Abstract
Objectives
To determine the impact of time between initiating highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and delivery – duration of antenatal HAART – on perinatal HIV infection.
Design
We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of pregnant HIV-infected women in Lusaka, Zambia. Women in our cohort were receiving HAART and had an infant HIV polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test between 3 and 12 weeks of life.
Methods
We examined factors associated with infant HIV infection and performed a locally weighted regression analysis to examine the effect of duration of antenatal HAART on perinatal HIV infection.
Results
From January 2007 to March 2010, 1,813 HIV-infected pregnant women met inclusion criteria. Mean gestational age at first antenatal visit was 21 weeks (standard deviation (SD)+/−6), median CD4+ cell count was 231 cells/uL (interquartile range (IQR) 164 – 329), and median duration of antenatal HAART was 13 weeks (IQR 8 – 19). 59 (3.3%) infants were HIV-infected. Duration of antenatal HAART was the most important predictor of perinatal HIV transmission. Compared to women initiating HAART at least 13 weeks prior to delivery, women on HAART for ≤ 4 weeks had a 5.2-fold increased odds of HIV transmission (95% confidence interval (CI): 2.5 –11.0). Locally weighted regression analysis suggested limited additional prophylactic benefit beyond 13 weeks on antenatal HAART.
Conclusions
Low rates of mother-to-child HIV transmission can be achieved within programmatic settings in Africa. Maximal effectiveness of prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) programs is achieved by initiating HAART at least 13 weeks prior to delivery.
Keywords: HIV, prevention of mother-to-child transmission, highly active antiretroviral therapy, pregnancy
INTRODUCTION
Of the more than 400,000 new pediatric HIV infections reported in 2008, the majority occurred in sub-Saharan Africa [1]. Maternal prophylaxis with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) has been shown to dramatically reduce the risk of mother-to-child HIV transmission even if a woman chooses to breastfeed [2–5]. Current World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines recommend that all pregnant women whose CD4+ count is < 350 cells/uL commence HAART. In resource-limited settings, identification of mothers who are candidates for HAART and/or prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission must typically be achieved within four or fewer antenatal care visits. However, the complexity of the PMTCT cascade – from identification of HIV-infected pregnant women to initiation of antiretroviral prophylaxis or treatment – often results in missed opportunities for intervention [6, 7].
For women receiving HAART during pregnancy and the breastfeeding period, maternal HIV viral load is among the most important predictors of perinatal transmission risk [8, 9]. Viral suppression is thus a central goal of antiretroviral therapy for PMTCT. Where available, HIV viral load monitoring is used to guide clinical management during pregnancy and to inform recommendations regarding mode of delivery. In sub-Saharan African settings, viral load monitoring is not commonly available as these assays are costly and require well-established laboratory infrastructure [10].
Although the common clinical practice is to start HAART in pregnancy as soon as a woman is determined to be eligible for therapy, the threshold duration of antenatal HAART required for maximal PMTCT benefit remains unclear. A European Collaborative Study showed that 93.4% (95% CI 66.0 – 99.0) of women receiving nevirapine-containing HAART achieved viral suppression by 15 weeks [11]. A subsequent study of South African women initiating HAART during pregnancy demonstrated that each additional week of treatment reduced the odds of perinatal HIV transmission by 8% [12]. These findings are similar to previously reported data from a French Perinatal Cohort in which a 6% reduction in the odds of perinatal HIV transmission was reported for each additional week of treatment with HAART during pregnancies delivered at term [13]. We report the findings of a retrospective cohort analysis in which we investigated the optimal time at which HAART should be initiated in pregnancy to maximize PMTCT effectiveness.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of pregnant HIV-infected women attending public antenatal care clinics in Lusaka, Zambia. Routine HIV screening is performed in antenatal clinics and the district’s “opt-out” HIV testing policy has resulted in over 90% of women being screened for HIV in recent years [14]. In addition, CD4+ cell counts are routinely obtained on HIV-infected pregnant women to assess eligibility for maternal HAART [15]. Pregnant women receive HAART either in HIV treatment clinics or in antenatal clinics with integrated antiretroviral treatment (ART) services. An electronic medical record system, the Zambia Electronic Perinatal Record System (ZEPRS), has been in use in Lusaka’s public antenatal care clinics since 2006 and collects comprehensive medical information on mothers and newborns up to 6 weeks of age.
