Abstract
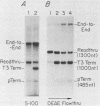
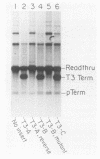
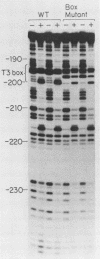
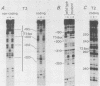
We describe a partially fractionated in vitro transcription system from Xenopus laevis for the assay of transcription termination by RNA polymerase I. Termination in vitro was found to require a specific terminator sequence in the DNA and a DNA-binding protein fraction that produces a footprint over the terminator sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartsch I., Schoneberg C., Grummt I. Purification and characterization of TTFI, a factor that mediates termination of mouse ribosomal DNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3891–3897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Clayton D. A. A tridecamer DNA sequence supports human mitochondrial RNA 3'-end formation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4502–4509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. A CCAAT box sequence in the adenovirus major late promoter functions as part of an RNA polymerase II termination signal. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. lac Repressor blocks transcribing RNA polymerase and terminates transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4134–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Rosenbauer H., Niedermeyer I., Maier U., Ohrlein A. A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):837–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse B., Narasimhan N., Attardi G. Termination of transcription in human mitochondria: identification and purification of a DNA binding protein factor that promotes termination. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A 12-base-pair sequence is an essential element of the ribosomal gene terminator in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1900–1905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A point mutation uncouples RNA 3'-end formation and termination during ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):269–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Ribosomal precursor 3' end formation requires a conserved element upstream of the promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90661-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene promoter contains a binding site for nuclear factor-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10657–10668. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]