Abstract
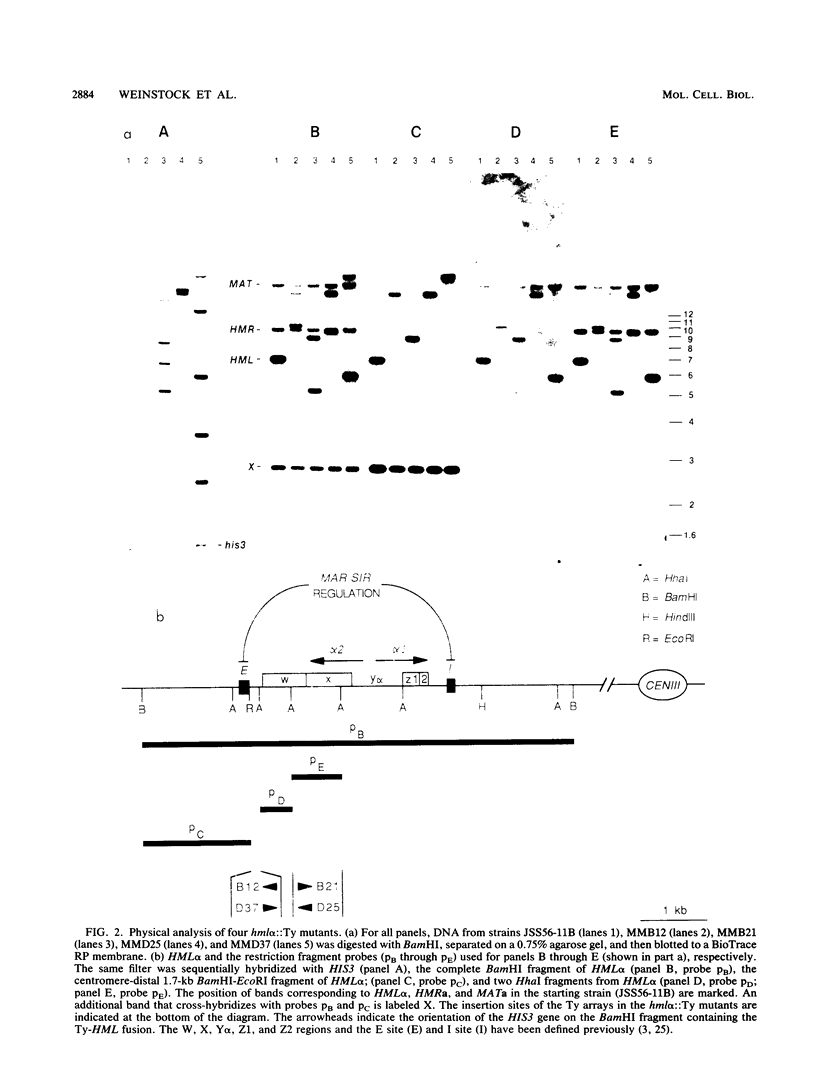
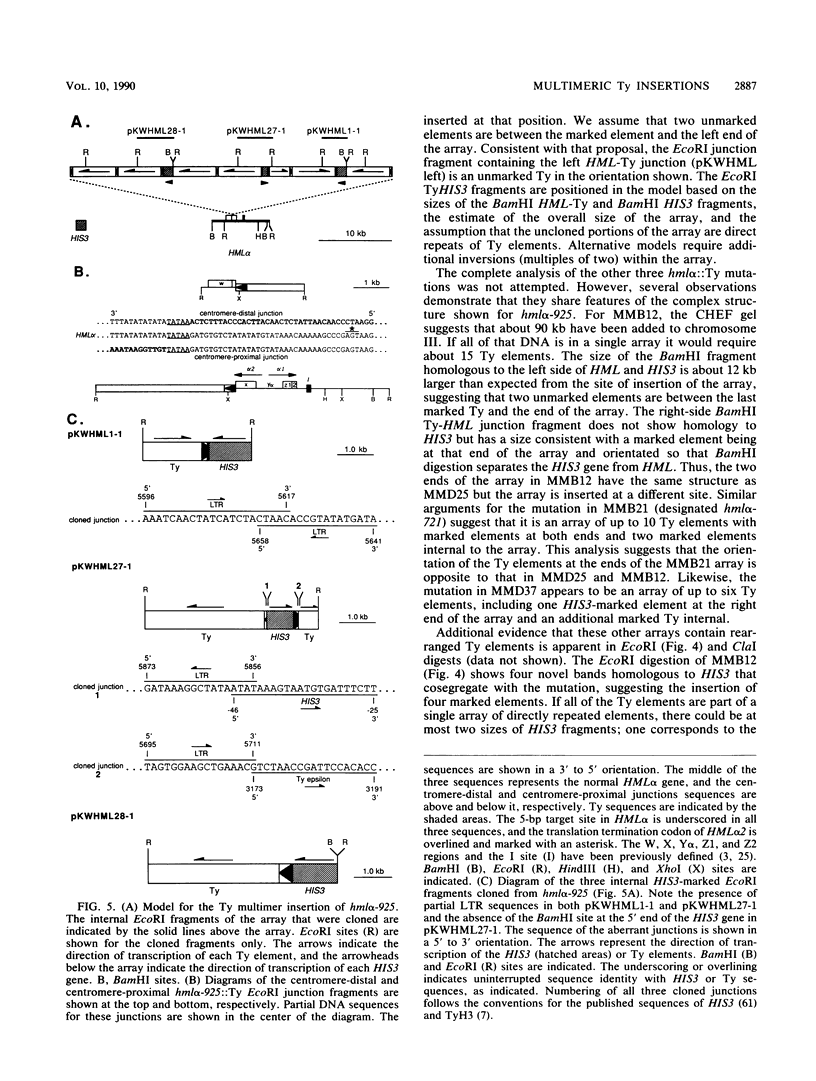
We have identified a novel integrated form of the yeast retrotransposon Ty consisting of multiple elements joined into large arrays. These arrays were first identified among Ty-induced alpha-pheromone-resistant mutants of MATa cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae which contain Ty insertions at HML alpha that result in the expression of that normally silent cassette. These insertions are multimeric arrays of both the induced genetically marked Ty element and unmarked Ty elements. Structural analysis of the mutations indicated that the arrays include tandem direct repeats of Ty elements separated by only a single long terminal repeat. The Ty-HML junction fragments of one mutant were cloned and shown to contain a 5-base-pair duplication of the target sequence that is characteristic of a Ty transpositional insertion. In addition, the arrays include rearranged Ty elements that do not have normal long terminal repeat junctions. We have also identified multimeric Ty insertions at other chromosomal sites and as insertions that allow expression of a promoterless his3 gene on a plasmid. The results suggest that Ty transposition includes an intermediate that can undergo recombination to produce multimers.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Feldman J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Sites required for position-effect regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):989–998. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5' and 3' to the regulated region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):307–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Eichinger D., Castrillon D., Fink G. R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome contains functional and nonfunctional copies of transposon Ty1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1432–1442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT3 gene is required for transposition and transpositional recombination of chromosomal Ty elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3575–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Xu H., Fink G. R. A general method for the chromosomal amplification of genes in yeast. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):280–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2827308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Hedge A. M., Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J. Ty RNA levels determine the spectrum of retrotransposition events that activate gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):213–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00260484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Sanders N. J., Garfinkel D. J. Transpositional competence and transcription of endogenous Ty elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: implications for regulation of transposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3571–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. The DNA intermediate in yeast Ty1 element transposition copurifies with virus-like particles: cell-free Ty1 transposition. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):955–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Cardillo T. S., Sherman F., Dubois E., Deschamps J., Wiame J. M. Mating signals control expression of mutations resulting from insertion of a transposable repetitive element adjacent to diverse yeast genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. Insertion of the eukaryotic transposable element Ty1 creates a 5-base pair duplication. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):352–356. doi: 10.1038/286352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. B., Hicks J. B., Broach J. R. Identification of sites required for repression of a silent mating type locus in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):815–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafner J., Philippsen P. The yeast transposon Ty1 generates duplications of target DNA on insertion. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):414–418. doi: 10.1038/286414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Mastrangelo M. F., Sanders N. J., Shafer B. K., Strathern J. N. Transposon tagging using Ty elements in yeast. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):95–108. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagino-Yamagishi K., Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. Retroviral DNA integrated during infection by an integration-deficient mutant of murine leukemia virus is oligomeric. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1964–1971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1964-1971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Laroche T., Brand A. H., Gasser S. M. RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90788-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Meeks-Wagner D. W., Fangman W. L., Botstein D. A rapid, efficient method for isolating DNA from yeast. Gene. 1986;42(2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T. W., Taylor J. M., Aldrich C., Townsend J. B., Seal G., Mason W. S. Tandem duplication of the proviral DNA in an avian sarcoma virus-transformed quail clone. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):219–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.219-223.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy J. M., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Cloning and characterization of four SIR genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):688–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E., Dewerchin M., Boeke J. D. Retrovirus-like vectors for Saccharomyces cerevisiae: integration of foreign genes controlled by efficient promoters into yeast chromosomal DNA. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90402-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Fogel S., Macleod K. MAR1-a Regulator of the HMa and HMalpha Loci in SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Genetics. 1979 Sep;93(1):37–50. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunes S., Botstein D., Fox M. S. Synapsis-mediated fusion of free DNA ends forms inverted dimer plasmids in yeast. Genetics. 1990 Jan;124(1):67–80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunes S., Botstein D., Fox M. S. Transformation of yeast with linearized plasmid DNA. Formation of inverted dimers and recombinant plasmid products. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. J., Broach J. R. The HML mating-type cassette of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is regulated by two separate but functionally equivalent silencers. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4621–4630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R., Woods V. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the alpha mating-type factor. Genetics. 