Abstract
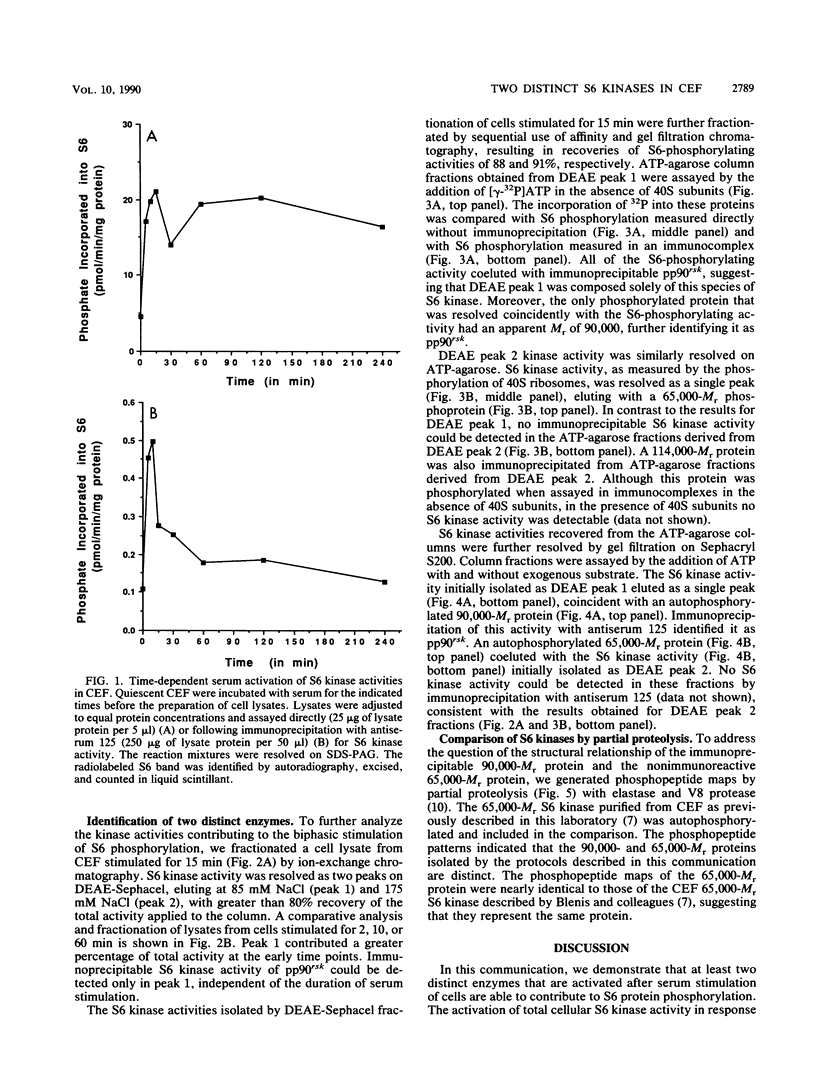
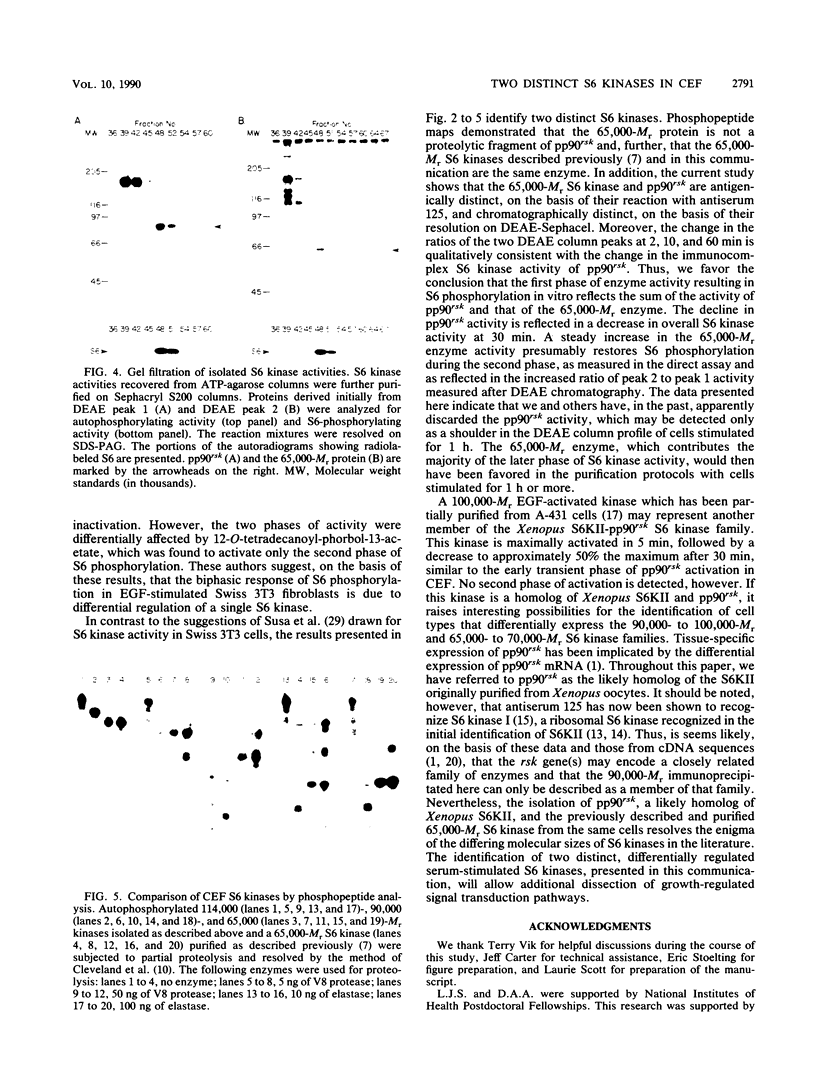
Serum stimulation of quiescent chicken embryo fibroblasts resulted in a time-dependent, biphasic activation of S6 kinase activity. Chromatographic fractionation of serum-stimulated cell lysates resolved two distinct S6 kinase activities. Anti-Xenopus S6 kinase II antiserum immunoprecipitated a 90,000-Mr S6 kinase but did not cross-react with a smaller, 65,000-Mr S6 kinase. Phosphopeptide analysis confirmed that the 90,000- and 65,000-Mr proteins were structurally unrelated and established that the 65,000-Mr protein isolated by the current protocol was the same serum-stimulated chicken embryo fibroblast S6 kinase as that previously characterized (J. Blenis, C. J. Kuo, and R. L. Erikson, J. Biol. Chem. 262:14373-14376, 1987). These results demonstrate the contribution of two distinct S6 kinases to total serum-stimulated ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcorta D. A., Crews C. M., Sweet L. J., Bankston L., Jones S. W., Erikson R. L. Sequence and expression of chicken and mouse rsk: homologs of Xenopus laevis ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Siegmann M., Thomas G. S6 kinase in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells is activated by phosphorylation in response to serum treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of protein kinase activities in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Alcorta D. A., Erikson R. L. Role of second messengers in regulating the growth-associated S6 protein kinase activity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;249:181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Spivack J. G., Erikson R. L. Phorbol ester, serum, and rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product induce similar phosphorylations of ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated ribosomal protein S6 kinase in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12994–12999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. In vivo phosphorylation and activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13711–13717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Stefanovic D., Blenis J., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Antibodies to Xenopus egg S6 kinase II recognize S6 kinase from progesterone- and insulin-stimulated Xenopus oocytes and from proliferating chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3147–3155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giugni T. D., Chen K., Cohen S. Activation of a cytosolic serine protein kinase by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18988–18995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Ballou L. M., Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Identification