Abstract
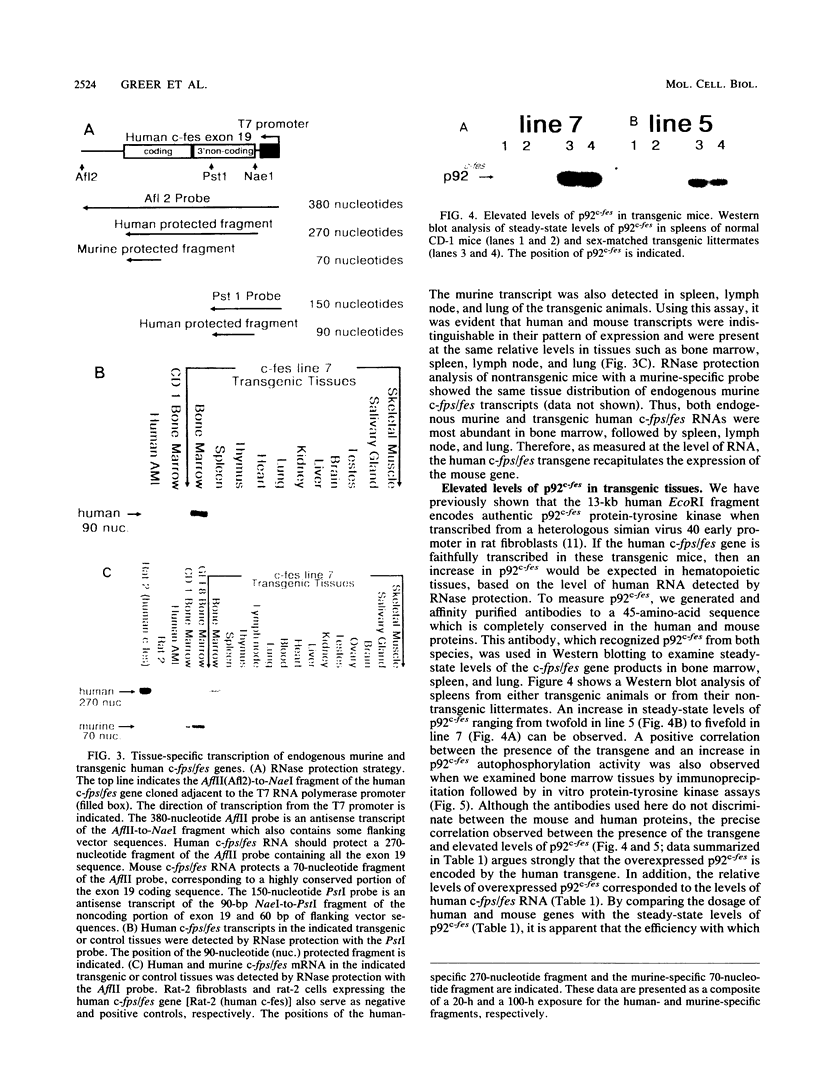
The mammalian c-fps/fes proto-oncogene encodes a 92-kilodalton cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinase (p92c-fes), which is expressed in immature and differentiated hematopoietic cells of the myeloid lineage. To determine the limits of the c-fps/fes locus and to investigate the cis-acting sequences required to direct appropriate tissue-specific expression, a 13-kilobase-pair fragment of human genomic DNA containing the entire c-fps/fes coding sequence was introduced into the mouse germ line. Transcription of the human c-fps/fes transgene was highest in bone marrow and showed a tissue distribution identical to that of the endogenous mouse gene. Macrophages cultured from transgenic mouse bone marrow contained particularly high levels of human and murine c-fps/fes RNA. Furthermore, expression of human c-fps/fes RNA induced a proportionate increase in the level of the p92c-fes protein-tyrosine kinase in bone marrow, bone marrow-derived macrophages, and spleen. Elevated levels of normal human p92c-fes had no obvious effect on mouse development or hematopoiesis. Remarkably, given the short 5'- and 3'-flanking sequences, expression of the human proto-oncogene in bone marrow was independent of integration site, was proportional to the transgene copy number, and was of comparable efficiency to that of the endogenous mouse c-fps/fes gene. The 13-kilobase-pair fragment therefore defines a genetic locus sufficient for the appropriate tissue-specific expression of the fps/fes protein-tyrosine kinase and includes a dominant cis-acting element that directs integration-independent myeloid expression in transgenic mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Gabrilove J. L., Tam J. P., Moore M. A., Hanafusa H. Specific expression of the human cellular fps/fes-encoded protein NCP92 in normal and leukemic myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Vass W. C., Tambourin P. E. Human cellular fps/fes cDNA rescued via retroviral shuttle vector encodes myeloid cell NCP92 and has transforming potential. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):441–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Takegawa S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Groudine M. Evidence for a locus activation region: the formation of developmentally stable hypersensitive sites in globin-expressing hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10159–10177. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transformation potential of the cellular fps gene. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer P. A., Meckling-Hansen K., Pawson T. The human c-fps/fes gene product expressed ectopically in rat fibroblasts is nontransforming and has restrained protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):578–587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Heisterkamp N., Grosveld F., Van de Ven W., Stephenson J. R. Isolation of human oncogene sequences (v-fes homolog) from a cosmid library. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1136–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.6281890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkemeyer M. J., Gertler F. B., Goodman W., Hoffmann F. M. The Drosophila Abelson proto-oncogene homolog: identification of mutant alleles that have pleiotropic effects late in development. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman S. A., Coffin J. M. Differential transcription from the long terminal repeats of integrated avian leukosis virus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):497–505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.497-505.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald I., Levy J., Pawson T. Expression of the mammalian c-fes protein in hematopoietic cells and identification of a distinct fes-related protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2543–2551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Pollard J. W., Stanley E. R. Isolation and characterization of a cloned growth factor dependent macrophage cell line, BAC1.2F5. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Mar;130(3):420–427. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., Schuermann M., Wagenaar E., Parren P., Weigel D., Nusse R. The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Bussemakers M. J., van Heerikhuizen H., Onnekink C., Debruyne F. M., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Characterization of human c-fes/fps reveals a new transcription unit (fur) in the immediately upstream region of the proto-oncogene. Mol Biol Rep. 1986;11(2):117–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00364823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Leunissen J. A., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Evolutionary conserved close linkage of the c-fes/fps proto-oncogene and genetic sequences encoding a receptor-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2197–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Verbeek J. S., Van den Ouweland A. M., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. The structure of the human c-fes/fps proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2897–2903. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarut J., Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa H. Preferential expression of the c-fps protein in chicken macrophages and granulocytic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter E. D., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor homolog (DER) gene is allelic to faint little ball, a locus essential for embryonic development. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1093–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90642-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., deKernion J. B., Verma I. M., Cline M. J. Expression of cellular oncogenes in human malignancies. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):256–262. doi: 10.1126/science.6538699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Kurban R. R. Isolation and structural analysis of murine c-fes cDNA clones. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wotton D., Flanagan B. F., Owen M. J. Chromatin configuration of the human CD2 gene locus during T-cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Mock D., Greer P., Maltby V., Rossant J., Bernstein A., Pawson T. Lymphoid and mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice expressing the v-fps protein-tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5491–5499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