Women who began HAART either prior to or during pregnancy were eligible for inclusion in this analysis. However, we restricted inclusion in the analysis to those women on HAART whose infant had been PCR tested between 3 and 12 weeks of life. In the case of multiple gestation, we restricted our analysis to the first-born child. We ascertained obstetric history, gestational age at initiation of antenatal care, results of lab tests (hemoglobin, syphilis, and CD4+ cell count), gestational age at delivery, and infant birth weight through review of ZEPRS records. Gestational age was calculated by last menstrual period for pregnancies less than 20 weeks at time of enrollment into antenatal care. For those at or over 20 weeks at enrollment, both last menstrual period and symphysis-fundal height were used. If these two methods yielded gestational ages within three weeks of each other, the date based on the last menstrual period was used. If not, the fundal height-derived gestational age was used. Dates of HAART initiation were also determined through ZEPRS review. We categorized duration on HAART as being ≤ 4 weeks, 5 – 8 weeks, 9 – 12 weeks, or ≥ 13 weeks.
Our primary outcome was infant HIV infection, assessed by PCR performed on dried blood spots using the Abbott M2000 assay (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, Illinois). We investigated predictors of mother-to-child HIV transmission in separate logistic regression models. In addition to maternal age and infant weight at delivery, variables for maternal characteristics statistically significant in univariable analyses (p ≤ 0.05) were included in a multivariable logistical regression model. In addition, we used a generalized additive model with a locally weighted regression to graphically depict the relationship between duration of antenatal HAART and HIV transmission. This analysis was restricted to women who initiated HAART during pregnancy. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.1.3 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, North Carolina). Ethical approval for this analysis of routinely collected clinical data was obtained from the University of Zambia Biomedical Research Ethics Committee (Lusaka, Zambia) and the University of Alabama at Birmingham Institutional Review Board (Birmingham, AL, USA).
RESULTS
Between January 2007 and March 2010, 4,254 live births in Lusaka district clinics were recorded among HIV-infected mothers on HAART. 1,813 mother-infant pairs had early infant diagnosis HIV PCR results documented and met inclusion criteria for this analysis. The mean age was 29 years (SD +/− 5 years) and nearly half of the women (48.4%) had completed some secondary or tertiary education. Most women in our cohort were married (93.4%) and had previously been pregnant (85.7%). The mean gestational age at first antenatal care visits was 21 weeks (SD +/− 6 weeks). The mean hemoglobin result was 11.0 g/dL (SD +/− 1.6 g/dL) and 72.6% of women had a negative syphilis screen at their first antenatal visit. Approximately half (52.8%) of the women in our cohort had a CD4+ count < 350 cells/uL at entry into antenatal care (Table 1).
Table 1.
Factors associated with mother-to-child HIV transmission
| N | Value | Mothers with infant HIV PCR results available (N = 1,813) | Mothers with HIV-negative infants (N = 1,754) | Mothers with HIV-positive infants (N = 59) | Crude OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1,813 | 29 years (SD +/− 5) | |||||
| ≤ 24 years | 327 | 315 (18.0%) | 12 (20.3%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| 25 – 29 years | 622 | 601 (34.3%) | 21 (35.6%) | 0.9 (0.5 – 1.9) | 0.9 (0.4 – 2.0) | ||
| 30 – 34 years | 560 | 540 (30.8%) | 20 (33.9%) | 1.0 (0.5 – 2.0) | 1.1 (0.5 – 2.4) | ||
| ≥ 35 years | 304 | 298 (17.0%) | 6 (10.2%) | 0.5 (0.2 – 1.4) | 0.6 (0.2 – 1.6) | ||
| Education | 1,813 | ||||||
| Secondary or tertiary | 878 | 858 (48.9%) | 20 (33.9%) | 1.0 | |||