and characterization of a mitogen-activated S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):406–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Jäggi N., Luther H., Siegmann M., Thomas G. Purification and characterization of a 40 S ribosomal protein S6 kinase from vanadate-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1293–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Thomas G. Unmasking a growth factor/oncogene-activated S6 phosphorylation cascade. Cell Signal. 1989;1(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Baltimore D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 on serine after microinjection of the Abelson murine leukemia virus tyrosine-specific protein kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):272–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Thomas G. Ordered phosphorylation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 after serum stimulation of quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):926–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Price D. J., Mendelsohn M. J., Carter E. A., Avruch J. An S6 kinase activated during liver regeneration is related to the insulin-stimulated S6 kinase in H4 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19455–19460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen E., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase differentially alters translation of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3518–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susa M., Olivier A. R., Fabbro D., Thomas G. EGF induces biphasic S6 kinase activation: late phase is protein kinase C-dependent and contributes to mitogenicity. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):817–824. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90796-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Alcorta D. A., Jones S. W., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of mitogen-responsive ribosomal protein S6 kinase pp90rsk, a homolog of Xenopus S6 kinase II, in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2413–2417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Garcia de Herreros A., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a bovine liver S6 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):891–899. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevillyan J. M., Perisic O., Traugh J. A., Byus C. V. Insulin- and phorbol ester-stimulated phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3041–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Chesterman C. N., Walker T., Morgan F. J. Phosphorylation sites for ribosomal S6 protein kinases in mouse 3T3 fibroblasts stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 3;162(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]