Abstract
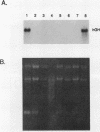
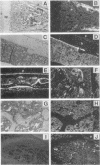
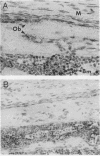
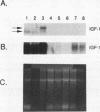
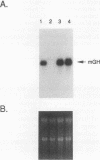
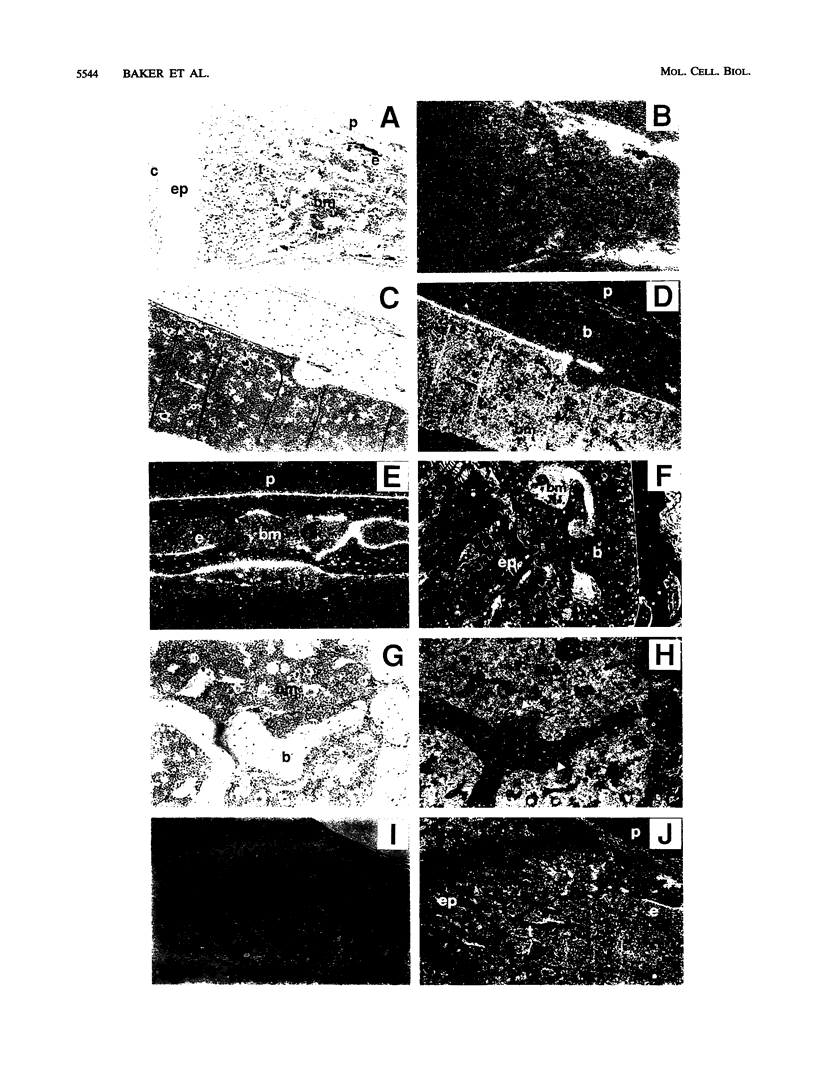
Growth hormone (GH) is an important regulator of postnatal growth, acting on a wide variety of target tissues. Here, we show that local production of GH in osteoblasts is able to stimulate bone growth directly without significant systemic effects. Mice were made transgenic by microinjection of an osteocalcin-human GH (osteocalcin-hGH) gene construct in which approximately 1,800 bp of the rat osteocalcin promoter was fused to the hGH gene. Five lines of transgenic mice, each with measurable amounts of serum hGH (ranging from 1 to 1,000 ng/ml), were analyzed. Northern (RNA) blot hybridization showed that the hGH transcript was detectable only in the bone. Further characterization of hGH mRNA distribution by in situ hybridization revealed that in neonates the most intense signal was found in periosteal osteoblasts, while in adults, trabecular and endosteal osteoblasts were favored. In one transgenic line (992-1), hGH was expressed at a much lower level and had minimal systemic effects; however, the local concentrations of hGH in bone were sufficient to stimulate bone growth in these animals.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Mathews L. S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Dwarf mice produced by genetic ablation of growth hormone-expressing cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):453–461. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresford J. N., Gallagher J. A., Poser J. W., Russell R. G. Production of osteocalcin by human bone cells in vitro. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3, 24,25(OH)2D3, parathyroid hormone, and glucocorticoids. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res. 1984;5(5):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0221-8747(84)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronckers A. L., Gay S., Dimuzio M. T., Butler W. T. Immunolocalization of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing proteins in developing molar tooth germs of the rat. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jan;5(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celeste A. J., Rosen V., Buecker J. L., Kriz R., Wang E. A., Wozney J. M. Isolation of the human gene for bone gla protein utilizing mouse and rat cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1885–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Beamer W. G. Inherited ateliotic dwarfism in mice. Characteristics of the mutation, little, on chromosome 6. J Hered. 1976 Mar-Apr;67(2):87–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst M., Froesch E. R. Growth hormone dependent stimulation of osteoblast-like cells in serum-free cultures via local synthesis of insulin-like growth factor I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90570-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Morikawa M., Nixon T. A dual effector theory of growth-hormone action. Differentiation. 1985;29(3):195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Jansson J. O., Gause I. A. Growth hormone stimulates longitudinal bone growth directly. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7079756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Lindahl A., Nilsson A., Isgaard J. Mechanism of the stimulatory effect of growth hormone on longitudinal bone growth. Endocr Rev. 1987 Nov;8(4):426–438. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-4-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isgaard J., Nilsson A., Lindahl A., Jansson J. O., Isaksson O. G. Effects of local administration of GH and IGF-1 on longitudinal bone growth in rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):E367–E372. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.4.E367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. B., Gundberg C. M. Osteocalcin. Biochemical considerations and clinical applications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988 Jan;(226):267–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl A., Isgaard J., Isaksson O. G. Growth hormone in vivo potentiates the stimulatory effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 in vitro on colony formation of epiphyseal chondrocytes isolated from hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1070–1075. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe W. L., Jr, Lasky S. R., LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Distribution and regulation of rat insulin-like growth factor I messenger ribonucleic acids encoding alternative carboxyterminal E-peptides: evidence for differential processing and regulation in liver. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jun;2(6):528–535. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-6-528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Hammer R. E., Behringer R. R., D'Ercole A. J., Bell G. I., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Growth enhancement of transgenic mice expressing human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1988 Dec;123(6):2827–2833. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-6-2827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Expression of insulin-like growth factor I in transgenic mice with elevated levels of growth hormone is correlated with growth. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):433–437. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Carlsson B., Isgaard J., Isaksson O. G., Rymo L. Regulation by GH of insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA expression in rat epiphyseal growth plate as studied with in-situ hybridization. J Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;125(1):67–74. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1250067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto S. K., Price P. A. Proof that the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing bone protein is synthesized in calf bone. Comparative synthesis rate and effect of coumadin on synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norstedt G., Palmiter R. Secretory rhythm of growth hormone regulates sexual differentiation of mouse liver. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Hammer R. E., Trumbauer M. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Birnberg N. C., Evans R. M. Dramatic growth of mice that develop from eggs microinjected with metallothionein-growth hormone fusion genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):611–615. doi: 10.1038/300611a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser J. W., Esch F. S., Ling N. C., Price P. A. Isolation and sequence of the vitamin K-dependent protein from human bone. Undercarboxylation of the first glutamic acid residue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8685–8691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser J. W., Price P. A. A method for decarboxylation of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in proteins. Properties of the decarboxylated gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein from calf bone. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):431–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaife C. J., Mathews L. S., Pinkert C. A., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Histopathology associated with elevated levels of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I in transgenic mice. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):40–48. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. T., Jr, Lasky S. R., Lowe W. L., Jr, Seaman W. T., LeRoith D. Molecular cloning of rat insulin-like growth factor I complementary deoxyribonucleic acids: differential messenger ribonucleic acid processing and regulation by growth hormone in extrahepatic tissues. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Mar;1(3):243–248. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-3-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Spencer E. M. Local injections of human or rat growth hormone or of purified human somatomedin-C stimulate unilateral tibial epiphyseal growth in hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2563–2567. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwander J. C., Hauri C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Synthesis and secretion of insulin-like growth factor and its binding protein by the perfused rat liver: dependence on growth hormone status. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):297–305. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Clift S., Pitts-Meek S., Martin L., Terrell T. G., Liggitt D., Oakley H. An evaluation of the functions of the 22-kilodalton (kDa), the 20-kDa, and the N-terminal polypeptide forms of human growth hormone using transgenic mice. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):405–414. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1727714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Hollingshead P. G., Pitts S. L. Multiple regulatory domains in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat revealed by analysis of fusion genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):473–479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. G., SIMPSON M. E., ASLING C. W., EVANS H. M. Growth and differentiation in the rat following hypophysectomy at 6 days of age. Anat Rec. 1950 Apr;106(4):536–554. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091060403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]