Abstract
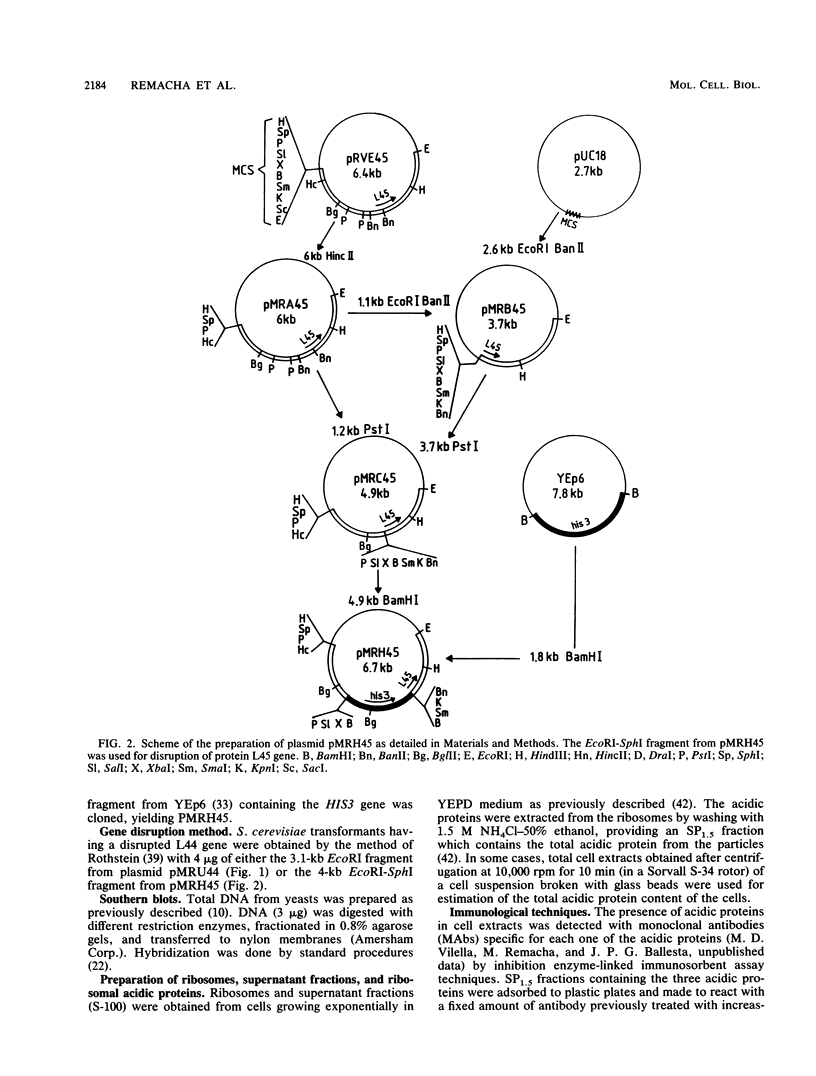
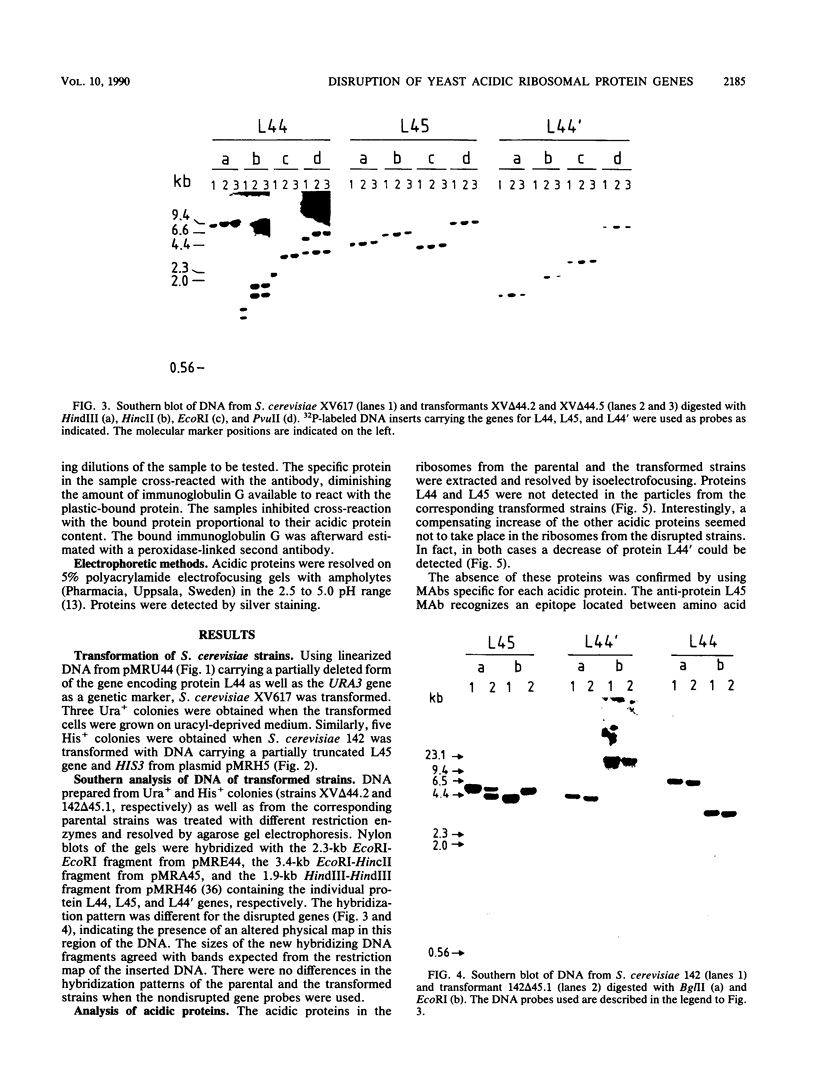
Using the cloned genes coding for the ribosomal acidic proteins L44 and L45, constructions were made which deleted part of the coding sequence and inserted a DNA fragment at that site carrying either the URA3 or HIS3 gene. By gene disruption techniques with linearized DNA from these constructions, strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae were obtained which lacked a functional gene for either protein L44 or protein L45. The disrupted genes in the transformants were characterized by Southern blots. The absence of the proteins was verified by electrofocusing and immunological techniques, but a compensating increase of the other acidic ribosomal proteins was not detected. The mutant lacking L44 grew at a rate identical to the parental strain in complex as well as in minimal medium. The L45-disrupted strain also grew well in both media but at a slower rate than the parental culture. A diploid strain was obtained by crossing both transformants, and by tetrad analysis it was shown that the double transformant lacking both genes is not viable. These results indicated that proteins L44 and L45 are independently dispensable for cell growth and that the ribosome is functional in the absence of either of them.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Gritz L., Tung L., Rosbash M. Effect of RP51 gene dosage alterations on ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3429–3435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abovich N., Rosbash M. Two genes for ribosomal protein 51 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae complement and contribute to the ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1871–1879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong I. L., Tate W. P. The requirement for the Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins L7 and L12 in release factor-dependent peptide chain termination. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 14;109(2):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. P.G., Vazquez D. Reconstitution of the 50S ribosome subunit. Role of proteins L 7 and L 12 in the GTPase activities. Site of action of thiostrepton. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 15;28(3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrame M., Bianchi M. E. Sequence of the cDNA for one acidic ribosomal protein of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9089–9089. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Koka M., Nakamoto T. Requirement of an Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal protein component for effective interaction of the ribosome with T and G factors and with guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):805–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Meeks-Wagner D. W., Fangman W. L., Botstein D. A rapid, efficient method for isolating DNA from yeast. Gene. 1986;42(2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono S., Isono K. Ribosomal protein modification in Escherichia coli. III. Studies of mutants lacking an acetylase activity specific for protein L12. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):473–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00268767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T. Primary structure of an acidic ribosomal protein YPA1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Isolation and characterization of peptides and the complete amino acid sequence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 30;671(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischa K., Möller W., Stöffler G. Reconstitution of a GTPase activity by a 50S ribosomal protein and E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio233062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruiswijk T., Planta R. J. Further analysis of the protein composition of yeast ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Witsenboer H. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Yeast contains two functional genes coding for ribosomal protein S10. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5027–5039. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Wittmann-Liebold B., McNally J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of the acidic phosphoprotein P2 from rat liver 60 S ribosomal subunits. Comparison with ribosomal 'A' proteins from other species. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9189–9197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucioli A., Presutti C., Ciafrè S., Caffarelli E., Fragapane P., Bozzoni I. Gene dosage alteration of L2 ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on ribosome synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4792–4798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Schop E. N., Brands J. H., van Hemert F. J., Lenstra J. A., Möller W. Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences for two ribosomal proteins from Artemia. The coordinate expression of genes for ribosomal proteins and elongation factor 1 during embryogenesis of Artemia. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 18;149(3):609–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacConnell W. P., Kaplan N. O. The role of ethanol extractable proteins from the 80S rat liver ribosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91517-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H. Control of ribosomal protein gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Endo Y., Yokota S., Tsurugi K. Characterization of a novel acidic protein of 38 kDa, A0, in yeast ribosomes which immunologically cross-reacts with the 13 kDa acidic ribosomal proteins, A1/A2. J Biochem. 1987 Dec;102(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Tsurugi K. Identification of A1 protein as the fourth member of 13 kDa-type acidic ribosomal protein family in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 30;161(3):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Tsurugi K. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of acidic ribosomal protein A2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3575–3575. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Woudt L. P., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Structure and organization of two linked ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7345–7358. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Slobin L. I., Amons R., Richter D. Isolation and characterization of two acidic proteins of 60s ribosomes from Artemia salina cysts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4744–4748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. H., Shimmin L. C., Yee J., Dennis P. P. A family of genes encode the multiple forms of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal proteins equivalent to the Escherichia coli L12 protein and a single form of the L10-equivalent ribosomal protein. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):579–588. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.579-588.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S., Zhang J. Y., Kay M. A., Jacobs-Lorena M. Structural analysis of the Drosophila rpA1 gene, a member of the eucaryotic 'A' type ribosomal protein family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):987–1003. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramagopal S., Subramanian A. R. Alteration in the acetylation level of ribosomal protein L12 during growth cycle of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2136–2140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
