Abstract
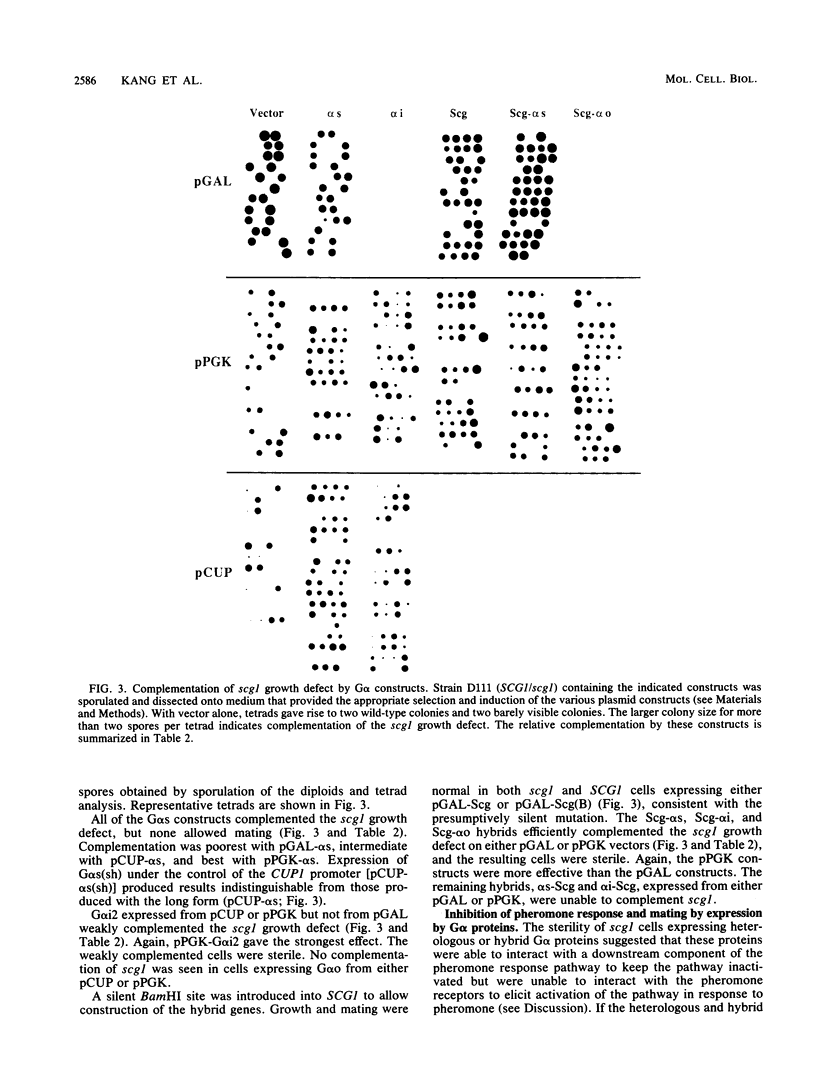
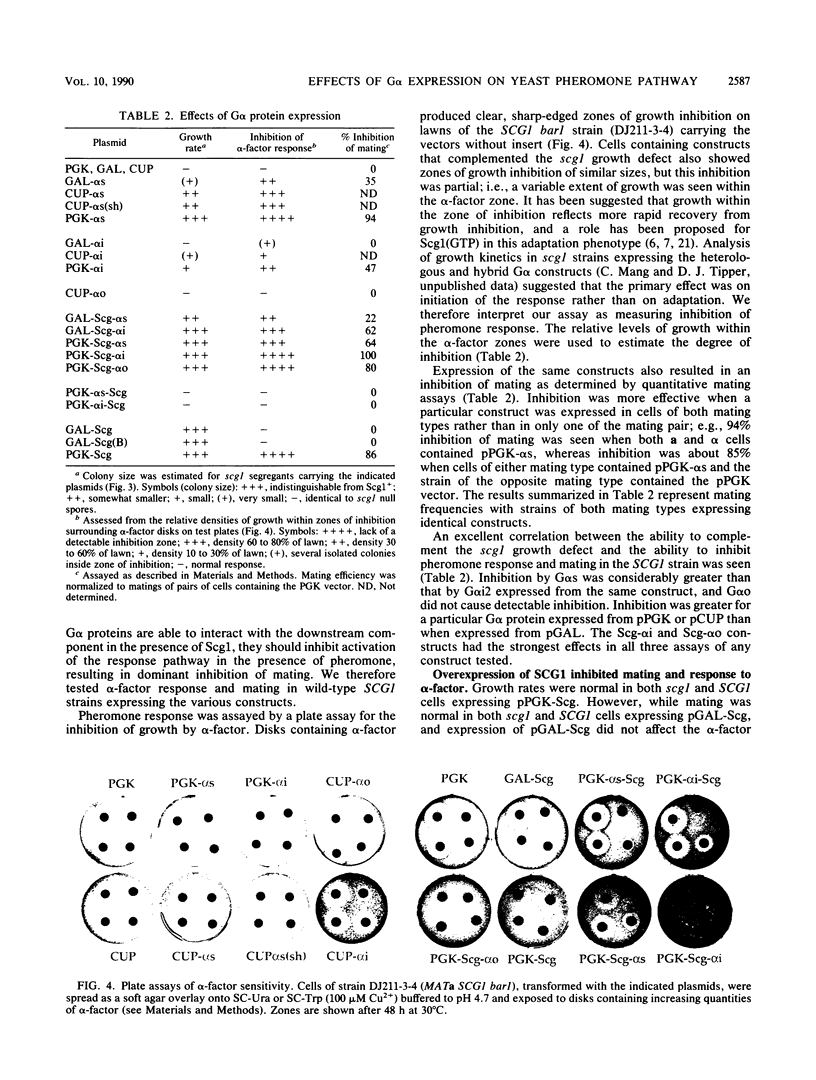
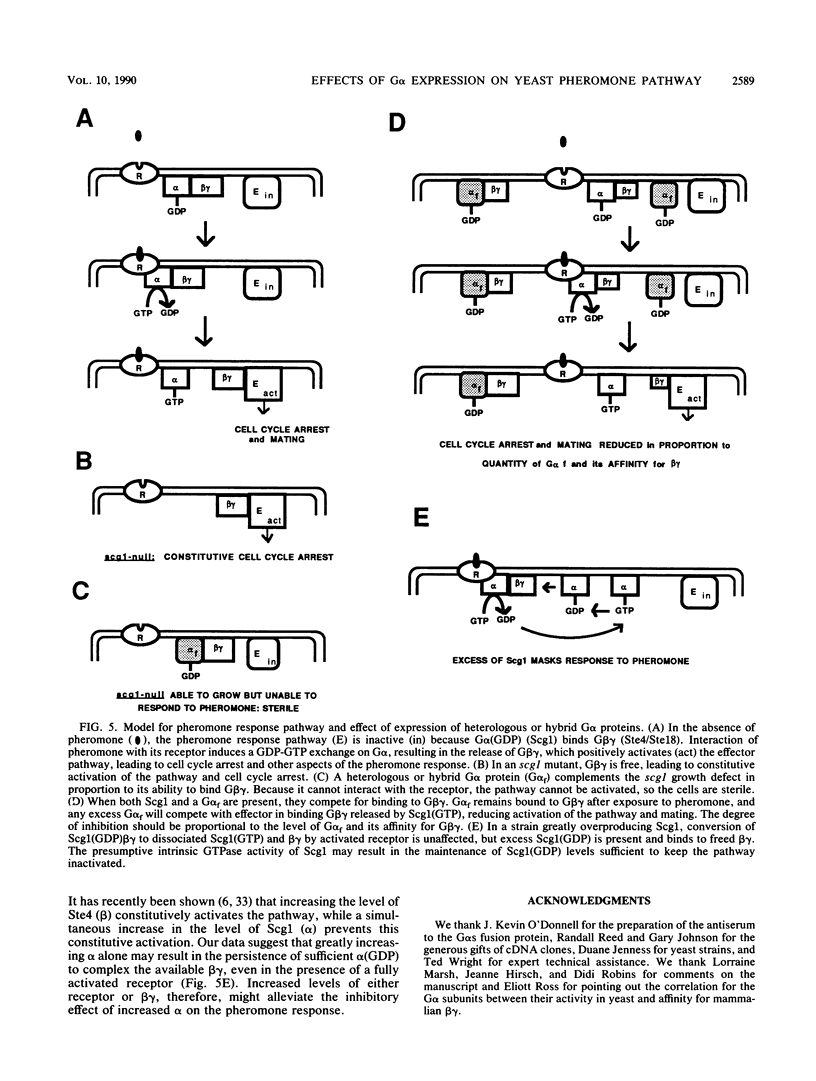
Scg1, the product of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SCG1 (also called GPA1) gene, is homologous to the alpha subunits of G proteins involved in signal transduction in mammalian cells. Scg1 negatively controls the pheromone response pathway in haploid cells. Either pheromonal activation or an scg1 null mutation relieves the negative control and leads to an arrest of cell growth in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Expression of rat G alpha s was previously shown to complement the growth defect of scg1 null mutants while not allowing mating. We have extended this analysis to examine the effects of the short form of G alpha s (which lacks 15 amino acids present in the long form), G alpha i2, G alpha o, and Scg1-mammalian G alpha hybrids. In addition, we have found that constructs able to complement scg1 are also able to inhibit the response to pheromone and mating when expressed in a wild-type SCG1 strain. Overexpression of Scg1 has a similar inhibitory effect. These results are consistent with a model proposed for the action of Scg1 as the alpha component of a heterotrimeric G protein in which the beta gamma component (Ste4/Ste18) activates the pheromone response after dissociation from Scg1. They suggest that the G alpha constructs able to complement scg1 can interact with beta gamma to prevent activation of the pathway but are unable to interact with pheromone receptors to activate the pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blinder D., Bouvier S., Jenness D. D. Constitutive mutants in the yeast pheromone response: ordered function of the gene products. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):479–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Halvorson H. O. Physiological control of repressible acid phosphatase gene transcripts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):839–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. G-protein subunits. Who carries what message? Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):504–504. doi: 10.1038/337504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Stone D. E., Reed S. I. Stoichiometry of G protein subunits affects the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating pheromone signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):510–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Khan M. I., Marsh J., Butt T. R., Crooke S. T. Chemical synthesis and expression of a cassette adapted ubiquitin gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3524–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahng K. Y., Ferguson J., Reed S. I. Mutations in a gene encoding the alpha subunit of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae G protein indicate a role in mating pheromone signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2484–2493. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D., Lewis D. L., Graziadei L., Neer E. J., Bar-Sagi D., Clapham D. E. G-protein beta gamma-subunits activate the cardiac muscarinic K+-channel via phospholipase A2. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):557–560. doi: 10.1038/337557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Beiderman B., Lopez N. G., Ramachandran J., Bourne H. R. Carboxyl terminal domain of Gs alpha specifies coupling of receptors to stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):448–451. doi: 10.1126/science.2899356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., Tuite M. F., Emtage J. S., White S., Lowe P. A., Patel T., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient synthesis of enzymatically active calf chymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Arai K., Matsumoto K. GPA1Val-50 mutation in the mating-factor signaling pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2289–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Occurrence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of a gene homologous to the cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of mammalian G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Kaziro Y., Arai K., Matsumoto K. Role of STE genes in the mating factor signaling pathway mediated by GPA1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3777–3783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Masters S. B., Beiderman B., Heideman W., Bourne H. R. Identification of receptor contact site involved in receptor-G protein coupling. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):758–760. doi: 10.1038/330758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L. A., de Vos A. M., Milburn M. V., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Structural differences between a ras oncogene protein and the normal protein. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):90–93. doi: 10.1038/337090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Thomas D. Y. Overexpression of the STE4 gene leads to mating response in haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):217–222. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. F., Desselberger U., Palese P., Ferguson B., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Efficient expression of influenza virus NS1 nonstructural proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6105–6109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]