Background: Dictyostelium discoideum encodes both class I and II RNRs.
Results: Both RNRs are expressed in D. discoideum, and depletion of class I RNR drastically reduces spore formation and viability.
Conclusion: Class I RNR is central for D. discoideum growth and differentiation, whereas class II function is enigmatic.
Significance: Our results underscore the evolutionary selection for this rare set of RNRs in D. discoideum.
Keywords: Development, Dictyostelium, Gene Expression, Phylogenetics, Ribonucleotide Reductase, 5′-Deoxyadenosylcobalamin, Hydroxyurea, Spore Formation
Abstract
Ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) catalyze the only pathway for de novo synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides needed for DNA replication and repair. The vast majority of eukaryotes encodes only a class I RNR, but interestingly some eukaryotes, including the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum, encode both a class I and a class II RNR. The amino acid sequence of the D. discoideum class I RNR is similar to other eukaryotic RNRs, whereas that of its class II RNR is most similar to the monomeric class II RNRs found in Lactobacillus spp. and a few other bacteria. Here we report the first study of RNRs in a eukaryotic organism that encodes class I and class II RNRs. Both classes of RNR genes were expressed in D. discoideum cells, although the class I transcripts were more abundant and strongly enriched during mid-development compared with the class II transcript. The quaternary structure, allosteric regulation, and properties of the diiron-oxo/radical cofactor of D. discoideum class I RNR are similar to those of the mammalian RNRs. Inhibition of D. discoideum class I RNR by hydroxyurea resulted in a 90% reduction in spore formation and decreased the germination viability of the surviving spores by 75%. Class II RNR could not compensate for class I inhibition during development, and an excess of vitamin B12 coenzyme, which is essential for class II activity, did not improve spore formation. We suggest that class I is the principal RNR during D. discoideum development and growth and is important for spore formation, possibly by providing dNTPs for mitochondrial replication.
Introduction
The slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum belongs to the Amoebozoa, the closest living relatives to animals and plants (1). This social amoeba lives as solitary cells that feed on bacteria and yeasts in decaying forest material (2). However, starvation triggers migration of up to 100,000 cells followed by a developmental program resulting in a differentiated multicellular structure consisting of a long stalk with a ball of spores ready to germinate when nutrients are available (2). The two major cell types in the developing organism are prestalk cells that differentiate to stalk cells, forming a cellulose-rich stalk, and prespore cells that constitute ∼80% of all cells and differentiate into spores protected from drought and other harsh conditions by a spore wall (3).
Unlike most eukaryotes D. discoideum encodes genes for more than one class of the essential enzyme ribonucleotide reductase (RNR)7 (4). RNR catalyzes the only pathway for de novo synthesis of DNA building blocks (deoxyribonucleotides or dNTPs) by reducing the 2′-hydroxy group of the corresponding ribonucleotides using radical chemistry (5). Three different classes of RNRs are currently known that share a common evolutionary origin but differ in radical-generating cofactors with specific oxygen dependences. The vast majority of eukaryotes encode a class I RNR, but D. discoideum encodes both a class I and a class II RNR. Class I RNRs consist of two subunits: the larger NrdA subunit contains the active site and usually two different allosteric sites, whereas the smaller NrdB subunit harbors a stable tyrosyl radical close to a diiron-oxo center. Together, NrdA and NrdB form α2β2 or larger oligomeric holoenzyme complexes (6). The tyrosyl radical can be scavenged by hydroxyurea (HU), leading to depletion of the class I RNR activity (5). Class II RNRs consist of one protein component, the NrdJ protein that requires the vitamin B12 coenzyme (5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl)) cofactor. In contrast to the oxygen-requiring class I RNR, the class II RNR activity is indifferent to oxygen. The only previously studied eukaryotic class II RNR is the Euglena gracilis NrdJ protein (7). In contrast to D. discoideum, E. gracilis encodes only a class II RNR.
RNRs provide a balanced dNTP supply via sophisticated allosteric regulations. Nucleoside triphosphates bound at the allosteric specificity site of RNRs determine which ribonucleotide will be reduced at a given time: ATP and dATP stimulate the reduction of cytidine and uridine nucleotides, dTTP stimulates guanosine nucleotide reduction, and dGTP stimulates adenosine nucleotide reduction. Balanced dNTP pools are crucial for cells, and abnormal pools result in increased mutational rates with downstream negative effects (8–10). Many class I RNRs have a second allosteric site called the overall activity site that regulates the total pool of dNTPs by shutting down enzyme activity in the presence of high dATP levels.
Here we report the first study of a eukaryotic organism that encodes both a class I and a class II RNR. We have cloned, expressed, purified, and characterized the D. discoideum class I RNR. We show that class I RNR mRNAs are present in growing cells and that class I RNR transcripts and proteins are highly induced in the tight aggregate stage during development. Interestingly, class I RNR activity is important for spore formation. Furthermore, we observed class II RNR expression in growing and developing cells. Together with phylogenetic data from close relatives to D. discoideum, this indicates that class II RNRs are functional in Dictyosteliida.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
D. discoideum Growth and Development
D. discoideum cells were cultivated in HL5 medium and developed at 22 °C on nitrocellulose membranes on top of pads saturated with PDF buffer (11).
Cloning of the D. discoideum nrdA and nrdJ Genes
The 2610-nucleotide-long nrdA (see Table 1 for dictyBase gene name) open reading frame (ORF) was amplified by PCR with cDNA synthesized from RNA harvested from growing D. discoideum cells (12) as template using the DdAf and DdAr primer pair (5′-ATGATAAGTAATAGTATTAATGTAACTC-3′ and 5′-TTAACTACCACAAACTAAACAACCTTC-3′, respectively, giving an amplicon of 2613 bp). The PCR contained 1× Pfu buffer with 2 mm MgSO4 (Fermentas), 0.2 mm dNTP mixture (Fermentas), 1 μm primers, 0.5 μl of 10×-diluted cDNA, 1.25 enzymatic units of Pfu polymerase (Fermentas), and 0.05 enzymatic unit of Taq polymerase (Fermentas). The PCR was initiated by 2 min of denaturation at 95 °C followed by 25 cycles of 30 s of denaturation at 95 °C, 30 s of annealing at 50 °C, and 3 min of elongation at 60 °C, and finally a 7-min extra elongation step at 60 °C was included. The resulting PCR fragment was purified, and prior to TA cloning, the PCR fragment was incubated for 10 min at 72 °C with Taq polymerase, nucleotides, and Taq buffer to ensure the presence of A overhangs. Subsequently, the PCR fragment was cloned into a pEXP5-CT/TOPO vector (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Colonies were screened by PCR for nrdA insertion, and plasmids were extracted from positive clones using standard kits (Qiagen) and sequenced. All clones contained mutations, and the one chosen contained one silent mutation and lacked the stop codon. A correct stop codon (underlined below) was generated by site-directed mutagenesis using the QuikChange XL site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene) according to the manufacturer's instructions using primers DdAmf and DdAmr (5′-GGTTGTTTAGTTTGTGGTAGTTAAGGGTCATCATCACCATCACC-3′ and 5′-GGTGATGGTGATGATGACCCTTAACTACCACAAACTAAACAACC-3′, respectively) followed by validation by sequencing of the resulting plasmid.
TABLE 1.
List of gene names used in this work and the corresponding gene names found in dictyBase (33) and Acytostelium gene database
The names used in the current work are mainly in accordance with the ribonucleotide reductase database (RNRdb) nomenclature (34).
| Organism | Class I RNR |
Class II RNR nrdJ genes |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mdA genes |
nrdB genes |
This work | dictyBase | dictyBase ID | |||||
| This work | dictyBasea | dictyBase IDb | This work | dictyBase | dictyBase ID | ||||
| D. discoideumc | nrdA | rnrA | DDB_G0284071 | nrdB1 | rnrB-1 | DDB_G0272616 | nrdJ | ndrJ | DDB_G0292654 |
| nrdB2 | rnrB-2 | DDB_G0274021 | |||||||
| nrdB_ps | DDB_G0291764 | ||||||||
| D. purpureumd | nrdA | DPU_G0059450 | nrdB | DPU_G0058582 | nrdJ | DPU_G0070122 | |||
| P. pallidume | nrdA | rnrA | PPA_G1339772 | nrdB1 | rnrB-2 | PPA_G1430112 | nrdJ | PPA_G1287280 | |
| nrdB2 | PPL_08999 | PPA_G1345902 | |||||||
| D. fasciculatume | nrdA | DFA_G1470658 | nrdB | rnrB-2 | DFA_G1484104 | nrdJ | DFA_G1578480 | ||
| A. subglobosumf | nrdA | ADB2009733g | nrdB | ADB2009702g | nrdJ | ADB0000099g | |||
The 2274-nucleotide-long nrdJ ORF (see Table 1 for dictyBase gene name) did not contain introns and was amplified by PCR with genomic DNA derived from growing AX4 D. discoideum cells as template using the DdJf and DdJr primer pair (5′-ATGTTAACTATTAAAAGATTACTTTTAAATC-3′ and 5′-TTATAAATTATTAAGTGTTTCAGAATTATCAG-3′, respectively, giving an amplicon of 2277 bp). The PCR mixture contained 1× Taq buffer with (NH4)2SO4, 2 mm MgCl4 (Fermentas), 0.2 mm dNTP mixture (Fermentas), 1 μm primers, 0.5 μl of 10×-diluted genomic DNA, and 1.25 enzymatic units of Taq polymerase (Fermentas). The PCR program was as for nrdA but 20 cycles and a 48 °C annealing temperature were used. The PCR fragment was inserted into a pEXP5-CT/TOPO vector (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Expression and Purification of the D. discoideum NrdA, NrdB, and NrdJ Proteins
All protein expression vectors were transformed into the Rosetta-2 Escherichia coli strain (Novagen) for protein expression. Growth and protein expression were carried out in LB medium supplemented with 100 μg/ml kanamycin and 17 μg/ml chloramphenicol.