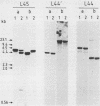
- Remacha M., Sáenz-Robles M. T., Vilella M. D., Ballesta J. P. Independent genes coding for three acidic proteins of the large ribosomal subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9094–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich B. E., Steitz J. A. Human acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins P0, P1, and P2: analysis of cDNA clones, in vitro synthesis, and assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4065–4074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
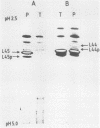
- Rotenberg M. O., Moritz M., Woolford J. L., Jr Depletion of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein L16 causes a decrease in 60S ribosomal subunits and formation of half-mer polyribosomes. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):160–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Copies of proteins L7 and L12 and heterogeneity of the large subunit of Escherichia coli ribosome. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 15;95(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Reyes R., Conde P., Ballesta J. P. Acidic ribosomal proteins from eukaryotic cells. Effect on ribosomal functions. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):409–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Effect of phosphorylation on the affinity of acidic proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar;114(3):609–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Functional role of acidic ribosomal proteins. Interchangeability of proteins from bacterial and eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3263–3266. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Collatz E., Todokoro K., Ulbrich N., Lightfoot H. N., Wool I. G. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of the 60 S ribosomal subunit proteins La, Lb, Lf, P1, P2, L13', L14, L18', L20, and L38. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):946–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidales F. J., Robles M. T., Ballesta J. P. Acidic proteins of the large ribosomal subunit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Effect of phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):390–396. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigboldus J. D. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of Drosophila rp21C, another 'A'-type ribosomal protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10064–10064. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S. P5/P5' the acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S., Warner J. R. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phosphorylated and exchangeable proteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A., Kriek J., Amons R., Möller W. Isolation and characterization of the acidic phosphoproteins of 60-S ribosomes from Artemia salina and rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):553–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]