| None or primary | 715 | 687 (39.2%) | 28 (47.5%) | 1.8 (1.0 – 3.1) | 1.8 (1.0 – 3.2) | ||
| Unknown | 220 | 209 (11.9%) | 11 (18.6%) | 2.3 (1.1 – 4.8) | 2.3 (1.1 – 5.1) | ||
| Marital status | 1,753 | ||||||
| Married/cohabiting | 1,637 | 1,585 (93.4%) | 52 (92.9%) | 1.0 | |||
| Other | 116 | 112 (6.6%) | 4 (7.1%) | 1.1 (0.4 – 3.1) | |||
| GA at 1st ANC visit | 1,813 | 21 weeks (SD +/− 6) | |||||
| ≤ 20 weeks | 605 | 584 (33.3%) | 21 (35.6%) | 1.0 | |||
| 21 – 27 weeks | 980 | 948 (54.0%) | 32 (54.2%) | 0.9 (0.5 – 1.6) | |||
| ≥ 28 weeks | 228 | 222 (12.7%) | 6 (10.2%) | 0.8 (0.3 – 1.9) | |||
| BMI | 977 | ||||||
| < 25 kg/m2 | 562 | 539 (57.6%) | 23 (56.1%) | 1.0 | |||
| 25 – 29 kg/m2 | 360 | 343 (36.6%) | 17 (41.5%) | 0.9 (0.4 – 1.9) | |||
| ≥ 30 kg/m2 | 55 | 54 (5.8%) | 1 (2.4%) | 0.4 (0.1 – 3.0) | |||
| Hemoglobin | 1,813 | 11.0 g/dL (SD +/− 1.6) | |||||
| ≥ 10.0 g/dL | 977 | 957 (54.6%) | 20 (33.9%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| 8.0 – 9.9 g/dL | 267 | 254 (14.5%) | 13 (22.0%) | 2.5 (1.2 – 5.0) | 1.7 (0.8 – 3.6) | ||
| ≤ 7.9 g/dL | 29 | 28 (1.6%) | 1 (1.7%) | 1.7 (0.2 – 13.2) | 0.8 (0.1 – 6.9) | ||
| Not done | 540 | 515 (29.4%) | 25 (42.4%) | 2.3 (1.3 – 4.2) | 2.3 (1.2 – 4.5) | ||
| Syphilis screen | 1,813 | ||||||
| RPR non-reactive | 1,316 | 1,275 (72.7%) | 41 (69.5%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| RPR reactive | 40 | 35 (2.0%) | 5 (8.5%) | 4.4 (1.7 – 11.9) | 3.8 (1.3 – 10.7) | ||
| Not done | 457 | 444 (25.3%) | 13 (22.0%) | 0.9 (0.5 – 1.7) | 0.9 (0.5 – 1.7) | ||
| CD4+ count at entry | 1,813 | 231 cells/uL (IQR 164 – 329) | |||||
| ≥ 350 cells/uL | 250 | 246 (14.0%) | 4 (6.8%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| 200–349 cells/uL | 511 | 501 (28.6%) | 10 (16.9%) | 1.2 (0.4 – 4.0) | 0.8 (0.2 – 2.6) | ||
| < 200 cells/uL | 446 | 422 (24.1%) | 24 (40.7%) | 3.5 (1.2 – 10.2) | 2.0 (0.6 – 6.3) | ||
| Not done | 606 | 585 (33.4%) | 21 (35.6%) | 2.2 (0.8 – 6.5) | 1.9 (0.6 – 5.8) | ||
| GA at delivery | 1,813 | 38 weeks (SD +/− 4) | |||||
| 37 – 41 weeks | 1,069 | 1,033 (58.9%) | 36 (61.0%) | 1.0 | |||
| < 32 weeks | 65 | 63 (3.6%) | 2 (3.4%) | 0.9 (0.2 – 3.9) | |||
| 32 – 36 weeks | 445 | 428 (24.4%) | 17 (28.8%) | 1.1 (0.6 – 2.1) | |||
| ≥ 42 weeks | 234 | 230 (13.1%) | 4 (6.8%) | 0.5 (0.2 – 1.4) | |||
| Birth weight | 1,792 | 2,900 g (SD +/− 400) | |||||
| ≥ 2,500 g | 1,568 | 1,519 (87.7%) | 49 (83.1%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| < 2,500 g | 224 | 214 (12.3%) | 10 (16.9%) | 1.5 (0.7 – 2.9) | 1.2 (0.6 – 2.5) | ||
| Duration of antenatal HAART | 1,813 | 13 weeks (IQR 8 – 19) | |||||
| ≥ 13 weeks | 1,188 | 1,161 (66.2%) | 27 (45.8%) | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| 9 – 12 weeks | 196 | 189 (10.8%) | 7 (11.9%) | 1.6 (0.7 – 3.7) | 1.8 (0.7 – 4.8) | ||
| 5–8 weeks | 242 | 234 (13.3%) | 8 (13.6%) | 1.5 (0.7 – 3.3) | 2.0 (0.8 – 5.1) | ||
| ≤ 4 weeks | 187 | 170 (9.7%) | 17 (28.8%) | 4.3 (2.3 – 8.1) | 5.5 (2.6 – 11.7) |
GA: gestational age; ANC: antenatal care; BMI: body mass index; SD: standard deviation; IQR: interquartile range; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval
59 of 1,813 (3.3%; 95% CI 2.5 – 4.2%) infants were HIV-infected at the time of their earliest PCR result (3 – 12 weeks of life). In univariable analysis, the odds of HIV transmission were elevated among women with unknown educational status (odds ratio (OR) 2.3; 95% CI 1.1 – 4.8), hemoglobin concentration ≤ 8.0 – 9.9 g/dL (OR 2.5; 95% CI 1.2 – 5.0), CD4+ cell count <200 cells/uL (OR 3.5; 95% CI 1.2 – 10.2), and those who screened positive for syphilis (OR 4.4; 95% CI 1.7 – 11.9). Additionally, the odds of mother-to-child HIV transmission was markedly elevated among women who had initiated HAART four or fewer weeks prior to delivery compared to women who had initiated HAART at least 13 weeks prior to delivery (OR 4.3; 95% CI 2.3 – 8.1).