NrdA expression and extraction were essentially as for the E. coli NrdA (13) except that the NrdA expression cells were moved to 12 °C before induction with 0.5 mm isopropyl β-d-thiogalactopyranoside and grown for 48 h. After crude protein extraction, ∼20% of the NrdA protein (as judged by SDS-PAGE) was left in solution, indicating that the majority of the expressed NrdA protein was insoluble. The ammonium sulfate pellet was resuspended in 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5 and 2 mm DTT (buffer A) and loaded onto a 1-ml γ-aminohexyl-dATP-Sepharose column (Jena Biosciences) pre-equilibrated with buffer A. The column was washed with 10 ml of buffer A, 10 ml of 0.2 m KCl in buffer A, and an additional 10 ml of buffer A. Subsequently, 10 ml of 10 mm ATP (Sigma-Aldrich) in buffer A was added, and the eluate was collected followed by addition of 10 ml of 50 mm ATP in buffer A to elute the strongly bound NrdA protein. The protein-containing fractions eluted after addition of 10 and 50 mm ATP were collected into separate pools, concentrated, and washed three times in buffer A in Centricon filters with a 50,000-kDa cutoff (Millipore), and subsequently, buffer A was replaced by 0.75 m ammonium sulfate and 2 mm DTT (buffer B). Samples were chromatographed on a hydrophobic column (HiLoad 16/10 phenyl-Sepharose HP, GE Healthcare) as described previously (13) to remove remaining ATP molecules. After Centricon filter concentration (50,000-kDa cutoff; Millipore), SDS-PAGE showed a protein band corresponding to the theoretical molecular mass of 98 kDa with a purity of ∼95%.
The AX2 nrdB gene cloned in the pET3a vector (Novagen) was kindly provided by P. Gaudet (see Table 1 for dictyBase gene name; the AX2 strain ORF corresponds to the AX4 rnrB-1). Recombinant expression was induced at 0.5 A600 by addition of isopropyl β-d-thiogalactopyranoside to 0.5 mm concentration in 37 °C growing cells. Cells were harvested after 3 h, and the procedure used to extract crude protein was identical to the NrdA procedure except that DTT was excluded from all buffers, and the final streptomycin concentration was 3.3%. Approximately 80% of the NrdB protein was soluble as judged by SDS-PAGE. The ammonium sulfate pellet was dissolved in 60% buffer B (without DTT) and 40% buffer A (without DTT) and separated on a HiLoad 16/10 phenyl-Sepharose HP column (GE Healthcare). The NrdB-containing fractions were pooled, concentrated, and desalted on a Centricon filter device with a 30,000-kDa cutoff. Subsequently, the buffer was changed to 50 mm Tris, pH 7.5 and 1 m NaCl (buffer C) on a NAP25 column (GE Healthcare), and the desalted protein was further purified on a strong anion exchange column (HiLoad 16/10 Q-Sepharose HP, GE Healthcare). The resulting NrdB protein was ∼90% pure, and the size corresponded to the theoretical molecular mass of 39 kDa.
The NrdJ protein was also recombinantly expressed to high levels as shown on SDS-PAGE (data not shown). Despite several expression attempts between 10 and 30 °C and addition of class II RNR-specific cofactor AdoCbl all expressed NrdJ protein was insoluble.
Reconstitution of the NrdB Protein and UV-visible Absorption Spectroscopy
Reconstitution of the diiron center in NrdB protein used in activity assays was performed as described previously (14) aiming for 4× iron excess followed by desalting on a NAP5 column (GE Healthcare) to remove excess irons. A PerkinElmer Life Sciences Lambda 35 spectrophotometer was used for recording spectra at 25 °C.
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Measurements
EPR spectra were recorded with Bruker Elexsys 500 series X-band spectrometers equipped with either an Oxford ESR900 cryostat for temperatures from 10 to 50 K or a liquid nitrogen flow system for temperatures above 90 K. The double integral of the spectrum was compared with that of a frozen copper standard solution to estimate the radical concentration in the sample. First derivative EPR spectra were recorded at different microwave powers (P) and various temperatures to determine the microwave power at half-saturation (P½) for each temperature. The experimental values were fit with the function I = 1/(1 + (P/P½))b/2 where I denotes the normalized intensity of the EPR signal and b is a component relating to the type of relaxation; the b factor is 1 for a completely inhomogeneous relaxation and 3 for a completely homogeneous relaxation (15). The temperature dependence of P½ gives information about the environment of the studied radical. In NrdB proteins the prominent environment is the diiron center and its particular properties (16).
RNR Enzyme Activity Assays
The standard RNR activity assay was performed in 50-μl reactions containing 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 10 mm DTT, 20 mm magnesium acetate, 5 mm ATP, and 0.5 mm [3H]CDP (or 0.7 mm [14C]GDP in assays with dTTP as effector), 1 μm NrdB, and 0.125–0.25 μm NrdA, but conditions were varied as seen in Fig. 3. Assays were incubated at 25 °C for 10 min, and the formed dCDP was analyzed as described in Thelander et al. (17), whereas the procedure reported in Hofer et al. (18) was used for monitoring dGDP formation. Km for the CDP substrate and half-maximum activation (KL) by the ATP allosteric effector were calculated using the Michaelis-Menten equation in Prism 5 (GraphPad Software Inc.). At the least, duplicate samples were performed for all assays.
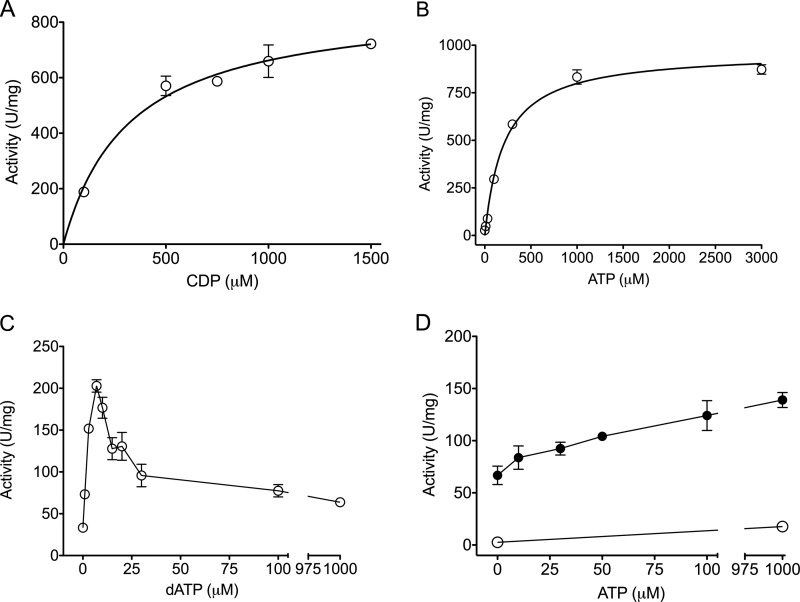
FIGURE 3.
Activity assay results showing the allosteric properties of the D. discoideum class I RNR. CDP reduction (A–C) and GDP reduction (D) are shown. A, titration of substrate CDP (100–1500 μm) in the presence of the allosteric effector ATP. B, titration of the positive effector ATP (0–3000 μm). C, titration of the inhibiting allosteric effector dATP (0–1000 μm). D, ATP titration (0–1000 μm) in the absence (○) and presence (●) of 2 mm dTTP. Mean values with error bars displaying ranges are shown. For details, see “Experimental Procedures.”
