Abstract
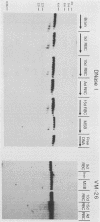
We have mapped DNase I-hypersensitive sites and topoisomerase II (topo II) sites in the chicken beta-globin locus, which contains four globin genes (5'-rho-beta H-beta A-epsilon-3'). In the 65 kilobases (kb) mapped, 12 strong hypersensitive sites were found clustered within the 25-kb region from 10 kb upstream of rho to just downstream of epsilon. The strong sites were grouped into several classes based on their tissue distribution, developmental pattern, and location. (i) One site was present in all cells examined, both erythroid and nonerythroid. (ii) Three sites, located upstream of the rho-globin gene, were present at every stage of erythroid development, but were absent from nonerythroid cells. (iii) Four sites at the 5' ends of each of the four globin genes were hypersensitive only in the subset of erythroid cells that were transcribing or had recently transcribed the associated gene. (iv) Another three sites, whose pattern of hypersensitivity also correlated with expression of the associated gene, were found 3' of rho, beta H, and epsilon. (v) A site 3' of beta A and 5' of epsilon was erythroid cell specific and present at all developmental stages, presumably reflecting the activity of this enhancer throughout erythroid development. We also mapped the topo II sites in this locus, as determined by teniposide-induced DNA cleavage. All strong teniposide-induced cleavages occurred at DNase I-hypersensitive sites, while lesser amounts of cleavage were observed in transcribed regions of DNA. Most but not all of the DNase I-hypersensitive sites were topo II sites. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that, in vivo, topo II preferentially acts on nucleosome-free regions of DNA but suggest that additional topo II regulatory mechanisms must exist.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974 Sep;17(3):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Kaye J. S., Pratt-Kaye S., Chambon P. Hormonally induced alterations of chromatin structure in the polyadenylation and transcription termination regions of the chicken ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):567–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G. A., Ingram V. M. The erythroid cells and haemoglobins of the chick embryo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Oct 25;266(877):225–305. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan P. N., Olah J., Birnstiel M. L. Major changes in the 5' and 3' chromatin structure of sea urchin histone genes accompany their activation and inactivation in development. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. L., Yang L., Rowe T. C., Halligan B. D., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13560–13566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V., Sollner-Webb B. Sites of topoisomerase I action on X. laevis ribosomal chromatin: transcriptionally active rDNA has an approximately 200 bp repeating structure. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Chromosomal arrangement of the chicken beta-type globin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Weber J. L., Gorski J. Chromatin structure, transcription, and methylation of the prolactin gene domain in pituitary tumors of Fischer 344 rats. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7086–7093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Nickol J. M., Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. Analysis of the tissue-specific enhancer at the 3' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., Evans T., Jackson P. D., Knezetic J., Lewis C., Nickol J., Reitman M. Regulatory protein action in the neighborhood of chicken globin genes during development. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;316A:73–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Takegawa S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Groudine M. Evidence for a locus activation region: the formation of developmentally stable hypersensitive sites in globin-expressing hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10159–10177. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin structure of the lysozyme gene in steroid hormone target and non-target cells. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Feb;368(2):111–119. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Elgin S. C. Localization of specific topoisomerase I interactions within the transcribed region of active heat shock genes by using the inhibitor camptothecin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant clones containing the chicken adult beta-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8099–8102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlaczky G., Praznovszky T., Sófi J., Udvardy A. Intracellular forms of Drosophila topoisomerase II detected with monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10013–10023. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. Topoisomerase II: A specific marker for cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2569–2581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Lieber M. R., Felsenfeld G. Regulated gene expression in transfected primary chicken erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Evans T., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. Developmental modulation of protein binding to beta-globin gene regulatory sites within chicken erythrocyte nuclei. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1860–1873. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. A method for mapping intranuclear protein-DNA interactions and its application to a nuclease hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. Protein-binding sites within the 5' DNase I-hypersensitive region of the chicken alpha D-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2059–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Felsenfeld G. Identification and characterization of a chicken alpha-globin enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):893–901. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Luse D. S. The presence of nucleosomes on a DNA template prevents initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsovali A., Müller M. M., Weber F., Marcaud L., Farache G., Schreiber E., Schaffner W., Scherrer K. A transcriptional enhancer located between adult beta-globin and embryonic epsilon-globin genes in chicken and duck. Gene. 1987;58(2-3):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois R., Martinson H. G. Chicken globin gene transcription is cell lineage specific during the time of the switch. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2281–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Havercroft J. C., Chow L. T., Cleveland D. W. Four unique genes required for beta tubulin expression in vertebrates. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Mehta V. B. DNase I hypersensitivity is independent of endogenous topoisomerase II activity during chicken erythrocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3661–3669. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Wallis K. T., Machlin P. S., Ratrie H., 3rd, Cleveland D. W. The sequence and expression of the divergent beta-tubulin in chicken erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14305–14312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. Bidirectional control of the chicken beta- and epsilon-globin genes by a shared enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2548–2552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl T. M., Martinson H. G. Transcription termination at the chicken beta H-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5369–5377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. Mutational analysis of the chicken beta-globin enhancer reveals two positive-acting domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6267–6271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. In vivo localization of DNA topoisomerase II cleavage sites on Drosophila heat shock chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):985–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. A consensus sequence for cleavage by vertebrate DNA topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5533–5556. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. L., Pao C. I., Sen S., Kuo T. High-resolution mapping of DNase I hypersensitive site in the chicken beta-tubulin gene transfected into monkey cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7764–7769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Costantini F. A 3' enhancer contributes to the stage-specific expression of the human beta-globin gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):954–961. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Topoisomerase II cleavage in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Landes G. M., Pankratz M. J., Martinson H. G. The chicken beta globin gene region. Delineation of transcription units and developmental regulation of interspersed DNA repeats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11015–11023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Martinson H. Isolation and characterization of the complete chicken beta-globin gene region: frequent deletion of the adult beta-globin genes in lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3731–3746. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wotton D., Flanagan B. F., Owen M. J. Chromatin configuration of the human CD2 gene locus during T-cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]