Abstract
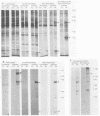
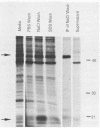
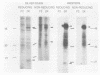
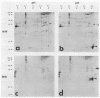
The decapentaplegic (dpp) gene of Drosophila melanogaster is required for pattern formation in the embryo and for viability of the epithelial cells in the imaginal disks. The dpp protein product predicted from the DNA sequence is similar to members of a family of growth factors that includes transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). We have produced polyclonal antibodies to a recombinant dpp protein made in bacteria and used a metallothionein promoter to express a dpp cDNA in Drosophila S2 cells. Similar to other proteins in the TGF-beta family, the dpp protein produced by the Drosophila cells was proteolytically cleaved, and both portions of the protein were secreted from the cells. The amino-terminal 47-kilodalton (kDa) peptide was found in the medium and in the proteins adhering to the plastic petri dish. The carboxy-terminal peptide, the region with sequence similarity to the active ligand portion of TGF-beta, was found extracellularly as a 30-kDa homodimer. Most of the 30-kDa homodimer was in the S2 cell protein adsorbed onto the surface of the plastic dish. The dpp protein could be released into solution by increased salt concentration and nonionic detergent. Under these conditions, the amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal portions of dpp were not associated in a stable complex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoit R., Ling N., Esch F. A new prosomatostatin-derived peptide reveals a pattern for prohormone cleavage at monobasic sites. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1126–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.2891188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourouis M., Jarry B. Vectors containing a prokaryotic dihydrofolate reductase gene transform Drosophila cells to methotrexate-resistance. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1099–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner A. M., Gentry L. E., Cooper J. A., Purchio A. F. Recombinant type 1 transforming growth factor beta precursor produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells is glycosylated and phosphorylated. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2229–2232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner A. M., Marquardt H., Malacko A. R., Lioubin M. N., Purchio A. F. Site-directed mutagenesis of cysteine residues in the pro region of the transforming growth factor beta 1 precursor. Expression and characterization of mutant proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13660–13664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. J. Localized cell death caused by mutations in a Drosophila gene coding for a transforming growth factor-beta homolog. Dev Biol. 1988 Aug;128(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunch T. A., Grinblat Y., Goldstein L. S. Characterization and use of the Drosophila metallothionein promoter in cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1043–1061. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Tizard R., Farber N. M., Cheung A., Ninfa E. G., Frey A. Z., Gash D. J., Chow E. P. Isolation of the bovine and human genes for Müllerian inhibiting substance and expression of the human gene in animal cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90783-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Weatherbee J. A., Tsang M. L., Anderson J. K., Mole J. E., Lucas R., Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta system, a complex pattern of cross-reactive ligands and receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Lioubin M. N., Purchio A. F., Marquardt H. Molecular events in the processing of recombinant type 1 pre-pro-transforming growth factor beta to the mature polypeptide. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4162–4168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann F. M. Roles of Drosophila proto-oncogene and growth factor homologs during development of the fly. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:1–29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. E., Scott M. P. The Drosophila patched gene encodes a putative membrane protein required for segmental patterning. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):751–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh A. J., Dahl K. D., Vaughan J., Tucker E., Rivier J., Bardin C. W., Vale W. Heterodimers and homodimers of inhibin subunits have different paracrine action in the modulation of luteinizing hormone-stimulated androgen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5082–5086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irish V. F., Gelbart W. M. The decapentaplegic gene is required for dorsal-ventral patterning of the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):868–879. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H., van der Straten A., Sweet R., Otto E., Maroni G., Rosenberg M. Regulated expression at high copy number allows production of a growth-inhibitory oncogene product in Drosophila Schneider cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):882–889. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S., Kelley M. R., Young M. W. Sequence of the notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster: relationship of the encoded protein to mammalian clotting and growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3094–3108. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopczynski C. C., Alton A. K., Fechtel K., Kooh P. J., Muskavitch M. A. Delta, a Drosophila neurogenic gene, is transcriptionally complex and encodes a protein related to blood coagulation factors and epidermal growth factor of vertebrates. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1723–1735. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Ying S. Y., Ueno N., Shimasaki S., Esch F., Hotta M., Guillemin R. Pituitary FSH is released by a heterodimer of the beta-subunits from the two forms of inhibin. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):779–782. doi: 10.1038/321779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons K., Graycar J. L., Lee A., Hashmi S., Lindquist P. B., Chen E. Y., Hogan B. L., Derynck R. Vgr-1, a mammalian gene related to Xenopus Vg-1, is a member of the transforming growth factor beta gene superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4554–4558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Hayflick J. S., Ling N., Esch F., Ueno N., Ying S. Y., Guillemin R., Niall H., Seeburg P. H. Complementary DNA sequences of ovarian follicular fluid inhibin show precursor structure and homology with transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):659–663. doi: 10.1038/318659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Role for carbohydrate structures in TGF-beta 1 latency. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):158–160. doi: 10.1038/338158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono K., Hellman U., Wernstedt C., Heldin C. H. Latent high molecular weight complex of transforming growth factor beta 1. Purification from human platelets and structural characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6407–6415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hoffmann F. M. Homologs of vertebrate growth factors in Drosophila melanogaster and other invertebrates. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1990;24:289–328. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Perutz M. F., Poyart C. Oxygen binding properties of human mutant hemoglobins synthesized in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7252–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. W., St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. A transcript from a Drosophila pattern gene predicts a protein homologous to the transforming growth factor-beta family. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):81–84. doi: 10.1038/325081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P., Mattaliano R. J., Manganaro T. F., Donahoe P. K., Cate R. L. Proteolytic processing of mullerian inhibiting substance produces a transforming growth factor-beta-like fragment. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18961–18964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., Schuermann M., Wagenaar E., Parren P., Weigel D., Nusse R. The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Laski F. A., Rubin G. M. Identification and immunochemical analysis of biologically active Drosophila P element transposase. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Transformation of cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells with a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1833–1838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg J. M., Hartley D. A., Walther Z., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. slit: an EGF-homologous locus of D. melanogaster involved in the development of the embryonic central nervous system. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1047–1059. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D., Gelbart W. M. Shortvein, a new component of the decapentaplegic gene complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):119–143. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields G., Dübendorfer A., Sang J. H. Differentiation in vitro of larval cell types from early embryonic cells of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1975 Feb;33(1):159–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Rubin G. M. Structure and activity of the sevenless protein: a protein tyrosine kinase receptor required for photoreceptor development in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8333–8337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer F. A., Hoffmann F. M., Gelbart W. M. Decapentaplegic: a gene complex affecting morphogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Assoian R. K. Transforming growth factor-beta: biological function and chemical structure. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):532–534. doi: 10.1126/science.3487831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Rivier J., Vaughan J., McClintock R., Corrigan A., Woo W., Karr D., Spiess J. Purification and characterization of an FSH releasing protein from porcine ovarian follicular fluid. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):776–779. doi: 10.1038/321776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B. Latent transforming growth factor-beta from human platelets. A high molecular weight complex containing precursor sequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7646–7654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Melton D. A. A maternal mRNA localized to the vegetal hemisphere in Xenopus eggs codes for a growth factor related to TGF-beta. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1528–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.3201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel M., Nusse R., Johnston P., Lawrence P. A. Distribution of the wingless gene product in Drosophila embryos: a protein involved in cell-cell communication. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]