Gas-phase Electrophoretic Mobility Molecular Analysis (GEMMA)
The general procedure and instrumental setup were as described (19). In samples containing the NrdA proteins, a running buffer consisting of 100 mm ammonium acetate buffer, pH 7.5, 0.005% Tween 20, and 1 mm DTT was used, whereas the NrdB protein in the absence of NrdA was analyzed in 20 mm ammonium acetate, pH 7.5. The NrdA protein concentration was 0.04 mg/ml (0.2 μm dimeric NrdA), whereas the NrdB protein concentration was 0.02 mg/ml (0.26 μm dimeric NrdB) when mixtures of NrdA and NrdB were analyzed. All effector nucleotide concentrations used were 50 μm in combination with 50 μm Mg2+ ions. Capillary pressures of 1.6–2.0 p.s.i. were used, and data shown are the sums of two to six scans.
Northern Blot
Total RNA was extracted by the TRIzol method (Invitrogen) from growing cells (0 h) and cells developed for 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 h. The NorthernMax-Gly kit (Ambion, Applied Biosystems) was used for Northern blotting according to the instructions. 10 μg of RNA and 1.25–3.75 μg of High Range RNA ladder (Fermentas) were separated on a 0.8% agarose gel. The RNA was transferred using a vacuum blot onto Hybond-XL nylon membrane (GE Healthcare) followed by UV cross-linking of the RNA. DNA probe templates were prepared by PCR using the following primer pairs: nrdA, dNrdAf (5′-ATTGCACCAATGCCAACCGC-3′) and dNrdAr (5′-AAAGCACCACGATCAGCAGC-3′) for a 308-bp amplicon; nrdB, dNrdBf (5′-GGTTTACATTGTGATTTCGC-3′) and dNrdBr (5′-TCCTTGAATTGCAACACCAG-3′) for a 336-bp amplicon; nrdB_ps, dNrdB2f (5′-AACACTTGCAAATCAATGGG-3′) and dNrdB2r (5′-TAGAAACATTTCGCTTCTGG-3′) for a 198-bp amplicon; nrdJ, dNrdJf (5′-GCATCAACTTAAGGATTGGTG-3′) and dNrdJr (5′-GTACTATTCTCAAAGGCTGGC-3′) for a 273-bp amplicon; and rnlA, dRnlaf (5′-CCAGTAAGGTAAGGGACTAA-3′) and dRnlar (5′-CTGCGCCTATAGTTACTACC-3′) for a 286-bp amplicon. The PCR program for the production of the probe templates was 2 min of denaturation at 95 °C followed by 28 cycles of 30 s of denaturation at 95 °C; 30 s of annealing at 56, 49, 49, and 53 °C for the nrdA, nrdB, nrdB_ps, and nrdJ primers, respectively; 45 s of elongation at 72 °C; and finally a 7-min elongation step at 72 °C. The PCR mixture consisted of 1× Taq buffer with (NH4)2SO4, 2 mm MgCl4 (Fermentas), 0.2 mm dNTP mixture (Fermentas), 1 μm primers, 0.5 μl of 10× diluted genomic DNA from axenic cells as template, and 1.25 enzymatic units of Taq polymerase (Fermentas). After purification of the PCR fragments using the PCR purification kit (Qiagen), the PCR fragments were used as template for synthesis of [α-32P]dATP-labeled DNA probes using the HexaLabel DNA labeling kit (Fermentas) according to the instructions but with 25 ng of template. Prehybridization and hybridization were conducted according to the NorthernMax kit instructions but with ULTRAhyb buffer supplemented with 2% blocking solution (Roche Applied Science), and hybridization was carried out overnight at 48 °C. The membrane was washed according to the instructions, and hybridization signals were detected by a PhosphorImager (GE Healthcare). Membrane blotted with the nrdA, nrdB, and rnlA probes was exposed for 1–3 h, and membrane blotted with nrdJ and nrdB_ps was exposed for 3 days or more.
Western Blot
D. discoideum AX4 cells were harvested by centrifugation for 5 min at 300 × g and washed twice in PBS buffer. Cells were resuspended in 1 ml of radioimmune precipitation assay buffer and incubated on ice for 20 min followed by 3 × 5 min of sonication at ice temperature. The supernatant was measured by Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad) after centrifugation for 20 min at 13,000 rpm in a table top centrifuge at 4 °C. 10 μg of protein was mixed with 2× Laemmli buffer, heated for 10 min at 95 °C, loaded for 8 or 10% SDS-PAGE together with Spectra multicolor high range ladder (Fermentas), and separated at 85–200 V. Subsequently, the proteins were blotted to Immobilon-P polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Millipore) using a wet blot apparatus (Bio-Rad). The membranes were blocked with Tris-buffered saline (TBS) buffer containing 2% bovine serum albumin for 1 h at room temperature. Polyclonal peptide antibodies against D. discoideum NrdA, NrdB, and NrdJ were ordered from GenScript, and 1:1000, 1:500, and 1:1000 concentrations were used, respectively. The primary antibodies were added to the blocking solution and incubated with gentle agitation overnight at 4 °C. Subsequently, the membranes were washed 3 × 5 min in TBS and Tween 20 (TBS-T buffer) followed by one wash in TBS and incubated with a 1:2000 dilution of goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (Dako) in TBS-T with 5% dry milk for 1 h at room temperature. Then the membrane was washed 5 × 5 min in TBS-T. For detection, the Super Signal Femto West (Thermo Scientific) reagent was used according to the instructions, and the signal was detected in a LAS-4000 detector (FujiFilm).
Development and Spore Studies
D. discoideum strain AX4 was grown and developed, and when indicated, the buffered filter pads were supplemented with 50 mm HU, 2 μg/ml AdoCbl (Sigma-Aldrich), or HU + AdoCbl. All developments were performed in duplicates and were placed in the dark at 22 °C, and photos were taken during development. After 41 h, all cells from each filter were collected in 5 ml of 20 mm KPO4, pH 6.2 and 20 mm EDTA buffer (buffer D). Cells were separated from each other by passing through a 18–21-gauge needle 10 times, and spore cells versus other cells were counted using a hemocytometer; each duplicate sample was counted at least three times. Subsequently, the suspensions were mixed 1:1 with buffer D with 0.5% Triton X-100 added and incubated for 1 h at room temperature to break all cells except spore cells. The remaining spores were counted at least three times for each sample. Spore efficiency was calculated as the percentage of cells originally transferred to the membrane that ended up as spore cells. Subsequently, 200 spores were plated in duplicates from each sample on SM plates (20) with Klebsiella bacteria. After a few days, the number of plaques (reflecting viable spores) were counted. Two independent experiments were performed as described above. Mean and S.E. were calculated for spore efficiency and viability and plotted in Fig. 7 where each result stems from six to nine data points.
FIGURE 7.
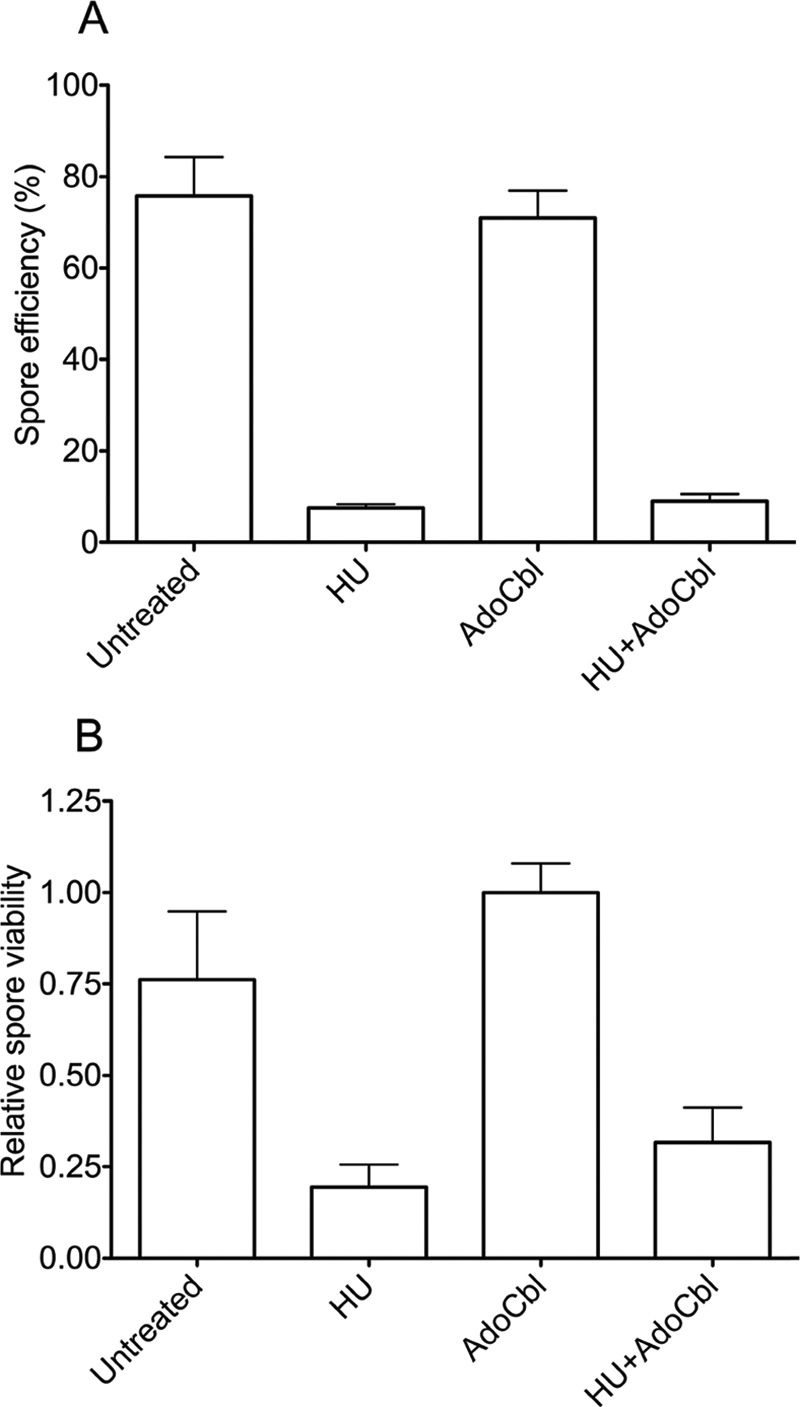
Spore characterizations. A, spore efficiency (the percentage of cells initially triggered to develop that ended up as spores). B, relative viability of the spores from the differently treated developed cells. Mean values with error bars displaying S.E. are shown. For details, see “Experimental Procedures.”
