Abstract
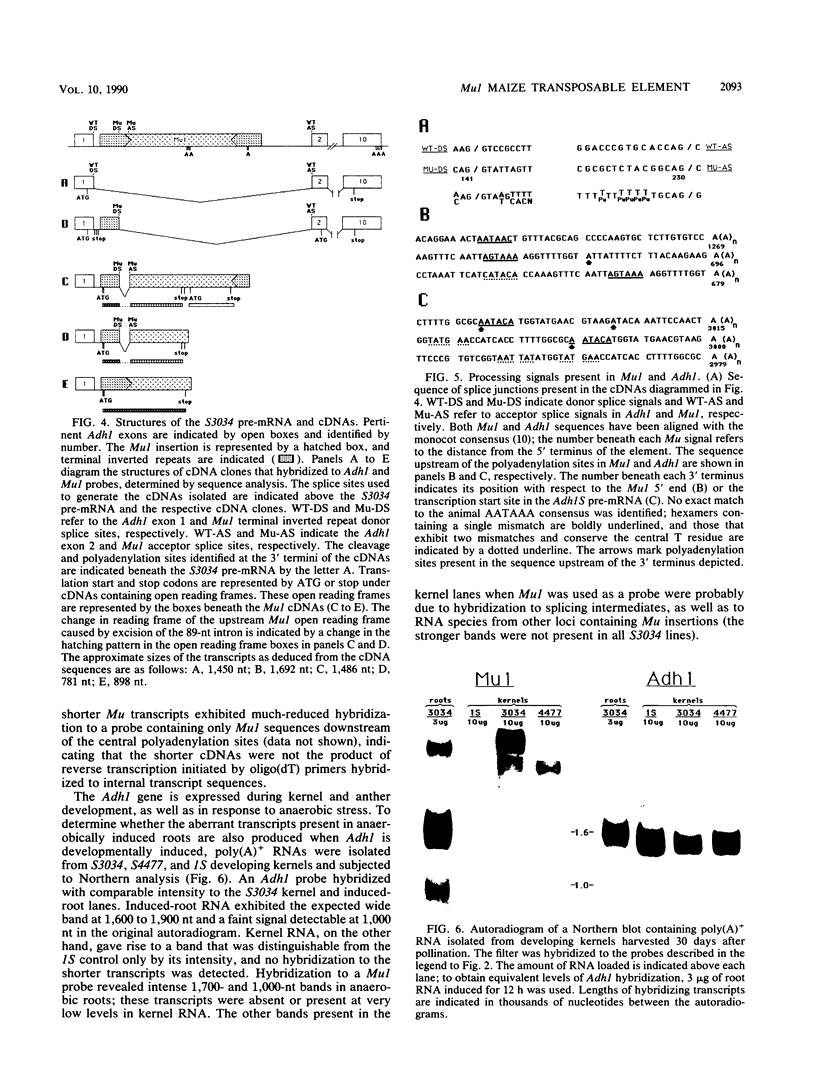
Insertions of the maize transposable element Robertson's Mutator (Mu) into intron 1 of the Adh1 gene have produced a number of mutant alleles altered in quantitative expression. It has previously been shown that transcription and mRNA accumulation are reduced for two of these alleles, Adh1-S3034 and Adh1-S4477. In this report, we describe the presence of Mu1-hybridizing polyadenylated transcripts in roots of anaerobically induced seedlings of these same mutants. Sequence analysis of Mu1-hybridizing clones from a cDNA library of S3034 RNA indicated that these transcripts originated from the Adh1 locus and were produced by alternative processing of S3034 pre-mRNA. Approximately half of the cDNAs represented transcripts that had not undergone excision of the intron containing the 1.4-kilobase Mu1 insertion but were processed in response to signals present in the transposable element. Mu1 contains a donor splice site in the 5'-terminal inverted repeat that can be joined to the Adh1 exon 2 acceptor, resulting in removal of most of the Mu1 sequences from the pre-mRNA; alternatively this donor can be spliced to an acceptor within Mu1, removing an 89-nucleotide intron. Mu1 also contains polyadenylation signals that are used to produce truncated transcripts. These Mu1 transcripts produced by aberrant splicing and polyadenylation were not detected in RNA isolated from developing kernels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker R. F., Thompson D. V., Talbot D. R., Swanson J., Bennetzen J. L. Nucleotide sequence of the maize transposable element Mul. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):5955–5967. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.5955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Walbot V. DNA modification of a maize transposable element correlates with loss of activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1767–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V., Rivin C., Walbot V. Stable non-mutator stocks of maize have sequences homologous to the Mu1 transposable element. Genetics. 1986 Nov;114(3):1007–1021. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Oishi K. K., Kloeckener-Gruissem B., Freeling M. Organ-specific expression of maize Adh1 is altered after a Mu transposon insertion. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):469–477. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Saedler H. Molecular interactions between the components of the En-I transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Filipowicz W. The AU-rich sequences present in the introns of plant nuclear pre-mRNAs are required for splicing. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):473–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley B. A., Schuler M. A. Plant intron sequences: evidence for distinct groups of introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7159–7176. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9627–9640. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martienssen R. A., Barkan A., Freeling M., Taylor W. C. Molecular cloning of a maize gene involved in photosynthetic membrane organization that is regulated by Robertson's Mutator. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1633–1639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz D. F., Rowland L. J., Gregerson R. G., Strommer J. N. Insertion of Mu into the Shrunken 1 gene of maize affects transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of Sh1 RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00340191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raboy V., Kim H. Y., Schiefelbein J. W., Nelson-Jr O. E. Deletions in a dspm insert in a maize bronze-1 allele alter RNA processing and gene expression. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):695–703. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. J., Strommer J. N. Anaerobic treatment of maize roots affects transcription of Adh1 and transcript stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3368–3372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. J., Strommer J. N. Insertion of an unstable element in an intervening sequence of maize Adh1 affects transcription but not processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2875–2879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Dennis E. S., Gerlach W. L., Peacock W. J. Two Alleles of Maize ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE 1 Have 3' Structural and Poly(a) Addition Polymorphisms. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):449–467. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer B., Werr W., Starlinger P., Bennett D. C., Zokolica M., Freeling M. The Shrunken gene on chromosome 9 of Zea mays L is expressed in various plant tissues and encodes an anaerobic protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):461–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00338083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor L. P., Walbot V. A deletion adjacent to the maize transposable element Mu-1 accompanies loss of Adh1 expression. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):869–876. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Isolation and characterization of a 1.7-kb transposable element from a mutator line of maize. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):297–307. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R., Baran G., Varagona M. The maize transposable element Ds is spliced from RNA. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.3039661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R. Phenotypic diversity mediated by the maize transposable elements Ac and Spm. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):399–405. doi: 10.1126/science.2845581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]