1976 Apr;82(4):639–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen J. R., Kayne P. S., Moerschell R. P., Tsunasawa S., Gribskov M., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M., Sherman F., Sternglanz R. Identification and characterization of genes and mutants for an N-terminal acetyltransferase from yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2067–2075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsoulis G., Thomas W., Roghmann M. C., Winston F., Boeke J. D. Ty1 transposition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is nonrandom. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):269–279. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picologlou S., Dicig M. E., Kovarik P., Liebman S. W. The same configuration of Ty elements promotes different types and frequencies of rearrangements in different yeast strains. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Feb;211(2):272–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00330604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Herskowitz I. Four genes responsible for a position effect on expression from HML and HMR in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):9–22. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B., Herskowitz I. A suppressor of mating-type locus mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for and identification of cryptic mating-type loci. Genetics. 1979 Dec;93(4):877–901. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Smith M., Lambie E. J. Intrachromosomal movement of genetically marked Saccharomyces cerevisiae transposons by gene conversion. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):703–711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Kidd S., Kelley M. R. An improved filamentous helper phage for generating single-stranded plasmid DNA. Gene. 1986;45(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Mann C., Davis R. W. Reversion of a promoter deletion in yeast. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):815–819. doi: 10.1038/298815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C., Hoffman J., Goff S. P., Baltimore D. Intramolecular integration within Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):164–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.164-172.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmington J. R., Waring R. B., Newlon C. S., Indge K. J., Oliver S. G. Nucleotide sequence characterization of Ty 1-17, a class II transposon from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6679–6693. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Freedman R., Van Arsdell S., Szostak J. W., Thorner J. The yeast ARD1 gene product is required for repression of cryptic mating-type information at the HML locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3713–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Szostak J. W. The ARD1 gene of yeast functions in the switch between the mitotic cell cycle and alternative developmental pathways. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke C. M., Liebman S. W. Integration of an aberrant retrotransposon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4096–4098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Durbin K. J., Fink G. R. The SPT3 gene is required for normal transcription of Ty elements in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. Mutationally altered 3' ends of yeast CYC1 mRNA affect transcript stability and translational efficiency. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 25;177(1):107–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]