Phylogeny Estimation
Sequences were aligned with Probcons (21) and analyzed with Zorro (22). Positions with a Zorro score greater than or equal to 6 were kept for phylogenetic estimation, which was performed with FastTree (23) using the WAG substitution model (24) and Shimodaira-Hasegawa branch support (25).
RESULTS
The Genome of D. discoideum Encodes Both Class I and Class II RNRs
Four class I RNR genes (nrdA, nrdB1, nrdB2, and the pseudogene nrdB_ps) and one class II RNR gene (nrdJ) are present in the sequenced D. discoideum AX4 genome (4) (see Table 1 for corresponding dictyBase sequence names). For the nrdA gene on chromosome 4, a class I large subunit NrdA protein with ≥60% amino acid identity to other eukaryotic NrdA proteins and 27% identity to E. coli NrdA is predicted. Similarly, for the nrdB1 gene on chromosome 2, a class I small subunit NrdB protein with ≥60% amino acid identity to other eukaryotic NrdB proteins and 25% identity to the corresponding E. coli protein is predicted. Due to a recent duplication on chromosome 2, there is an identical second nrdB gene copy in the sequenced AX4 strain (here called nrdB2). In contrast, for the nrdB_ps gene on chromosome 6, a protein with 50 extra N-terminal residues compared with NrdB, lacking 120 C-terminal residues including the region essential for interaction with the NrdA protein, and lacking four of the six crucial metal-ligating side chains and three of the four side chains involved in radical transfer is predicted. Together, this suggests that the nrdB_ps gene does not code for a functional RNR component. Phylogenies estimated from the class I RNR protein sequences are consistent with established eukaryotic supergroups, placing Dictyostelium spp. sequences among other Amoebozoa (26).
For the nrdJ gene on chromosome 6, a class II RNR NrdJ protein that is ≥50% identical to the relatively few known eukaryotic NrdJs is predicted. The D. discoideum NrdJ protein sequence could be modeled to the known three-dimensional structure of the Lactobacillus leichmannii monomeric NrdJ protein (33% identical residues) but not to the structure of the Thermotoga maritima dimeric NrdJ protein (28% identical residues), suggesting that the D. discoideum NrdJ protein is of the monomeric NrdJ subtype (data not shown). In contrast to the class I RNR, the phylogeny of the eukaryotic monomeric class II RNRs indicates horizontal gene transfer of monomeric RNR class II genes from bacteria on at least two occasions followed by horizontal gene transfer among representatives from different eukaryotic supergroups (Fig. 1). The clan containing Dictyostelium spp. proteins also contains the distantly related Stramenopiles as well as the excavates E. gracilis and Naegleria gruberi plus the more closely related ophistokont Capsaspora owczarzaki. Relatively nearby in the class II protein phylogeny, although forming a well supported clan of their own, lie the sequences from green algae (Viridiplantae) as well as the ophistokonts Salpingoeca and Monosiga brevicollis that are quite closely related to Dictyostelium spp. and C. owczarzaki. The latter clan also contains bacterial and viral sequences, hinting at a possible source as well as vector for the transfer.
FIGURE 1.
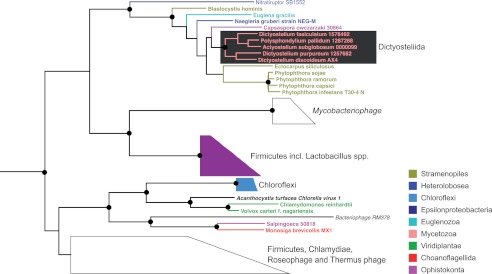
Maximum likelihood phylogeny of eukaryotic class II RNR proteins. Nodes with black circles have more than 0.9 Shimodaira-Hasegawa support (25). The tree was rooted and colored similarly to Fig 7 in Ref. 26.
Using D. discoideum RNA and DNA, we cloned the nrdA and nrdJ genes, whereas the expression derivative of the nrdB was a generous gift from P. Gaudet. Following heterologous expression in E. coli, the NrdA protein was highly expressed and isolated at ∼95% purity, whereas the NrdB protein was isolated at ∼90% purity. In contrast, no soluble NrdJ protein was obtained despite expression attempts at different temperatures and in the absence or presence of the cofactor AdoCbl.
Characterization of the D. discoideum Class I RNR
The active form of a class I RNR consists of a complex between the NrdA and NrdB components. The D. discoideum NrdA protein could be used as isolated to form the holoenzyme. In contrast, the NrdB protein was isolated as an apoprotein and needed reactivation to acquire the diiron-oxo/tyrosyl radical cofactor. The activated D. discoideum NrdB showed a typical UV-visible spectrum with diiron-oxo absorption bands at 330 and 370 nm and tyrosyl radical absorption bands at 396 and 416 nm (Fig. 2A) very similar to those in the corresponding mammalian NrdB cofactor (27). Likewise, the EPR spectrum of the tyrosyl radical showed that the D. discoideum NrdB radical is similar to that of the mammalian radical (Fig. 2B). It displays well resolved hyperfine couplings from the ring protons 3 and 5 of the tyrosyl ring at temperatures up to ∼35 K. At higher temperatures, the resolution and amplitude decrease as the signal becomes broader in a manner very similar to that of the mammalian tyrosyl radical. At 100 K, the signal is considerably broadened due to interaction with the fast relaxation of the diiron site, and no hyperfine structure is resolved (Fig. 2B). Analysis of the saturation behavior of the D. discoideum tyrosyl radical at different temperatures (data not shown; see “Experimental Procedures”) groups it together with that of mammalian NrdB and shows that it is different from the tyrosyl radical in E. coli NrdB and tyrosyl radicals produced by light irradiation (16, 28). This reflects the strong interaction between the tyrosyl radical and the diiron site in both D. discoideum (see Fig. 2B) and mouse NrdB proteins (16). From the EPR signal, we calculated a content of 0.8 radical per NrdB dimer, suggesting that the NrdB protein had been properly reactivated.
FIGURE 2.
