Abstract
Potential DNA replication accessory factors from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae have previously been identified by their ability to bind to DNA polymerase alpha protein affinity matrices (J. Miles and T. Formosa, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:1276-1280, 1992). We have now used genetic methods to characterize the gene encoding one of these DNA polymerase alpha-binding proteins (POB1) to determine whether it plays a role in DNA replication in vivo. We find that yeast cells lacking POB1 are viable but display a constellation of phenotypes indicating defective DNA metabolism. Populations of cells lacking POB1 accumulate abnormally high numbers of enlarged large-budded cells with a single nucleus at the neck of the bud. The average DNA content in a population of cells lacking POB1 is shifted toward the G2 value. These two phenotypes indicate that while the bulk of DNA replication is completed without POB1, mitosis is delayed. Deleting POB1 also causes elevated levels of both chromosome loss and genetic recombination, enhances the temperature sensitivity of cells with mutant DNA polymerase alpha genes, causes increased sensitivity to UV radiation in cells lacking a functional RAD9 checkpoint gene, and causes an increased probability of death in cells carrying a mutation in the MEC1 checkpoint gene. The sequence of the POB1 gene indicates that it is identical to the CTF4 (CHL15) gene identified previously in screens for mutations that diminish the fidelity of chromosome transmission. These phenotypes are consistent with defective DNA metabolism in cells lacking POB1 and strongly suggest that this DNA polymerase alpha-binding protein plays a role in accurately duplicating the genome in vivo.
Full text
PDF




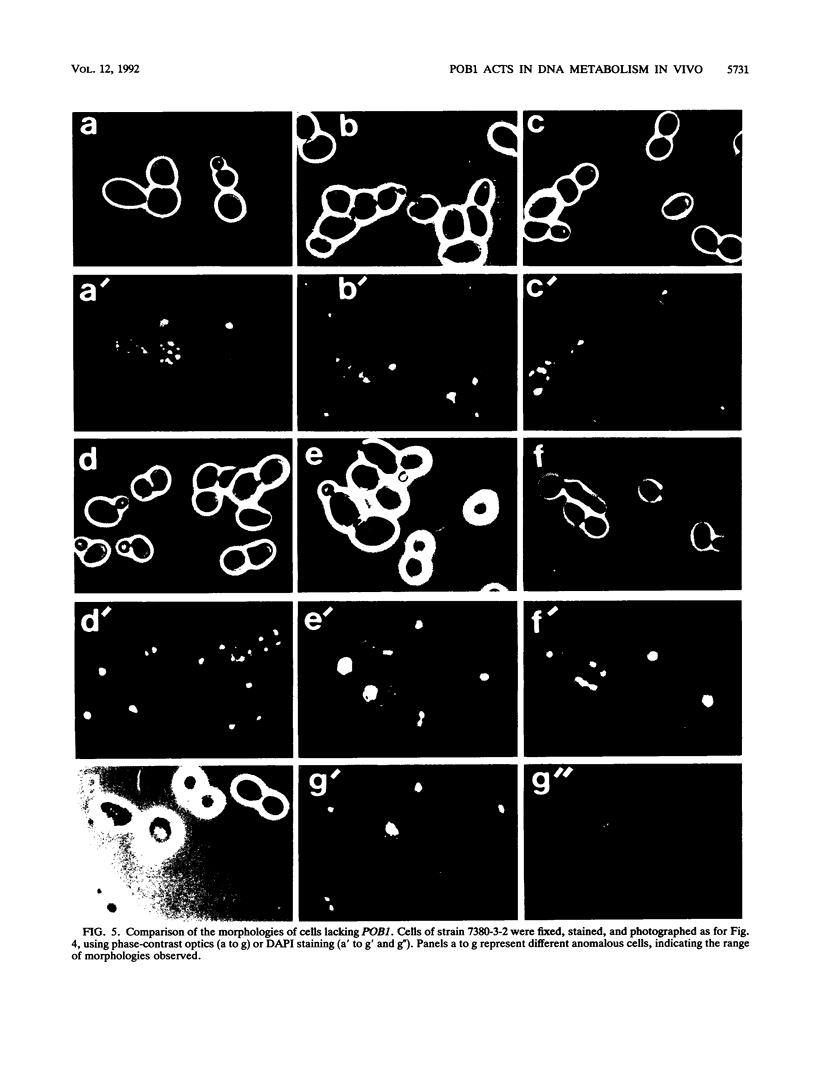
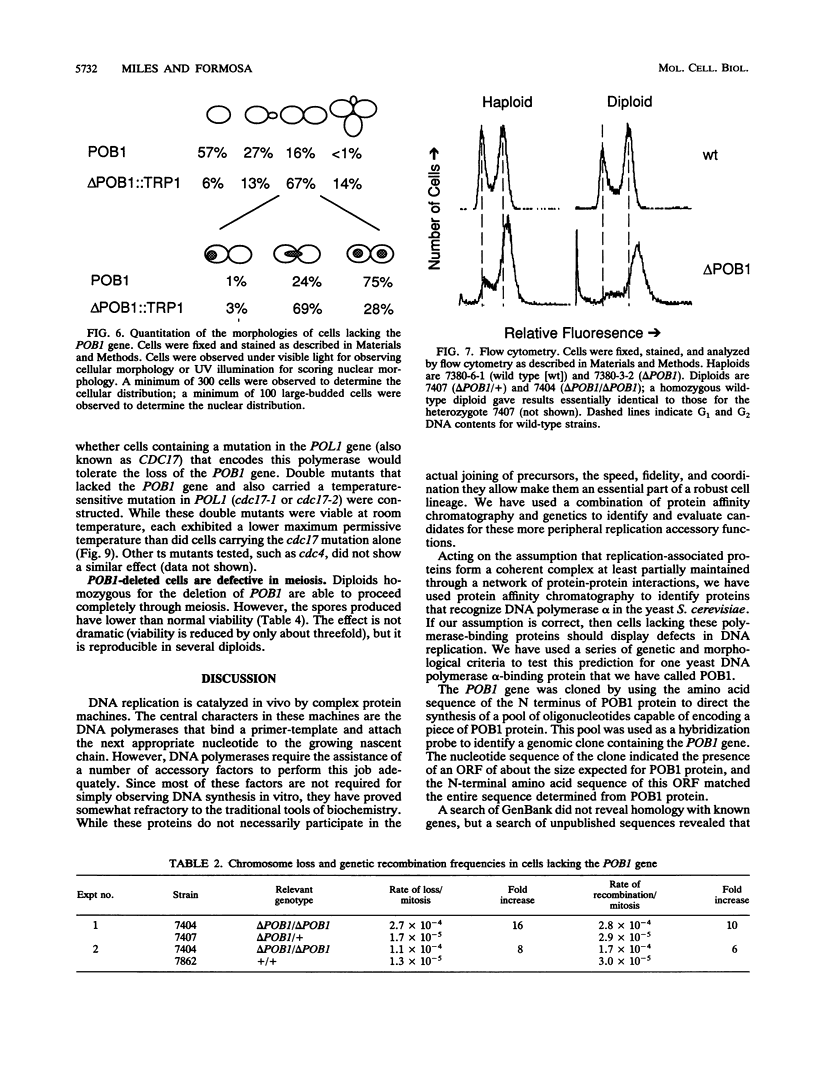
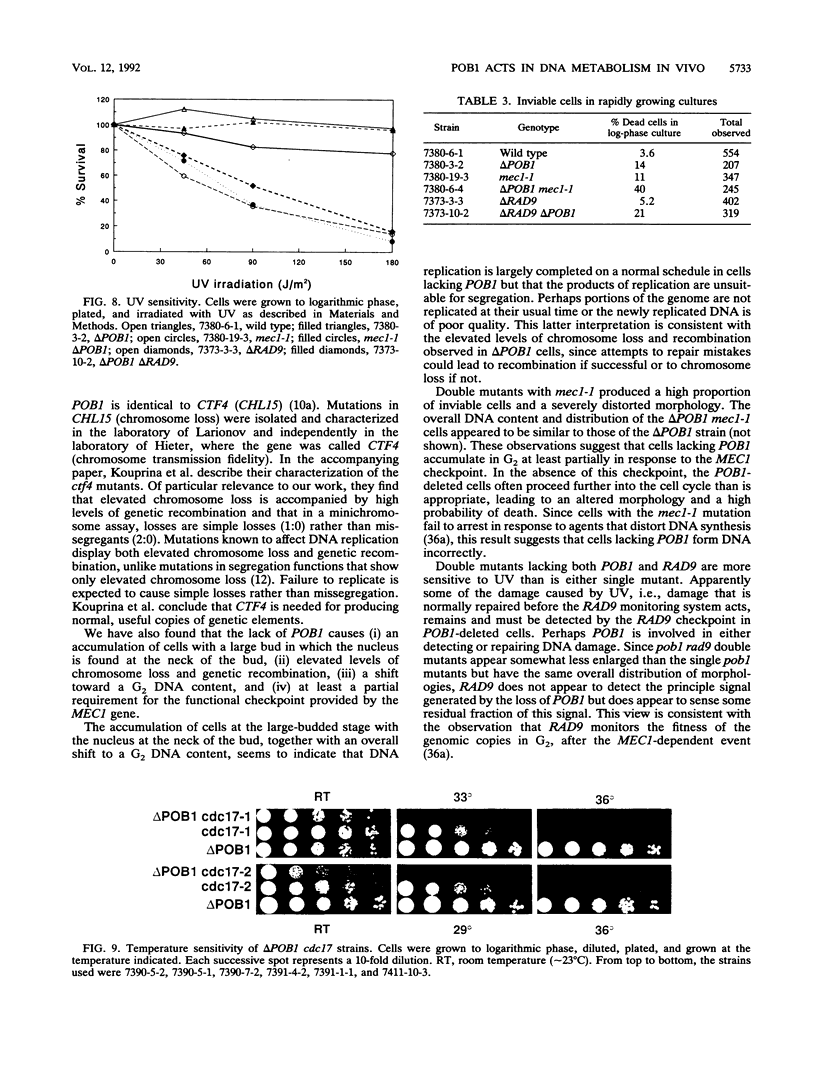


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M. The DNA enzymology of protein machines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:1–12. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bambara R. A., Jessee C. B. Properties of DNA polymerases delta and epsilon, and their roles in eukaryotic DNA replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90147-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Newlon C. S. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc2 mutants fail to replicate approximately one-third of their nuclear genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1000–1012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. N., Thorner J. Isolation of the yeast calmodulin gene using synthetic oligonucleotide probes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;139:248–262. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)39090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. The initiation of chromosomal DNA replication in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90305-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formosa T., Barry J., Alberts B. M., Greenblatt J. Using protein affinity chromatography to probe structure of protein machines. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:24–45. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerring S. L., Spencer F., Hieter P. The CHL 1 (CTF 1) gene product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for chromosome transmission and normal cell cycle progression in G2/M. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4347–4358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Macromolecule synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1662–1670. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1662-1670.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Smith D. Altered fidelity of mitotic chromosome transmission in cell cycle mutants of S. cerevisiae. Genetics. 1985 Jul;110(3):381–395. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouprina NYu, Pashina O. B., Nikolaishwili N. T., Tsouladze A. M., Larionov V. L. Genetic control of chromosome stability in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1988 Dec;4(4):257–269. doi: 10.1002/yea.320040404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouprina N., Kroll E., Bannikov V., Bliskovsky V., Gizatullin R., Kirillov A., Shestopalov B., Zakharyev V., Hieter P., Spencer F. CTF4 (CHL15) mutants exhibit defective DNA metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5736–5747. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes N. F., Johnson A. L., Johnston L. H. Coordination of expression of DNA synthesis genes in budding yeast by a cell-cycle regulated trans factor. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):247–250. doi: 10.1038/350247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J., Formosa T. Protein affinity chromatography with purified yeast DNA polymerase alpha detects proteins that bind to DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Hogan E., Koshland D. Mitotic transmission of artificial chromosomes in cdc mutants of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):763–774. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. G., Downey K. M. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(1-2):129–155. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer F., Gerring S. L., Connelly C., Hieter P. Mitotic chromosome transmission fidelity mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):237–249. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Faye G. MSS18, a yeast nuclear gene involved in the splicing of intron aI5 beta of the mitochondrial cox1 transcript. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1455–1464. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02963.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Enzymes and proteins acting at the fork. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):699–712. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma R., Patapoutian A., Gordon C. B., Campbell J. L. Identification and purification of a factor that binds to the Mlu I cell cycle box of yeast DNA replication genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7155–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Collins K. L., Simancek P., Russo A., Wold M. S., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Reconstitution of simian virus 40 DNA replication with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8692–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. Characterization of RAD9 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and evidence that its function acts posttranslationally in cell cycle arrest after DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6554–6564. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]