Abstract
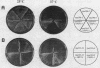
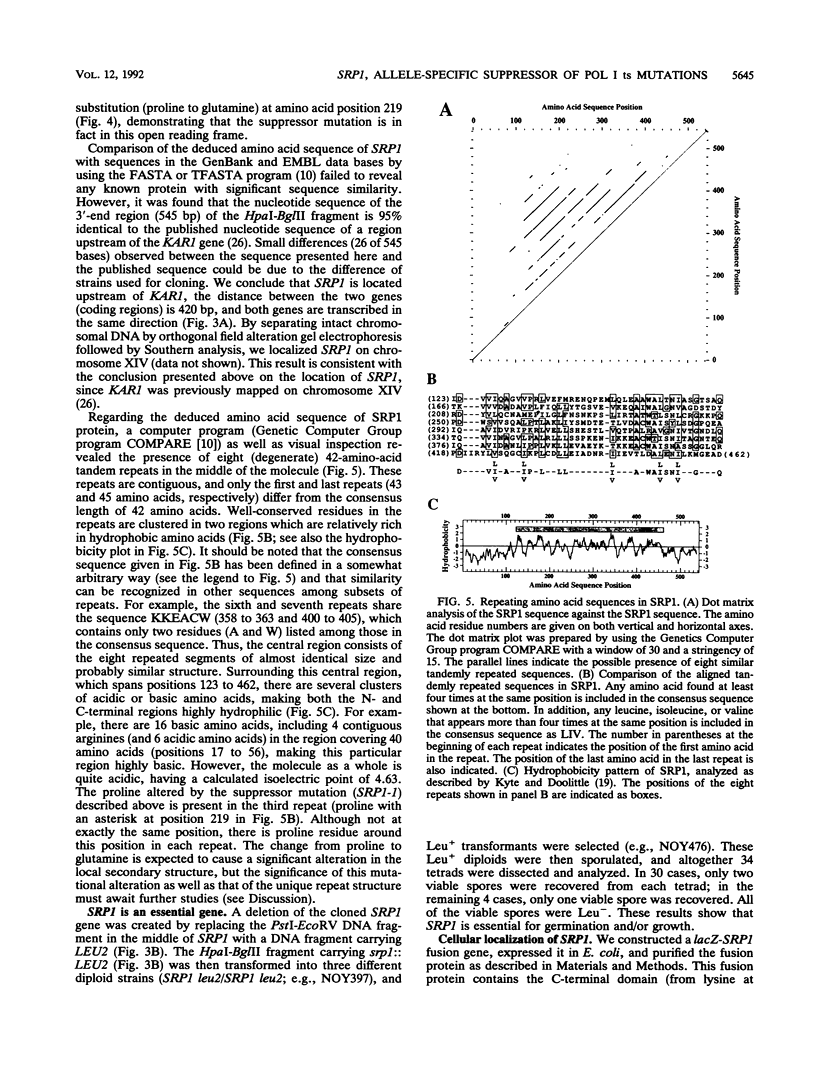
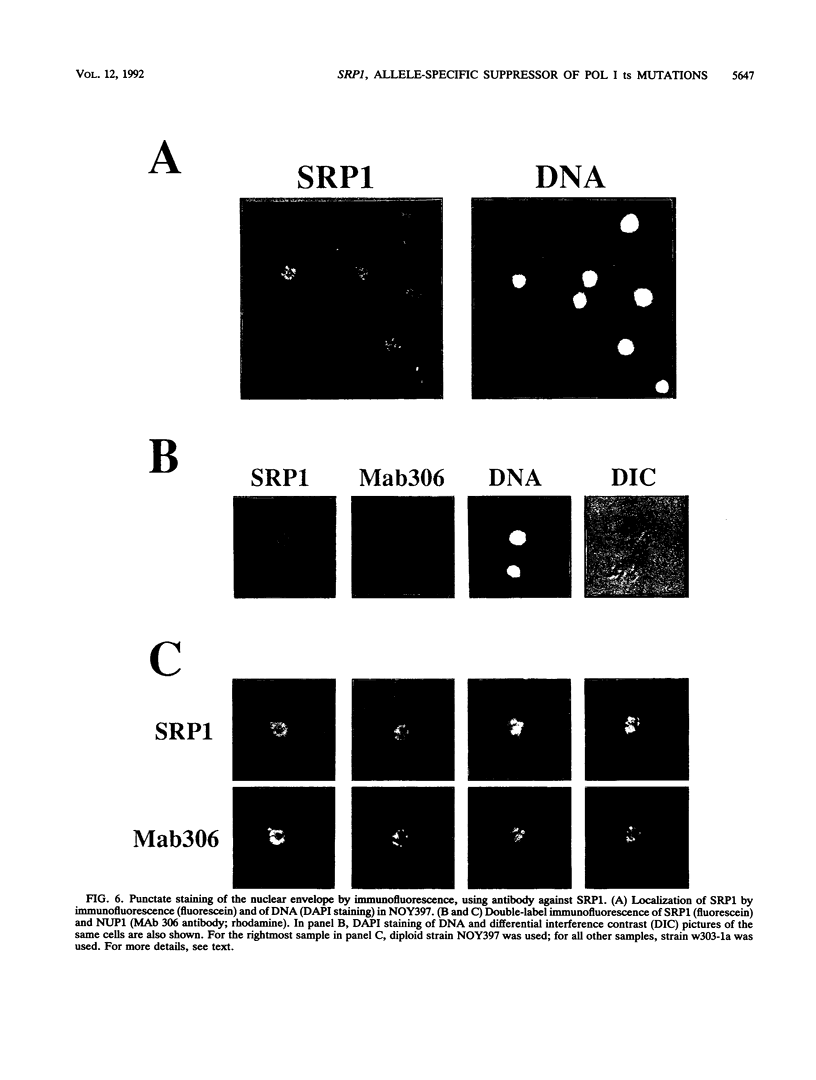
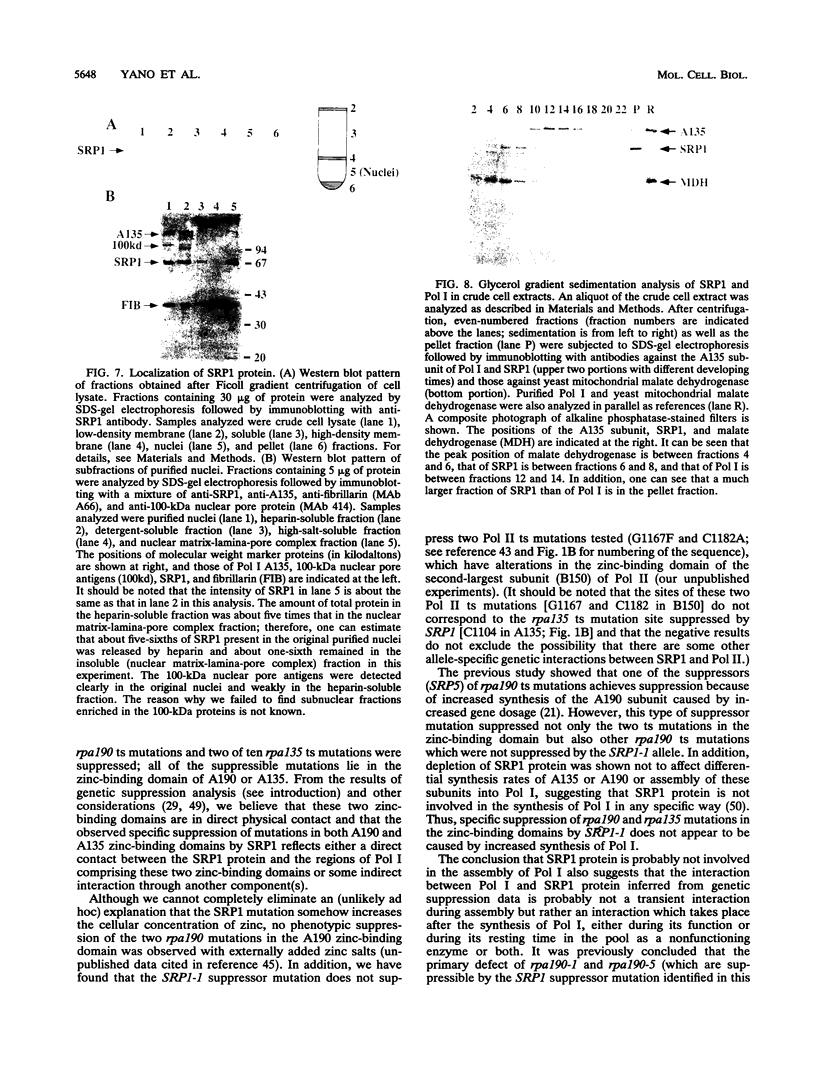
The SRP1-1 mutation is an allele-specific dominant suppressor of temperature-sensitive mutations in the zinc-binding domain of the A190 subunit of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase I (Pol I). We found that it also suppresses temperature-sensitive mutations in the zinc-binding domain of the Pol I A135 subunit. This domain had been suggested to be in physical proximity to the A190 zinc-binding domain. We have cloned the SRP1 gene and determined its nucleotide sequence. The gene encodes a protein of 542 amino acids consisting of three domains: the central domain, which is composed of eight (degenerate) 42-amino-acid contiguous tandem repeats, and the surrounding N-terminal and C-terminal domains, both of which contain clusters of acidic and basic amino acids and are very hydrophilic. The mutational alteration (P219Q) responsible for the suppression was found to be in the central domain. Using antibody against the SRP1 protein, we have found that SRP1 is mainly localized at the periphery of the nucleus, apparently more concentrated in certain regions, as suggested by a punctate pattern in immunofluorescence microscopy. We suggest that SRP1 is a component of a larger macromolecular complex associated with the nuclear envelope and interacts with Pol I either directly or indirectly through other components in the structure containing SRP1.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. L., Douglas M. G. Organization of the nuclear pore complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1989 Aug;102(2):95–108. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(89)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Isolation of yeast nuclei. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:735–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94056-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Yeast nuclear envelope proteins cross react with an antibody against mammalian pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2059–2067. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carles C., Treich I., Bouet F., Riva M., Sentenac A. Two additional common subunits, ABC10 alpha and ABC10 beta, are shared by yeast RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24092–24096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. W., Abelson J. The subnuclear localization of tRNA ligase in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1515–1526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. W., Yip M. L., Campbell J., Abelson J. SSB-1 of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a nucleolar-specific, silver-binding protein that is associated with the snR10 and snR11 small nuclear RNAs. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1741–1751. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. The nucleoskeleton and the topology of transcription. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 20;185(3):487–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Fink G. R. The NUP1 gene encodes an essential component of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):965–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson P., Cook P. R., Jackson D. A. Active RNA polymerase I is fixed within the nucleus of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2207–2214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M., Yanagida M. The TPR snap helix: a novel protein repeat motif from mitosis to transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90070-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henríquez R., Blobel G., Aris J. P. Isolation and sequencing of NOP1. A yeast gene encoding a nucleolar protein homologous to a human autoimmune antigen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2209–2215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Hiraoka Y., Yanagida M. A temperature-sensitive mutation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene nuc2+ that encodes a nuclear scaffold-like protein blocks spindle elongation in mitotic anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1171–1183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kinoshita N., Morikawa K., Yanagida M. Snap helix with knob and hole: essential repeats in S. pombe nuclear protein nuc2+. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90746-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E. G. Interpreting nucleolar structure: where are the transcribing genes? J Cell Sci. 1991 Apr;98(Pt 4):437–442. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker J. H., Yamagishi M., Kolb J. M., Nomura M. Suppressor analysis of temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase I mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: suppression of mutations in a zinc-binding motif by transposed mutant genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):746–753. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Kern H., Mutvei A., Horstmann H., Marshallsay B., Hurt E. C. NSP1: a yeast nuclear envelope protein localized at the nuclear pores exerts its essential function by its carboxy-terminal domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90063-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Vu L., Nomura M. An approach for isolation of mutants defective in 35S ribosomal RNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7026–7030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Genetic applications of yeast transformation with linear and gapped plasmids. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva M., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P., Hawthorne D. C. Natural variation in yeast RNA polymerase A. Formation of a mosaic RNA polymerase A in a meiotic segregant from an interspecific hybrid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4570–4577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Fink G. R. KAR1, a gene required for function of both intranuclear and extranuclear microtubules in yeast. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Rose K. M. Localization of RNA polymerase I in interphase cells and mitotic chromosomes by light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1431–1435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmang T., Tollervey D., Kern H., Frank R., Hurt E. C. A yeast nucleolar protein related to mammalian fibrillarin is associated with small nucleolar RNA and is essential for viability. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4015–4024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boguski M. S., Goebl M., Hieter P. A repeating amino acid motif in CDC23 defines a family of proteins and a new relationship among genes required for mitosis and RNA synthesis. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90745-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan J. S., McAlister-Henn L. Structural and functional effects of mutations altering the subunit interface of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Jun;287(2):276–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90479-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Lehtonen H., Carmo-Fonseca M., Hurt E. C. The small nucleolar RNP protein NOP1 (fibrillarin) is required for pre-rRNA processing in yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):573–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treich I., Riva M., Sentenac A. Zinc-binding subunits of yeast RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21971–21976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Batut J., Klose K. E., Keener J., Kustu S. The phosphorylated form of the enhancer-binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity that is essential for activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90579-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Hermann-Le Denmat S., Treich I., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Effect of mutations in a zinc-binding domain of yeast RNA polymerase C (III) on enzyme function and subunit association. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1087–1095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind M., Dodd J., Vu L., Kolb J. M., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Nomura M. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutations in RPA190, the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):3997–4008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind M., Kolb J. M., Dodd J., Yamagishi M., Mémet S., Buhler J. M., Nomura M. Conditional expression of RPA190, the gene encoding the largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase I: effects of decreased rRNA synthesis on ribosomal protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2049–2059. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida M. Higher-order chromosome structure in yeast. J Cell Sci. 1990 May;96(Pt 1):1–3. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Nomura M. Suppressor analysis of temperature-sensitive mutations of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a suppressor gene encodes the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):754–764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]