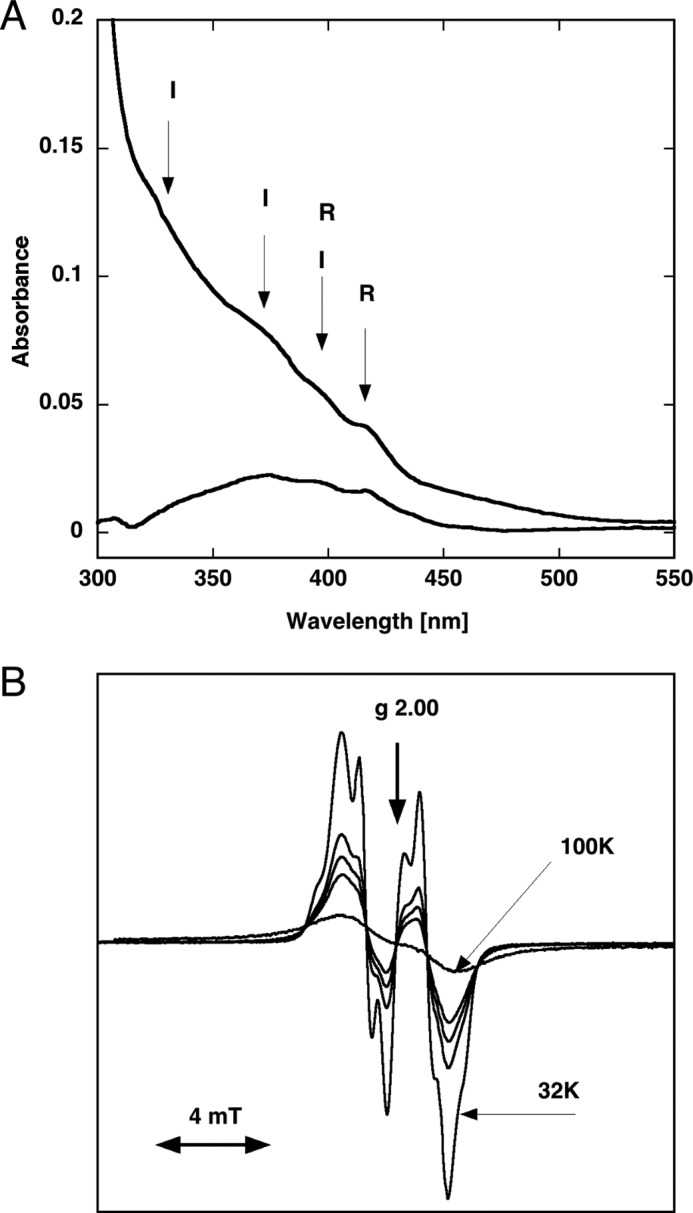
Spectroscopic analyses of D. discoideum NrdB protein. A, UV-visible spectra of 13 μm (dimer) iron-reconstituted D. discoideum NrdB protein. Absorption peaks from the tyrosyl radical (R) and the iron center (I) plus combined absorption from the radical and iron center (R + I) are indicated. A spectrum of NrdB protein lacking radical was subtracted from the radical-containing protein spectrum, giving the lower spectrum mainly from the tyrosyl radical. B, first derivative X-band EPR spectra of the reconstituted D. discoideum NrdB protein. Spectra were recorded at unsaturating conditions (2-milliwatt microwave power) at the following temperatures: 32.5 K, which displays well resolved hyperfine splittings, and 48, 53, 59, and 100 K. The 32.5 and 100 K spectra are indicated; the 48, 53, and 59 K spectra have increasing broadening and follow in order between these two. The 100 K spectrum is severely broadened due to interactions with the diiron center. mT, millitesla.
The enzymatic activity of the recombinant D. discoideum NrdA and NrdB proteins was characterized in vitro with CDP or GDP as substrate using the standard RNR activity assays (17, 18). Addition of Fe3+ in the assay had no effect, indicating that the regenerated NrdB cofactor kept its diiron site during the course of the assay. The Km for the CDP substrate was determined to 322 ± 66 μm in presence of the positive effector ATP (see Fig. 3A and “Experimental Procedures”), and the KL for the positive effector ATP was determined to be 209 ± 26 μm in the presence of CDP (Fig. 3B). The highest activity (884 units/mg of NrdA) was achieved between pH 7.2 and 7.8 in the presence of 10 mm reducing agent DTT and saturating concentrations of substrate and positive allosteric effector and is to our knowledge the highest reported enzyme activity for a eukaryotic RNR. Similar to other class I RNRs, the D. discoideum enzyme showed an initial activation by dATP with a maximum at 7 μm dATP when the effector presumably binds to the allosteric specificity site (Fig. 3C). Likewise, higher concentrations of dATP mediated increasing inhibition, indicating that dATP also binds to a functional allosteric overall activity site. GDP reduction was stimulated by dTTP (Fig. 3D). When the dTTP concentration (2 mm) was high enough to saturate the specificity site, addition of ATP, which binds to the allosteric activity site, increased enzyme activity up to 2-fold, whereas ATP alone had very little effect on GDP reduction (Fig. 3D).
Using GEMMA, we studied the oligomeric forms of the D. discoideum class I RNR in the absence and presence of nucleotides. In the absence of effector, both the NrdA protein (α2; theoretical molecular mass,196 kDa) and the NrdB protein (β2; theoretical molecular mass, 79 kDa) appeared as homodimers (Fig. 4A, traces A and B). Addition of effector dTTP that only binds to the allosteric specificity site had no effect on the NrdA oligomeric states (Fig. 4A, trace C). In contrast, a non-saturating concentration of ATP (50 μm) (Fig. 4A, trace D) and especially a saturating concentration of dATP (50 μm) (Fig. 4A, trace E), both binding to the allosteric overall activity site in addition to the specificity site, induced near complete transformation into NrdA hexamers (α6; theoretical molecular mass, 588 kDa). When NrdA and NrdB were mixed, a high degree of α2β2 complex (theoretical molecular mass, 275 kDa) assembled even in the absence of allosteric effector (Fig. 4B, trace A). Addition of 50 μm dTTP did not alter the complex composition (Fig. 4B, trace B), whereas ATP and dATP instead gave almost complete formation of α6β2 complexes (theoretical molecular mass, 667 kDa) (Fig. 4B, traces C and D). These findings are similar to previous results for the mammalian RNR (29) with a few exceptions. The mammalian NrdA protein is monomeric in the absence of effector and needs dTTP to dimerize (29). Also, formation of mammalian NrdA α6 and NrdA + NrdB α6β2 complexes are less efficient compared with those of D. discoideum even at higher protein concentrations. Thus, the D. discoideum class Ia complexes seem generally tighter and less effector-dependent. All in all, our biochemical characterization of the D. discoideum class I RNR shows that it generally behaves as a typical eukaryotic RNR.
FIGURE 4.
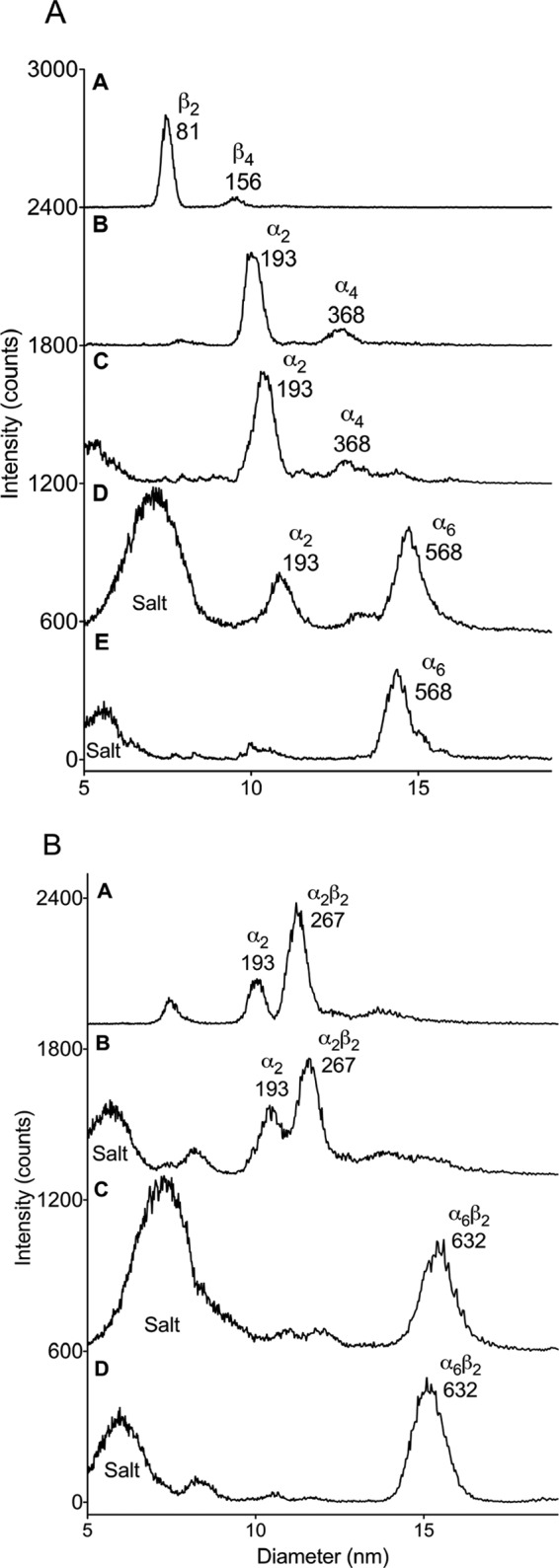
GEMMA data of the separate D. discoideum NrdA and NrdB proteins (A) and NrdA and NrdB mixtures (B) with and without allosteric effectors. The indicated numbers show experimental molecular masses in kDa. The NrdA concentration was 0.04 mg/ml, the NrdB concentration was 0.02 mg/ml, and all effector concentrations were 50 μm in combination with 50 μm Mg2+ ions. The base lines have been shifted by 600–700 intensity counts for each trace. A, NrdB (trace A), NrdA (trace B), NrdA + dTTP (trace C), NrdA + ATP (trace D), and NrdA + dATP (trace E). B, NrdA + NrdB (trace A), NrdA + NrdB + dTTP (trace B), NrdA + NrdB + ATP (trace C), and NrdA + NrdB + dATP (trace D).