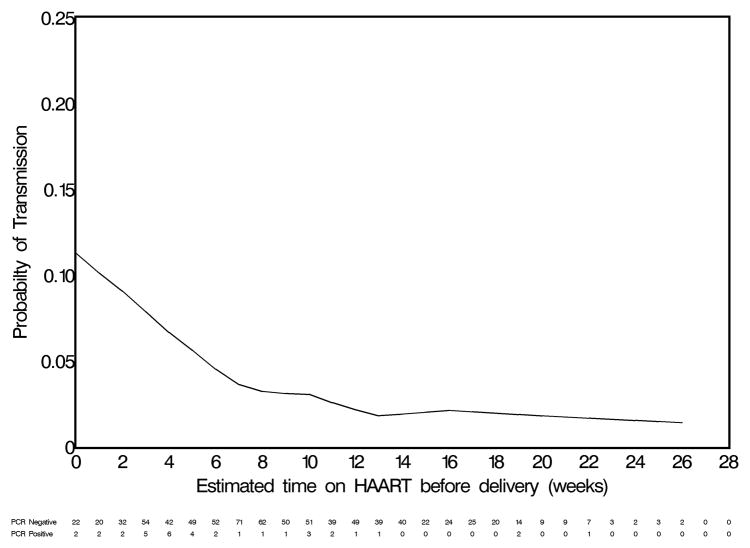
In multivariable analysis, a short duration of antenatal HAART (i.e., ≤ 4 weeks) compared to an interval of at least 13 weeks (adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 5.2; 95% CI 2.6 – 11.7) and a positive syphilis screen compared to a negative one (AOR 3.8; 95% CI 1.3 – 10.7) remained associated with higher odds of mother-to-child HIV transmission. We also observed a trend towards increased odds of mother-to-child HIV transmission among women starting HAART 5 – 8 weeks prior to delivery (AOR 2.0; 95% CI 0.8 – 5.1) and 9 – 12 weeks prior to delivery (AOR 1.8; 95% CI 0.7 – 4.8). However, this trend was not statistically significant. A locally weighted regression line generated with a generalized additive model suggested limited additional benefit beyond 13 weeks on HAART during the antenatal period (Figure 1). An exploratory analysis limited to women on HAART for fewer than 13 weeks demonstrated that for each additional week on HAART prior to delivery the odds of mother-to-child HIV transmission were reduced by 14% (OR 0.86; 95% CI 0.77 – 0.96).
Figure 1.
Locally weighted regression line depicting the association between duration of antenatal HAART and HIV transmission. (Note: This analysis is restricted to women who initiated HAART during pregnancy.)
DISCUSSION
In this cohort analysis of women on antenatal HAART, we observed an encouragingly low overall mother-to-child HIV transmission rate of 3.3% (95% CI 2.5 – 4.2%) between 3 and 12 weeks of life. The most important predictor of vertical HIV transmission in this cohort was time on HAART prior to delivery. Women who received HAART for four or fewer weeks during pregnancy had a 5.2-fold increased odds of transmitting HIV to their infants compared to women on HAART for at least 13 weeks. A positive syphilis screen during pregnancy was also found to be an independent risk factor for mother-to-child HIV transmission (AOR 3.8; 95% CI 1.3 – 10.7). This association is consistent with findings previously reported in a Malawian PMTCT study in which the risk of perinatal HIV transmission was 2 – 3 times higher among women diagnosed with syphilis [16].
