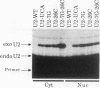
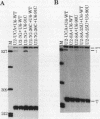
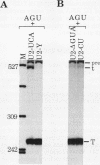
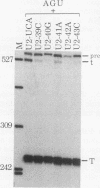
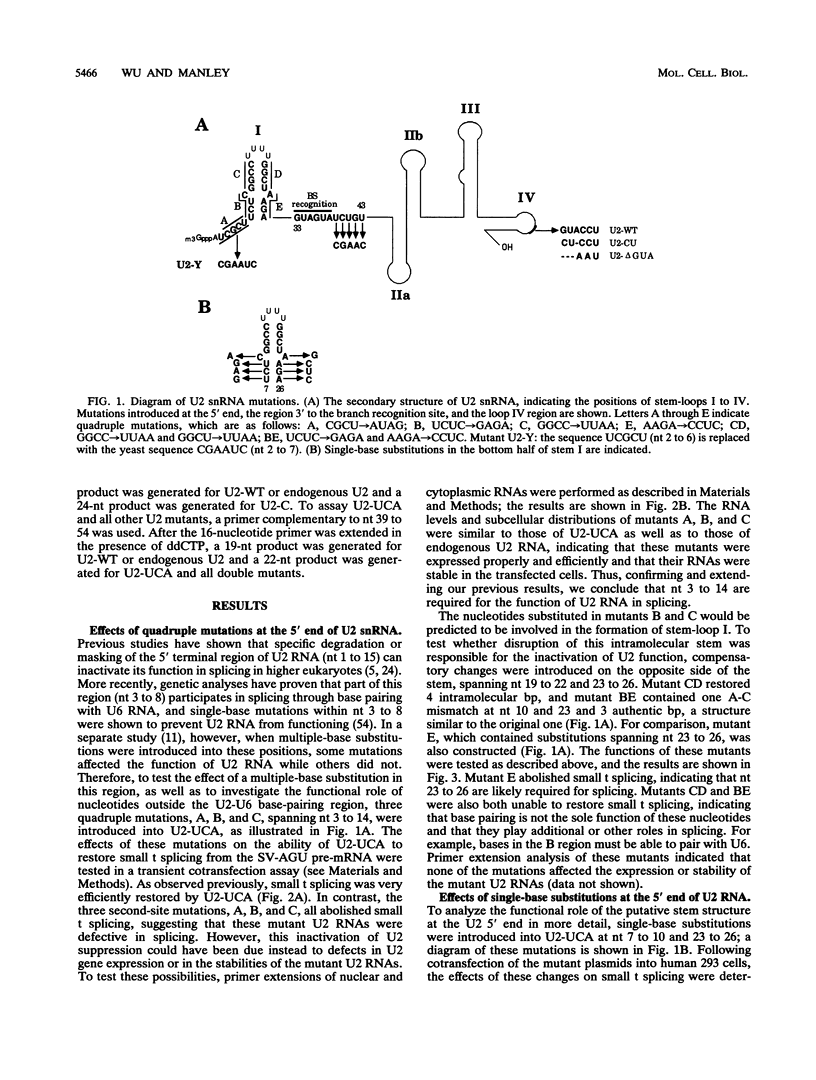
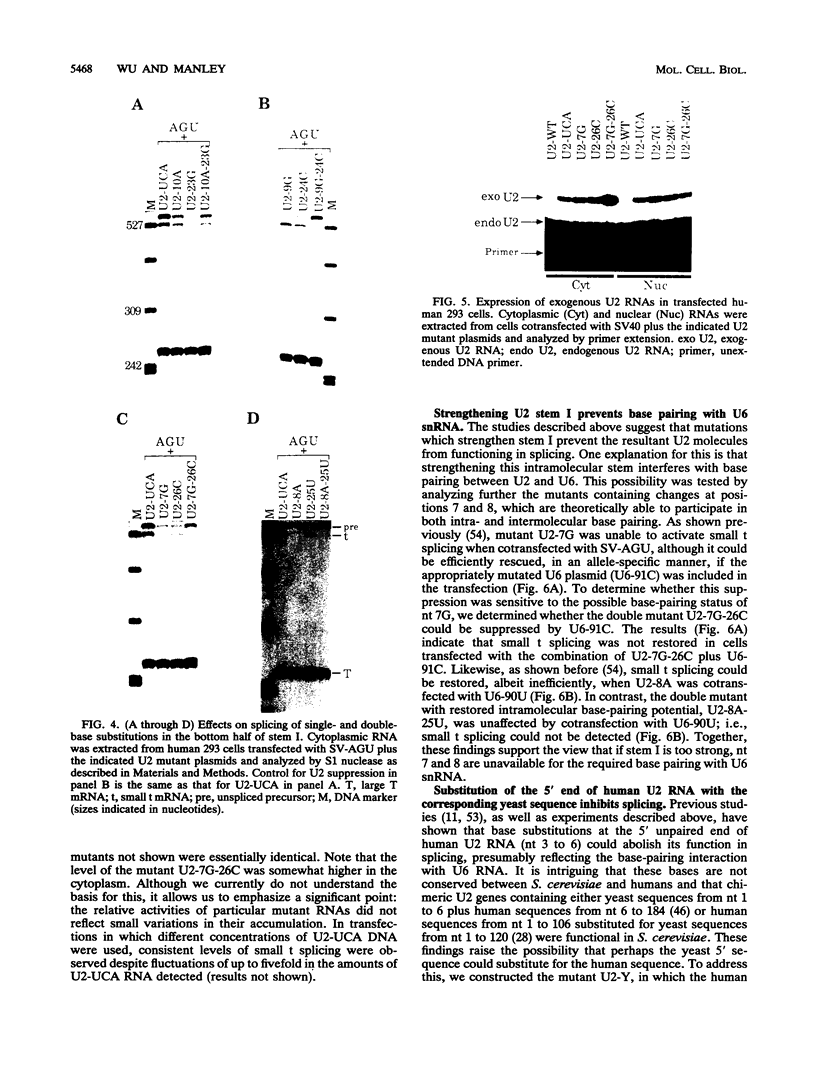
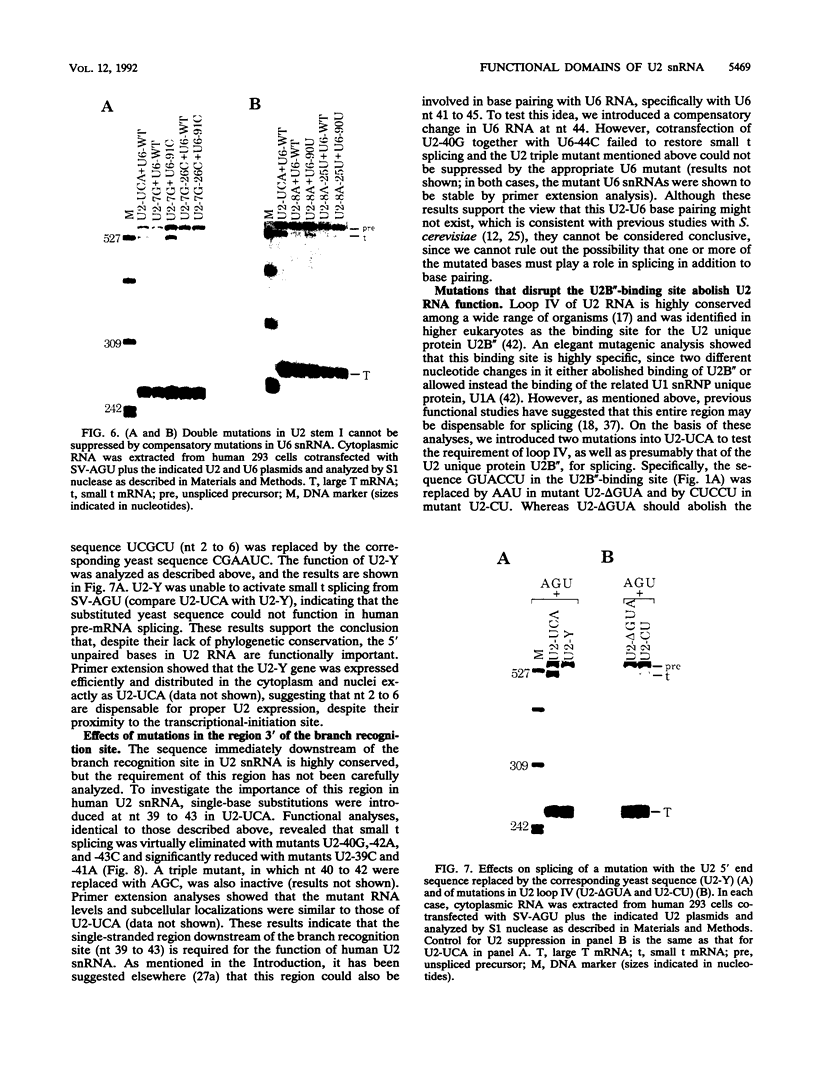
We showed previously that a branch site mutation in simian virus 40 early pre-mRNA that prevented small t antigen mRNA splicing could be efficiently suppressed by a compensatory mutation in a coexpressed U2 small nuclear (sn) RNA gene. We have now generated second-site mutations in this suppressor gene to investigate regions of U2 RNA required for function. A number of mutations in a putative stem at the 5' end of the molecule inhibited splicing, indicating that bases in this region are important for activity. However, several lines of evidence suggested that formation of the entire stem is not essential for splicing. Indeed, mutations that strengthen the stem actually inhibited splicing, and evidence that this prevents a required base-pairing interaction with U6 snRNA is presented. These results suggest that the relative stabilities of competing intra- and intermolecular base-pairing interactions play an important role in the splicing reaction. Mutations in a conserved single-stranded region immediately 3' to the branch site recognition sequence all inhibited splicing, indicating that this region is required for U2 function, although its exact role remains unknown. Finally, two mutations in the loop of stem IV at the 3' end of the molecule, which destroy the binding site of U2 sn ribonucleoprotein B", prevented small t splicing; this finding contrasts with previous studies which utilized different assay systems. Analysis of the accumulation and subcellular localization of all of the mutant RNAs showed that they were similar to those of the parental suppressor U2 RNA, indicating that the effects observed indeed reflect defects in splicing.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr, Igel A. H. Lethal and temperature-sensitive mutations and their suppressors identify an essential structural element in U2 small nuclear RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2132–2145. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr U2 RNA from yeast is unexpectedly large and contains homology to vertebrate U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear RNAs. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe B. J., Sproat B. S., Ryder U., Barabino S., Lamond A. I. Antisense probing of the human U4/U6 snRNP with biotinylated 2'-OMe RNA oligonucleotides. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordonné R., Banroques J., Abelson J., Guthrie C. Domains of yeast U4 spliceosomal RNA required for PRP4 protein binding, snRNP-snRNP interactions, and pre-mRNA splicing in vivo. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1185–1196. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Splicing a spliceosomal RNA. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):14–15. doi: 10.1038/337014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Steitz J. A. Multiple interactions between the splicing substrate and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in spliceosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):281–293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Spliceosome assembly in yeast. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1014–1027. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta B., Weiner A. M. Genetic evidence for base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNA in mammalian mRNA splicing. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):821–824. doi: 10.1038/352821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., Abelson J. Two domains of yeast U6 small nuclear RNA required for both steps of nuclear precursor messenger RNA splicing. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):404–409. doi: 10.1126/science.2145630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., McPheeters D. S., Abelson J. In vitro assembly of yeast U6 snRNP: a functional assay. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2137–2150. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A., Parisot R., Newmeyer D., De Robertis E. M. Small nuclear U-ribonucleoproteins in Xenopus laevis development. Uncoupled accumulation of the protein and RNA components. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Manley J. L. Factors influencing alternative splice site utilization in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Functional analysis of mutant Xenopus U2 snRNAs. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90878-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Giglio L. M., Weiner A. M. Evidence for base-pairing between mammalian U2 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2146–2156. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs V., Bach M., Winkelmann G., Lührmann R. U1-specific protein C needed for efficient complex formation of U1 snRNP with a 5' splice site. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):69–72. doi: 10.1126/science.2136774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in formation of spliceosomes. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Spliceosome assembly involves the binding and release of U4 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):411–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Sproat B., Ryder U., Hamm J. Probing the structure and function of U2 snRNP with antisense oligonucleotides made of 2'-OMe RNA. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90852-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Bordonné R., Guthrie C. Multiple roles for U6 snRNA in the splicing pathway. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2264–2277. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Fabrizio P., Abelson J. In vitro reconstitution of functional yeast U2 snRNPs. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2124–2136. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia L., Seiwert S., Igel A. H., Ares M., Jr Limited functional equivalence of phylogenetic variation in small nuclear RNA: yeast U2 RNA with altered branchpoint complementarity inhibits splicing and produces a dominant lethal phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottram J., Perry K. L., Lizardi P. M., Lührmann R., Agabian N., Nelson R. G. Isolation and sequence of four small nuclear U RNA genes of Trypanosoma brucei subsp. brucei: identification of the U2, U4, and U6 RNA analogs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1212–1223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Norman C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A., Norman C. Mutations in yeast U5 snRNA alter the specificity of 5' splice-site cleavage. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90413-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Pan Z. Q., Prives C., Manley J. L. Splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA to large T and small t mRNAs utilizes different patterns of lariat branch sites. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Prives C., Manley J. L. Alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA is determined by branch site selection. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1460–1475. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orum H., Nielsen H., Engberg J. Spliceosomal small nuclear RNAs of Tetrahymena thermophila and some possible snRNA-snRNA base-pairing interactions. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90208-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Q., Prives C. U2 snRNA sequences that bind U2-specific proteins are dispensable for the function of U2 snRNP in splicing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1887–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Shimura Y. Association of U6 snRNA with the 5'-splice site region of pre-mRNA in the spliceosome. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):244–254. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K. W., Guthrie C. Suppressors of a U4 snRNA mutation define a novel U6 snRNP protein with RNA-binding motifs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):773–785. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster E. O., Guthrie C. Human U2 snRNA can function in pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):270–273. doi: 10.1038/345270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster E. O., Guthrie C. Two conserved domains of yeast U2 snRNA are separated by 945 nonessential nucleotides. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. 5' splice site selection in yeast: genetic alterations in base-pairing with U1 reveal additional requirements. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1258–1267. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Kretzner L., Rosbash M. A U1 snRNA:pre-mRNA base pairing interaction is required early in yeast spliceosome assembly but does not uniquely define the 5' cleavage site. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2533–2538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Ohshima Y. The gene for the U6 small nuclear RNA in fission yeast has an intron. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):87–90. doi: 10.1038/337087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Ohshima Y. mRNA-type introns in U6 small nuclear RNA genes: implications for the catalysis in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1022–1031. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff T., Bindereif A. Reconstituted mammalian U4/U6 snRNP complements splicing: a mutational analysis. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):345–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. A., Manley J. L. Base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNAs is necessary for splicing of a mammalian pre-mRNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):818–821. doi: 10.1038/352818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Manley J. L. Mammalian pre-mRNA branch site selection by U2 snRNP involves base pairing. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1553–1561. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Weiner A. M. Genetic analysis of the role of human U1 snRNA in mRNA splicing: I. Effect of mutations in the highly conserved stem-loop I of U1. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):697–707. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavanelli M. I., Ares M., Jr Efficient association of U2 snRNPs with pre-mRNA requires an essential U2 RNA structural element. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2521–2533. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in human U2 snRNA can suppress a branch site mutation. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1545–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]