RNR mRNA and Protein Expression
We used Northern blot analysis to study the mRNA levels from the nrd genes in non-synchronized growing cells (0 h) and during development (4–24 h). The class I RNR nrdA mRNA was most abundant during development. A clear accumulation was evident, starting at 8 h and peaking at 12 and 16 h into development with severalfold higher levels of mRNA than in growing cells and early (4 h) into development (Fig. 5A). A similar pattern was seen for the class I RNR nrdB mRNA. As expected, the proposed non-functional nrdB_ps mRNA was not detected as indicated by both the lack of a Northern blot signal and the lack of nrdB_ps DNA amplification from cDNA (data not shown). The class II RNR nrdJ mRNA showed highest abundance in growing cells (0 h) and at 12 and 16 h (Fig. 5A), but the Northern blot analysis of nrdJ required a much longer exposure time compared with the nrdA and nrdB analyses (see “Experimental Procedures”). In addition, we confirmed the presence of nrdJ mRNA in growing cells by reverse transcription-PCR (Fig. 5B). Our expression data largely agree with RNA-seq data available via the dictyExpress database (30, 31) showing that nrdA and nrdB abundance is strongly increased during development and nrdJ mRNA is present at very low levels. Moreover, the existence of nrdA, nrdB, and nrdJ expressed sequence tags in dictyBase (32, 33) further supports that these nrd genes are active. To find out whether the nrd mRNA levels are related to the protein levels, we performed Western blots with polyclonal antibodies raised against D. discoideum NrdA, NrdB, and NrdJ peptides. Both the NrdA and NrdB protein levels increased at 8 h of development and remained constant for the next 12 h with the highest abundance of NrdA at 20 h of development (Fig. 5C). In contrast, we could not detect any NrdJ protein from the low expression of the nrdJ transcript.
FIGURE 5.
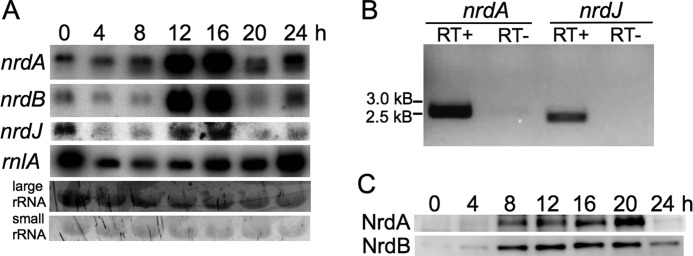
D. discoideum RNR mRNA and protein expression analyses. A, Northern blot analysis. Expression analysis of nrd genes and the mitochondrial large ribosomal RNA (rnlA) of vegetative cells (0 h) and during different stages of D. discoideum development is shown. The two lowest rows show ethidium bromide staining of the agarose gel prior to blotting from which the presence of the large and small rRNAs show equal loading of the RNA. B, reverse transcription-PCR of D. discoideum nrdJ with nrdA. Both nrdJ and nrdA transcripts are present in cDNA prepared from axenically growing cells (RT+ lanes), whereas no specific DNA fragment was amplified from the negative control template when reverse transcriptase was excluded (RT−). Gene-specific primers amplifying the full-length genes were used for comparison. C, Western blot analysis on protein extracts from different developmental stages.
Class I RNR Inhibitor HU Restricts Spore Formation
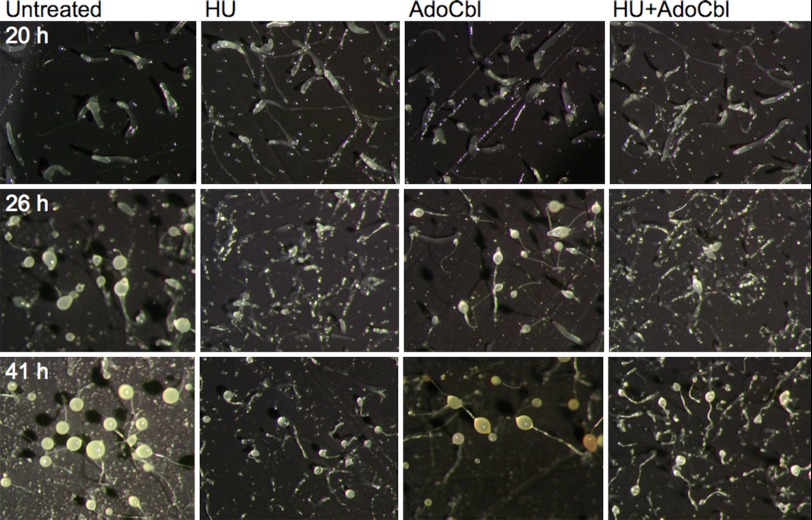
We next investigated the function of the D. discoideum RNRs during development. The cells were depleted of nutrients and developed in the presence of the specific RNR class I inhibitor HU and/or the essential class II RNR cofactor AdoCbl and compared with untreated cells. We speculated that an HU-specific phenotype rescued by AdoCbl would indicate that the class II RNR could compensate for the function of the class I RNR. As AdoCbl is light-sensitive, the D. discoideum cells were placed in the dark during development, and a somewhat slower development due to the lack of light was observed. Obvious differences between the various treated cells were seen at the slug stage and onward (Fig. 6). At 20 h from the onset of development, the HU-treated slugs were thinner and left more slime trails during migration (Fig. 6). The AdoCbl-treated cells were similar to the untreated cells. At 26 h, fewer sori (balls of spores) had formed in the HU ± AdoCbl-treated cells compared with cells developed in the absence of HU (Fig. 6), a persisting trend in fully developed cells (41 h; Fig. 6) where we also noted that the sori of the HU-treated cells generally were more transparent and smaller in size. After 41 h, the developed cells were harvested, and the ratio between spores and non-spore cells was calculated. Untreated and AdoCbl-treated cells had normal ratios of spores (83 ± 3 and 80 ± 4%, respectively). In contrast, the HU- and HU + AdoCbl-treated cells had much lower fractions of spores (9 ± 2 and 9 ± 4%, respectively), supporting the observed phenotypes and indicating that AdoCbl did not influence the HU-induced spore deficiency. To check whether these cells were true spores, the harvested cells were detergent-treated to break all non-spore cells. The results confirmed that about 10 times fewer spores had been formed in the HU-treated cells, a defect that AdoCbl could not rescue (Fig. 7A). In addition, we studied the germination viability of the spores by plating out equal numbers of spores from all treatments on plates with Klebsiella bacteria. Not only did HU treatment result in drastically fewer spores, the HU treatment also clearly decreased the viability of the few spores that were formed (Fig. 7B).
FIGURE 6.
D. discoideum cells treated with 50 mm class I RNR inhibitor HU, 1. 3 mm (2 mg/ml) class II RNR essential cofactor AdoCbl, and the combination of HU + AdoCbl and untreated cells during development. All pictures were taken with 2× magnification with conserved equal scale.
DISCUSSION
The social amoeba D. discoideum encodes genes for the common class I RNR found in almost all eukaryotes but also encodes a class II RNR gene only found in a few eukaryotes (4, 7, 26, 34). We have shown that the properties of D. discoideum class I RNR are similar to those of mammalian class I RNR as suggested by previous phylogenetic analysis (26). The tyrosyl radical cofactor in the NrdB protein has properties similar to those of the mammalian tyrosyl radical, and the allosteric regulation of D. discoideum class I RNR shares many characteristics with that of mammalian RNRs. For example, the combined ATP + dTTP activation observed for D. discoideum RNR has previously only been shown for the mammalian RNR (29, 35). Furthermore, α6β2 complexes of D. discoideum RNR were formed both in the presence of the activating effector ATP and in the presence of the inhibiting effector dATP in line with previous mammalian GEMMA data (29) and the recently published low resolution Saccharomyces cerevisiae α6 crystal structure and electron microscopy α6ββ′ structures (36). Our D. discoideum results strengthen the notion that the eukaryotic class I RNR allosteric regulation is different from that of the bacterial E. coli class Ia RNR where the ATP + dTTP combination is inhibitory and all active complexes have an α2β2 composition (19, 37, 38). To our knowledge, the D. discoideum class I RNR has the highest observed in vitro activity of investigated eukaryotic RNRs (39–41), and the GEMMA results indicate that unusually strong polypeptide complexes are formed.