The Zambia Exclusive Breastfeeding Study demonstrated that nearly 70% of HIV-infected women enrolled in antenatal care in Lusaka meet current criteria for initiation of HAART [17, 18]. In many developing country settings, women commonly present for antenatal care in the second trimester, which would allow adequate time for initiation of HAART. However, delays in CD4+ cell triage and in linking HIV-infected mothers with PMTCT and HIV treatment services commonly result in suboptimal prophylaxis and preventable perinatal HIV infections [19]. Our study highlights the importance of encouraging women to seek antenatal care early in pregnancy and instilling a sense of urgency in providers to determine eligibility for HAART and initiate treatment in a timely manner. Design and implementation of programs that support routine HIV counseling and testing (e.g., “opt-out” testing) [20, 21] and improvements in clinical and laboratory services are critically important for program success. Additional strategies to improve management of HIV-infection in pregnancy and reduce perinatal HIV transmission may include point of care CD4+ cell counts [22], integration of ART services into antenatal clinic settings, and credentialing non-physician providers (such as nurses or midwives) to prescribe HAART [23–25]. Enhancing antenatal care services, promoting prevention, screening, and treatment of preventable conditions such as syphilis and anemia could also improve women’s health and decrease perinatal HIV transmissions.
The strengths of our study include its large sample size and use of a robust electronic medical record. Our results are limited by the absence of routine ultrasonography confirming gestational age and routine data on plasma viral load, neither of which is widely available in Zambia. Where accessible, viral load monitoring may be used to guide HIV management and decisions regarding mode of delivery in order to further minimize risk of vertical HIV transmission. However, in the common circumstances where viral load monitoring is neither readily available nor affordable, pregnant women should initiate HAART at least 4 weeks prior to delivery to optimally reduce mother-to-child HIV transmission.
Our study confirms that, in the era of HAART, rates of perinatal HIV transmission below 5% can be achieved in African settings. In order to maximize PMTCT effectiveness, however, women eligible for HAART should receive at least 4 weeks – and preferably 13 weeks – of treatment prior delivery. To achieve this, PMTCT and ART services will need to be substantially improved and expanded.
Acknowledgments
FUNDING: Trainee support was provided by the National Institutes of Health through the International Clinical Research Fellows Program at Vanderbilt University (R24 TW007988) and the Vanderbilt-CIDRZ AIDS International Research and Training Program (D43 TW001035). Additional investigator salary was provided through a Clinical Scientist Development Award from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (2007061). Funding agencies played no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, or manuscript preparation.
CJC designed and interpreted the analysis, drafted the manuscript, and substantially revised it. MJG analyzed study data, interpreted the analysis, and substantially revised the manuscript. NP, NC, JM, and BJD participated in data interpretation and manuscript revision. BHC, JSAS, and EMS designed the analysis, interpreted the analysis, and substantially revised the manuscript. We thank Jessica Joseph for her assistance in preparing this manuscript.
Trainee support was provided by the National Institutes of Health through the International Clinical Research Fellows Program at Vanderbilt University (R24 TW007988) and the Vanderbilt-CIDRZ AIDS International Research and Training Program (D43 TW001035). Additional investigator salary was provided through a Clinical Scientist Development Award from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (2007061).
Footnotes
DISCLOSURE: The authors have no financial interests to disclose. Data presented in this manuscript were presented, in part, at the XVIIIth International AIDS Conference and published as abstract MOPE0261.
