Abstract
Sphingolipids comprise a large, widespread family of complex eucaryotic-membrane constituents of poorly defined function. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is particularly suited for studies of sphingolipid function because it contains a small number of sphingolipids and is amenable to molecular genetic analysis. Moreover, it is the only eucaryote in which mutants blocked in sphingolipid biosynthesis have been isolated. Beginning with a nonreverting sphingolipid-defective strain that requires the addition of the long-chain-base component of sphingolipids to the culture medium for growth, we isolated two strains carrying secondary, suppressor mutations that permit survival in the absence of exogenous long-chain base. Remarkably, the suppressor strains made little if any sphingolipid. A study of how the suppressor gene products compensate for the lack of sphingolipids may reveal the function(s) of these membrane lipids in yeast cells.
Full text
PDF


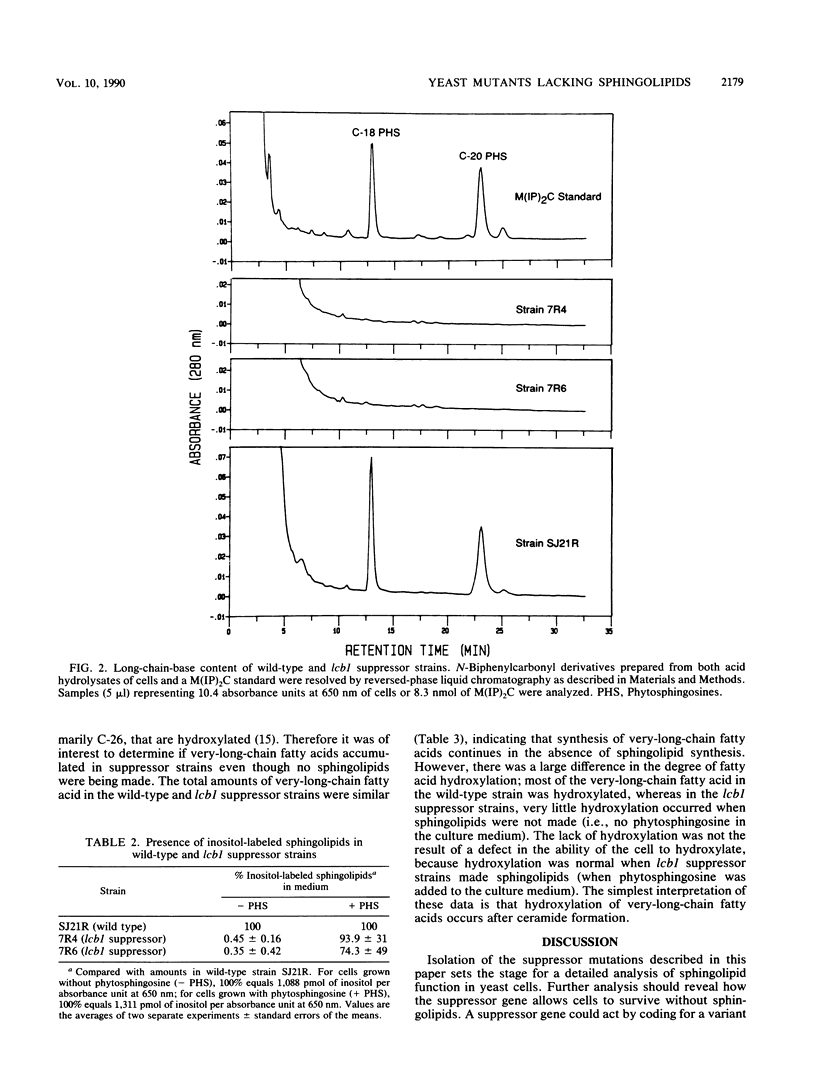
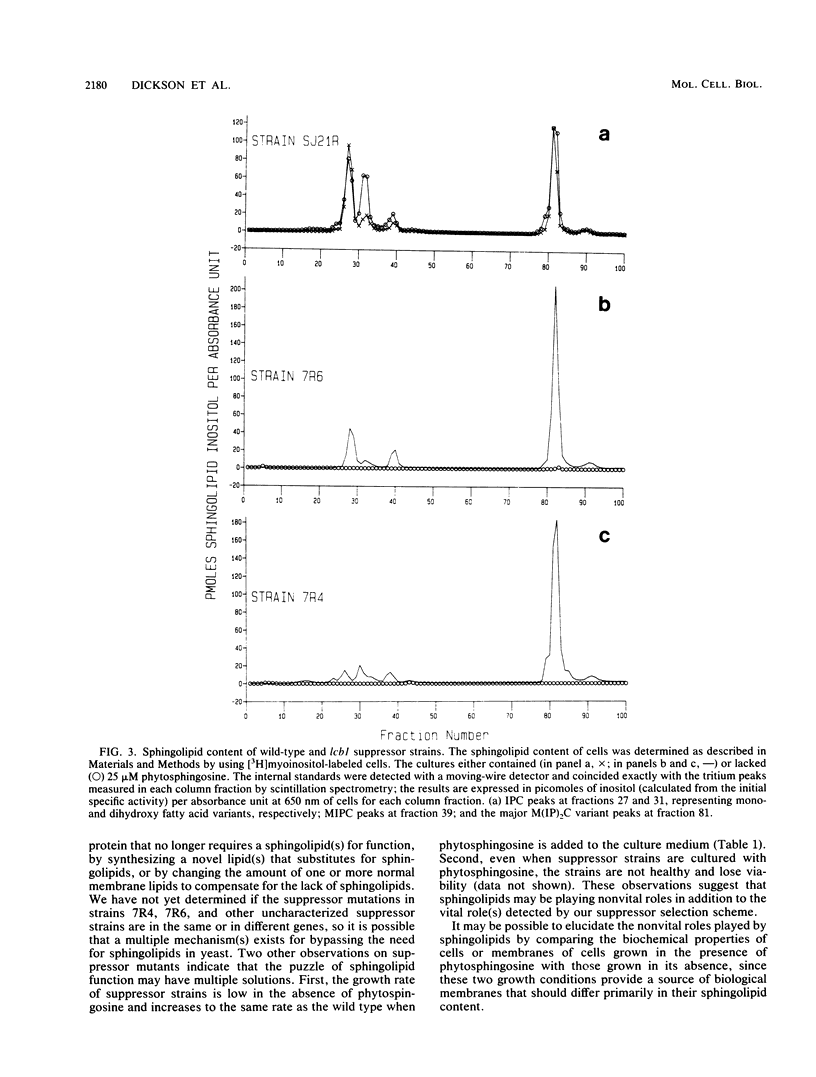

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson K. D. Two recessive suppressors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cho1 that are unlinked but fall in the same complementation group. Genetics. 1985 Sep;111(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/genetics/111.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr K., Lester R. L. Occurrence of novel antigenic phosphoinositol-containing sphingolipids in the pathogenic yeast Histoplasma capsulatum. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5581–5588. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Functions of sphingolipids and sphingolipid breakdown products in cellular regulation. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):500–507. doi: 10.1126/science.2643164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J., Botstein D. Conditional-lethal mutations that suppress genetic defects in morphogenesis by altering structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Evans J. E., Bremer E., McCluer R. H. Analysis of sphingoid bases by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1983 Oct;24(10):1380–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Animal glycosphingolipids as membrane attachment sites for bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:309–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya K., Ramesha C. S., Thompson G. A., Jr On the formation of alpha-hydroxy fatty acids. Evidence for a direct hydroxylation of nonhydroxy fatty acid-containing sphingolipids. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3548–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Koenig-Rauseo I., Hinnen A. One-step gene replacement in yeast by cotransformation. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigematsu H., Kishimoto Y. Alpha-hydroxylation of lignoceroyl-CoA by a cyanide-sensitive oxygenase in rat brain microsomes. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. W., Lester R. L. Inositol phosphorylceramide, a novel substance and the chief member of a major group of yeast sphingolipids containing a single inositol phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3395–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner S., Smith S., Waechter C. J., Lester R. L. Isolation and partial characterization of a major inositol-containing lipid in baker's yeast, mannosyl-diinositol, diphosphoryl-ceramide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells G. B., Lester R. L. The isolation and characterization of a mutant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that requires a long chain base for growth and for synthesis of phosphosphingolipids. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10200–10203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]