The D. discoideum class II RNR is of the monomeric subtype exemplified by the L. leichmannii NrdJ (42). Class II genes are also found in the closely related and recently sequenced genomes of Dictyostelium purpureum, Dictyostelium fasciculatum, Polysphondylium pallidum, and Acytostelium subglobosum (43, 44) (Acytostelium gene database) (Fig. 1 and Table 1). D. discoideum, D. purpureum, and A. subglobosum nrdJ expressed sequence tags speak in favor of functional NrdJ proteins (32, 33) (Acytostelium gene database). Although the eukaryotic class I RNR genes probably were horizontally transferred from bacteria after the last common ancestor of archaea and eukaryotes but prior to the last eukaryotic common ancestor, the monomeric eukaryotic class II RNR gene was suggested to be a more recent transfer from bacteria to one or two eukaryotic branches (26). The recent completion of genome sequences from C. owczarzaki, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and Salpingoeca strengthens this hypothesis and also suggests another more recent transfer between eukaryotes (see positioning of C. owczarzaki NrdJ in Fig. 1). Unfortunately, we were not able to express soluble D. discoideum class II RNR protein, but its properties are likely similar to those of the previously studied E. gracilis NrdJ protein based on sequence conservation (7). Interestingly, both E. gracilis and Blastocystis hominis appear to lack class I RNR genes, suggesting that the NrdJ is physiologically functional in these organisms. Taken together, our finding that the nrdJ gene in D. discoideum is expressed and its presence in RNA-seq and expressed sequence tag data (30–33, 45) speak in favor of a functional role also for the D. discoideum NrdJ.
To better understand the functions of the two RNR classes in D. discoideum, we analyzed the expression during development. The class I RNR mRNAs and proteins were expressed simultaneously, and the highest class I RNR expression was found in the tight aggregation stage, the stage at which differentiation of cells into prestalk and prespore cells takes off. In contrast, the class II RNR gene was only weakly expressed, and no concomitant protein expression could be detected. Our nrdB gene expression data are supported by a previous study that in addition showed the prespore cell location of the NrdB protein (46). We confirmed the important role of class I RNR in prespore cells by developing cells in the presence of the class I RNR inhibitor HU, which drastically decreased spore formation and reduced the viability of the 10% surviving spores by 75%. The γ-proteobacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes three classes of RNRs, and it has been shown that including the class II RNR essential cofactor AdoCbl could rescue HU-induced growth inhibition in this pathogen (28, 47, 48). In contrast, addition of AdoCbl to D. discoideum did not rescue the spore deficiency of HU-treated developing cells.
Why would D. discoideum promote high expression of an RNR enzyme providing DNA precursors during spore formation? DNA synthesis is known to occur in prespore cells during development, but it is still debated whether the DNA synthesis stems from S phase nuclear chromosomal DNA replication or mitochondrial DNA replication. Mitotic cell division has been claimed in several studies (49–52), whereas exclusive mitochondrial spore cell DNA synthesis was found in other studies (53, 54). Interestingly, inhibition of mitochondrial DNA replication (55) or respiration (56) leads to defective or depleted fruiting body formation, a phenotype similar to the phenotype we observed upon class I RNR inhibition. Thus, the spore formation deficiency in class I RNR-inhibited cells could be the result of dNTP pool depletion affecting primarily mitochondrial DNA replication. Furthermore, the observed increased levels of the large mitochondrial rRNA (rnlA) a few hours after the induction of class I RNR transcripts (Fig. 5A) might also favor the importance of increased mitochondrial activity during development.
The role of the class II RNR in D. discoideum is enigmatic. Eukaryotes do not synthesize the vitamin B12 coenzyme AdoCbl (57) essential for function of class II RNRs but have to rely on external sources. D. discoideum in addition encodes two other AdoCbl-dependent enzymes, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and methionine synthase (58), and likely can acquire AdoCbl from phagocytosed bacteria that synthesize the vitamin B12 coenzyme. Perhaps the tolerance to hypoxia is a valuable class II RNR feature in D. discoideum when growth conditions with high nutrient but low oxygen levels are encountered. There is evidence for an oxygen-sensing mechanism in D. discoideum (59) as the oxygen level controls the expression of two cytochrome c oxidase isoforms. Clearly, selection for class II RNR function exists as the class II RNR is expressed in D. discoideum, D. purpureum, and A. subglobosum, and the gene is present in the genomes of several closely related organisms.
Acknowledgments
We thank Pascale Gaudet and Adrian Tsang for the kind gift of the plasmid used to produce NrdB protein and Anders Hofer for kind support with the GEMMA.
This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council (to B. M. S. and F. S.), the Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning (the Swedish Research Council Formas) (to F. S.), and the European Community (Function of Small RNAs across Kingdoms (FOSRAK) Grant EC005120) (to F. S.).
- RNR
- ribonucleotide reductase
- AdoCbl
- 5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin
- GEMMA
- gas-phase electrophoretic mobility molecular analysis
- HU
- hydroxyurea.
REFERENCES
- 1. Paps J., Medina-Chacón L. A., Marshall W., Suga H., Ruiz-Trillo I. (2013) Molecular phylogeny of unikonts: new insights into the position of Apusomonads and Ancyromonads and the internal relationships of Opisthokonts. Protist 164, 2–12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kessin R. H. (2001) Dictyostelium: Evolution, Cell Biology, and the Development of Multicellularity, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK [Google Scholar]
- 3. Srinivasan S., Alexander H., Alexander S. (2000) Crossing the finish line of development: regulated secretion of Dictyostelium proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 215–219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Eichinger L., Pachebat J. A., Glöckner G., Rajandream M. A., Sucgang R., Berriman M., Song J., Olsen R., Szafranski K., Xu Q., Tunggal B., Kummerfeld S., Madera M., Konfortov B. A., Rivero F., Bankier A. T., Lehmann R., Hamlin N., Davies R., Gaudet P., Fey P., Pilcher K., Chen G., Saunders D., Sodergren E., Davis P., Kerhornou A., Nie X., Hall N., Anjard C., Hemphill L., Bason N., Farbrother P., Desany B., Just E., Morio T., Rost R., Churcher C., Cooper J., Haydock S., van Driessche N., Cronin A., Goodhead I., Muzny D., Mourier T., Pain A., Lu M., Harper D., Lindsay R., Hauser H., James K., Quiles M., Madan Babu M., Saito T., Buchrieser C., Wardroper A., Felder M., Thangavelu M., Johnson D., Knights A., Loulseged H., Mungall K., Oliver K., Price C., Quail M. A., Urushihara H., Hernandez J., Rabbinowitsch E., Steffen D., Sanders M., Ma J., Kohara Y., Sharp S., Simmonds M., Spiegler S., Tivey A., Sugano S., White B., Walker D., Woodward J., Winckler T., Tanaka Y., Shaulsky G., Schleicher M., Weinstock G., Rosenthal A., Cox E. C., Chisholm R. L., Gibbs R., Loomis W. F., Platzer M., Kay R. R., Williams J., Dear P. H., Noegel A. A., Barrell B., Kuspa A. (2005) The genome of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 435, 43–57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Nordlund P., Reichard P. (2006) Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75, 681–706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hofer A., Crona M., Logan D. T., Sjöberg B. M. (2012) DNA building blocks: keeping control of manufacture. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 47, 50–63 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Torrents E., Trevisiol C., Rotte C., Hellman U., Martin W., Reichard P. (2006) Euglena gracilis ribonucleotide reductase: the eukaryote class II enzyme and the possible antiquity of eukaryote B12 dependence. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 5604–5611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kunz B. A., Kohalmi S. E., Kunkel T. A., Mathews C. K., McIntosh E. M., Reidy J. A. (1994) International Commission for Protection against Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens. Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate levels: a critical factor in the maintenance of genetic stability. Mutat. Res. 318, 1–64 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Mathews C. K. (2006) DNA precursor metabolism and genomic stability. FASEB J. 20, 1300–1314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kumar D., Abdulovic A. L., Viberg J., Nilsson A. K., Kunkel T. A., Chabes A. (2011) Mechanisms of mutagenesis in vivo due to imbalanced dNTP pools. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 1360–1371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Sussman M. (1987) Cultivation and synchronous morphogenesis of Dictyostelium under controlled experimental conditions. Methods Cell Biol. 28, 9–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hinas A., Larsson P., Avesson L., Kirsebom L. A., Virtanen A., Söderbom F. (2006) Identification of the major spliceosomal RNAs in Dictyostelium discoideum reveals developmentally regulated U2 variants and polyadenylated snRNAs. Eukaryot. Cell 5, 924–934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Birgander P. L., Bug S., Kasrayan A., Dahlroth S. L., Westman M., Gordon E., Sjöberg B.-M. (2005) Nucleotide-dependent formation of catalytically competent dimers from engineered monomeric ribonucleotide reductase protein R1. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 14997–15003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Atkin C. L., Thelander L., Reichard P., Lang G. (1973) Iron and free radical in ribonucleotide reductase. Exchange of iron and Mössbauer spectroscopy of the protein B2 subunit of the Escherichia coli enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 248, 7464–7472 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Sahlin M., Gräslund A., Ehrenberg A. (1986) Determination of relaxation times for a free radical from microwave saturation studies. J. Magn. Reson. 67, 135–137 [Google Scholar]