References
- 1.WHO. Global Summary of the HIV/AIDS Epidemic. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Palombi L, Marazzi MC, Voetberg A, Magid NA. Treatment acceleration program and the experience of the DREAM program in prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV. AIDS. 2007;21 (Suppl 4):S65–71. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000279708.09180.f5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kilewo C, Karlsson K, Ngarina M, Massawe A, Lyamuya E, Swai A, et al. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 through breastfeeding by treating mothers with triple antiretroviral therapy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: the Mitra Plus study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;52:406–416. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181b323ff. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chasela CS, Hudgens MG, Jamieson DJ, Kayira D, Hosseinipour MC, Kourtis AP, et al. Maternal or infant antiretroviral drugs to reduce HIV-1 transmission. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2271–2281. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McIntyre J. Use of antiretrovirals during pregnancy and breastfeeding in low-income and middle-income countries. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2010;5:48–53. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e328333b8ab. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mnyani CN, McIntyre JA. Preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV. BJOG. 2009;116 (Suppl 1):71–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stringer EM, Ekouevi DK, Coetzee D, Tih PM, Creek TL, Stinson K, et al. Coverage of Nevirapine-Based Services to Prevent Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission in 4 African Countries. JAMA. 2010;304:293–302. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Taha TE, Hoover DR, Kumwenda NI, Fiscus SA, Kafulafula G, Nkhoma C, et al. Late postnatal transmission of HIV-1 and associated factors. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2007;196:10–14. doi: 10.1086/518511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mmiro FA, Aizire J, Mwatha AK, Eshleman SH, Donnell D, Fowler MG, et al. Predictors of early and late mother-to-child transmission of HIV in a breastfeeding population: HIV Network for Prevention Trials 012 experience, Kampala, Uganda. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;52:32–39. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181afd352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mepham SO, Bland RM, Newell ML. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV in resource-rich and -poor settings. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology. 2011;118:202–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Patel D, Cortina-Borja M, Thorne C, Newell ML. Time to undetectable viral load after highly active antiretroviral therapy initiation among HIV-infected pregnant women. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1647–1656. doi: 10.1086/518284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hoffman RM, Black V, Technau K, van der Merwe KJ, Currier J, Coovadia A, et al. Effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy duration and regimen on risk for mother-to-child transmission of HIV in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;54:35–41. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181cf9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Warszawski J, Tubiana R, Le Chenadec J, Blanche S, Teglas JP, Dollfus C, et al. Mother-to-child HIV transmission despite antiretroviral therapy in the ANRS French Perinatal Cohort. AIDS. 2008;22:289–299. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3282f3d63c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stringer EM, Chintu NT, Levy JW, Sinkala M, Chi BH, Muyanga J, et al. Declining HIV prevalence among young pregnant women in Lusaka, Zambia. Bull World Health Organ. 2008;86:697–702. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.045260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chi BH, Chintu N, Lee A, Stringer EM, Sinkala M, Stringer JS. Expanded services for the prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission: field acceptability of a pilot program in Lusaka, Zambia. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;45:125–127. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318050d28f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mwapasa V, Rogerson SJ, Kwiek JJ, Wilson PE, Milner D, Molyneux ME, et al. Maternal syphilis infection is associated with increased risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV in Malawi. AIDS. 2006;20:1869–1877. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000244206.41500.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kuhn L, Aldrovandi GM, Sinkala M, Kankasa C, Semrau K, Mwiya M, et al. Effects of early, abrupt weaning on HIV-free survival of children in Zambia. The New England journal of medicine. 2008;359:130–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa073788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kuhn L, Aldrovandi GM, Sinkala M, Kankasa C, Mwiya M, Thea DM. Potential impact of new WHO criteria for antiretroviral treatment for prevention of mother-to- child HIV transmission. AIDS. 2010;24:1374–1377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Killam WP, Tambatamba BC, Chintu N, Rouse D, Stringer E, Bweupe M, et al. Antiretroviral therapy in antenatal care to increase treatment initiation in HIV-infected pregnant women: a stepped-wedge evaluation. AIDS. 2010;24:85–91. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833298be. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Spensley A, Sripipatana T, Turner AN, Hoblitzelle C, Robinson J, Wilfert C. Preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV in resource-limited settings: the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation experience. Am J Public Health. 2009;99:631–637. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2007.114421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bolu OO, Allread V, Creek T, Stringer E, Forna F, Bulterys M, et al. Approaches for scaling up human immunodeficiency virus testing and counseling in prevention of mother-to-child human immunodeficiency virus transmission settings in resource-limited countries. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;197:S83–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mtapuri-Zinyowera S, Chideme M, Mangwanya D, Mugurungi O, Gudukeya S, Hatzold K, et al. Evaluation of the PIMA Point-of-Care CD4 Analyzer in VCT Clinics in Zimbabwe. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;55:1–7. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181e93071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shumbusho F, van Griensven J, Lowrance D, Turate I, Weaver MA, Price J, et al. Task shifting for scale-up of HIV care: evaluation of nurse-centered antiretroviral treatment at rural health centers in Rwanda. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sanne I, Orrell C, Fox MP, Conradie F, Ive P, Zeinecker J, et al. Nurse versus doctor management of HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy (CIPRA-SA): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2010;376:33–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60894-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stringer JS, Zulu I, Levy J, Stringer EM, Mwango A, Chi BH, et al. Rapid scale-up of antiretroviral therapy at primary care sites in Zambia: feasibility and early outcomes. JAMA. 2006;296:782–793. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.7.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]