- 16. Sahlin M., Petersson L., Gräslund A., Ehrenberg A., Sjöberg B.-M., Thelander L. (1987) Magnetic interaction between the tyrosyl free radical and the antiferromagnetically coupled iron center in ribonucleotide reductase. Biochemistry 26, 5541–5548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Thelander L., Sjöberg B. R., Eriksson S. (1978) Ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase (Escherichia coli). Methods Enzymol. 51, 227–237 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Hofer A., Ekanem J. T., Thelander L. (1998) Allosteric regulation of Trypanosoma brucei ribonucleotide reductase studied in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 34098–34104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Rofougaran R., Crona M., Vodnala M., Sjöberg B. M., Hofer A. (2008) Oligomerization status directs overall activity regulation of the Escherichia coli class Ia ribonucleotide reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 35310–35318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Sussman M. (1966) in Methods in Cell Physiology (Prescott D., ed) pp. 397–410, Academic Press, New York [Google Scholar]
- 21. Do C. B., Mahabhashyam M. S., Brudno M., Batzoglou S. (2005) ProbCons: probabilistic consistency-based multiple sequence alignment. Genome Res. 15, 330–340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wu M., Chatterji S., Eisen J. A. (2012) Accounting for alignment uncertainty in phylogenomics. PLoS One 7, e30288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Price M. N., Dehal P. S., Arkin A. P. (2010) FastTree 2—approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One 5, e9490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Whelan S., Goldman N. (2001) A general empirical model of protein evolution derived from multiple protein families using a maximum-likelihood approach. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18, 691–699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Shimodaira H., Hasegawa M. (1999) Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16, 1114–1116 [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lundin D., Gribaldo S., Torrents E., Sjöberg B. M., Poole A. M. (2010) Ribonucleotide reduction—horizontal transfer of a required function spans all three domains. BMC Evol. Biol. 10, 383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Mann G. J., Gräslund A., Ochiai E., Ingemarson R., Thelander L. (1991) Purification and characterization of recombinant mouse and herpes simplex virus ribonucleotide reductase R2 subunit. Biochemistry 30, 1939–1947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Torrents E., Poplawski A., Sjöberg B. M. (2005) Two proteins mediate class II ribonucleotide reductase activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: expression and transcriptional analysis of the aerobic enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 16571–16578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Rofougaran R., Vodnala M., Hofer A. (2006) Enzymatically active mammalian ribonucleotide reductase exists primarily as an α6β2 octamer. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 27705–27711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Rot G., Parikh A., Curk T., Kuspa A., Shaulsky G., Zupan B. (2009) dictyExpress: a Dictyostelium discoideum gene expression database with an explorative data analysis web-based interface. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Parikh A., Miranda E. R., Katoh-Kurasawa M., Fuller D., Rot G., Zagar L., Curk T., Sucgang R., Chen R., Zupan B., Loomis W. F., Kuspa A., Shaulsky G. (2010) Conserved developmental transcriptomes in evolutionarily divergent species. Genome Biol. 11, R35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gaudet P., Fey P., Basu S., Bushmanova Y. A., Dodson R., Sheppard K. A., Just E. M., Kibbe W. A., Chisholm R. L. (2011) dictyBase update 2011: web 2.0 functionality and the initial steps towards a genome portal for the Amoebozoa. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, D620–D624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Kreppel L., Fey P., Gaudet P., Just E., Kibbe W. A., Chisholm R. L., Kimmel A. R. (2004) dictyBase: a new Dictyostelium discoideum genome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D332–D333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Lundin D., Torrents E., Poole A. M., Sjöberg B. M. (2009) RNRdb, a curated database of the universal enzyme family ribonucleotide reductase, reveals a high level of misannotation in sequences deposited to GenBank. BMC Genomics 10, 589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Eriksson S., Thelander L., Akerman M. (1979) Allosteric regulation of calf thymus ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase. Biochemistry 18, 2948–2952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Fairman J. W., Wijerathna S. R., Ahmad M. F., Xu H., Nakano R., Jha S., Prendergast J., Welin R. M., Flodin S., Roos A., Nordlund P., Li Z., Walz T., Dealwis C. G. (2011) Structural basis for allosteric regulation of human ribonucleotide reductase by nucleotide-induced oligomerization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 316–322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Larsson A., Reichard P. (1966) Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides. IX. Allosteric effects in the reduction of pyrimidine ribonucleotides by the ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase system of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 241, 2533–2539 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Brown N. C., Reichard P. (1969) Ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase. Formation of active and inactive complexes of proteins B1 and B2. J. Mol. Biol. 46, 25–38 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Sauge-Merle S., Falconet D., Fontecave M. (1999) An active ribonucleotide reductase from Arabidopsis thaliana cloning, expression and characterization of the large subunit. Eur. J. Biochem. 266, 62–69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Domkin V., Thelander L., Chabes A. (2002) Yeast DNA damage-inducible Rnr3 has a very low catalytic activity strongly stimulated after the formation of a cross-talking Rnr1/Rnr3 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 18574–18578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wang J., Lohman G. J., Stubbe J. (2007) Enhanced subunit interactions with gemcitabine-5′-diphosphate inhibit ribonucleotide reductases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 14324–14329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Sintchak M. D., Arjara G., Kellogg B. A., Stubbe J., Drennan C. L. (2002) The crystal structure of class II ribonucleotide reductase reveals how an allosterically regulated monomer mimics a dimer. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 293–300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Sucgang R., Kuo A., Tian X., Salerno W., Parikh A., Feasley C. L., Dalin E., Tu H., Huang E., Barry K., Lindquist E., Shapiro H., Bruce D., Schmutz J., Salamov A., Fey P., Gaudet P., Anjard C., Babu M. M., Basu S., Bushmanova Y., van der Wel H., Katoh-Kurasawa M., Dinh C., Coutinho P. M., Saito T., Elias M., Schaap P., Kay R. R., Henrissat B., Eichinger L., Rivero F., Putnam N. H., West C. M., Loomis W. F., Chisholm R. L., Shaulsky G., Strassmann J. E., Queller D. C., Kuspa A., Grigoriev I. V. (2011) Comparative genomics of the social amoebae Dictyostelium discoideum and Dictyostelium purpureum. Genome Biol. 12, R20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Heidel A. J., Lawal H. M., Felder M., Schilde C., Helps N. R., Tunggal B., Rivero F., John U., Schleicher M., Eichinger L., Platzer M., Noegel A. A., Schaap P., Glöckner G. (2011) Phylogeny-wide analysis of social amoeba genomes highlights ancient origins for complex intercellular communication. Genome Res. 21, 1882–1891 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Urushihara H., Morio T., Saito T., Kohara Y., Koriki E., Ochiai H., Maeda M., Williams J. G., Takeuchi I., Tanaka Y. (2004) Analyses of cDNAs from growth and slug stages of Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1647–1653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Tsang A., Bonfils C., Czaika G., Shtevi A., Grant C. (1996) A prespore-specific gene of Dictyostelium discoideum encodes the small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1309, 100–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Sjöberg B. M., Torrents E. (2011) Shift in ribonucleotide reductase gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa during infection. Infect. Immun. 79, 2663–2669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Lee K. M., Go J., Yoon M. Y., Park Y., Kim S. C., Yong D. E., Yoon S. S. (2012) Vitamin B12-mediated restoration of defective anaerobic growth leads to reduced biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 80, 1639–1649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Durston A. J., Vork F. (1978) The spatial pattern of DNA synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum slugs. Exp. Cell Res. 115, 454–457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Zada-Hames I. M., Ashworth J. M. (1978) The cell cycle and its relationship to development in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev. Biol. 63, 307–320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Zimmerman W., Weijer C. J. (1993) Analysis of cell cycle progression during the development of Dictyostelium and its relationship to differentiation. Dev. Biol. 160, 178–185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Muramoto T., Chubb J. R. (2008) Live imaging of the Dictyostelium cell cycle reveals widespread S phase during development, a G2 bias in spore differentiation and a premitotic checkpoint. Development 135, 1647–1657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Shaulsky G., Loomis W. F. (1995) Mitochondrial DNA replication but no nuclear DNA replication during development of Dictyostelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 5660–5663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Chen G., Shaulsky G., Kuspa A. (2004) Tissue-specific G1-phase cell-cycle arrest prior to terminal differentiation in Dictyostelium. Development 131, 2619–2630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Chida J., Yamaguchi H., Amagai A., Maeda Y. (2004) The necessity of mitochondrial genome DNA for normal development of Dictyostelium cells. J. Cell Sci. 117, 3141–3152 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Matsuyama S. I., Maeda Y. (1995) Involvement of cyanide-resistant respiration in cell-type proportioning during Dictyostelium development. Dev. Biol. 172, 182–191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Warren M. J., Raux E., Schubert H. L., Escalante-Semerena J. C. (2002) The biosynthesis of adenosylcobalamin (vitamin B12). Nat. Prod. Rep. 19, 390–412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Zhang Y., Gladyshev V. N. (2010) General trends in trace element utilization revealed by comparative genomic analyses of Co, Cu, Mo, Ni, and Se. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 3393–3405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Sandonà D., Gastaldello S., Rizzuto R., Bisson R. (1995) Expression of cytochrome c oxidase during growth and development of Dictyostelium. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 5587–5593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]