Abstract
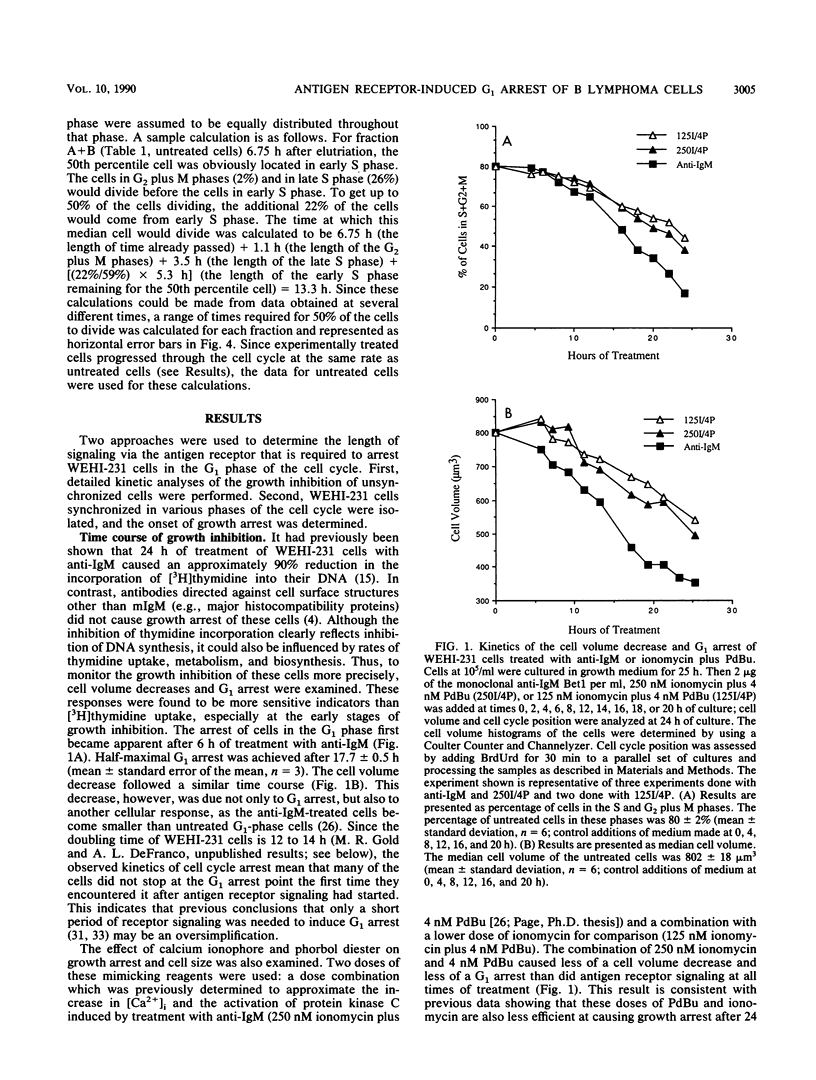
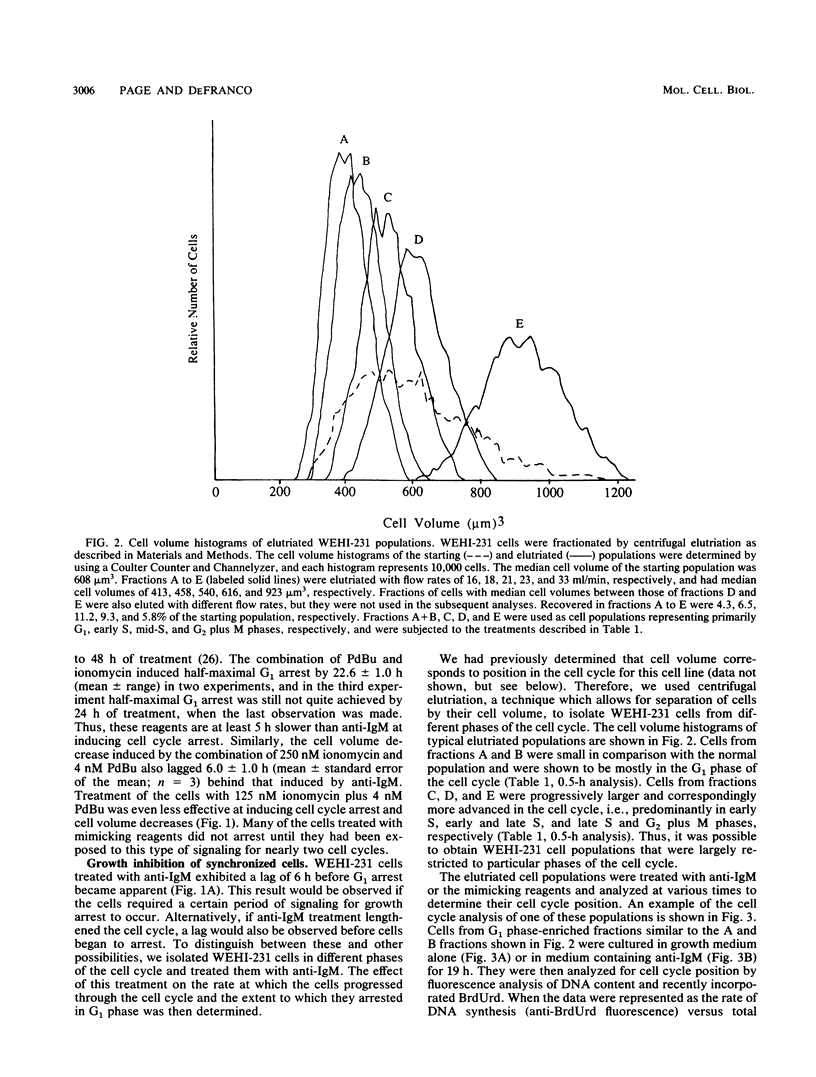
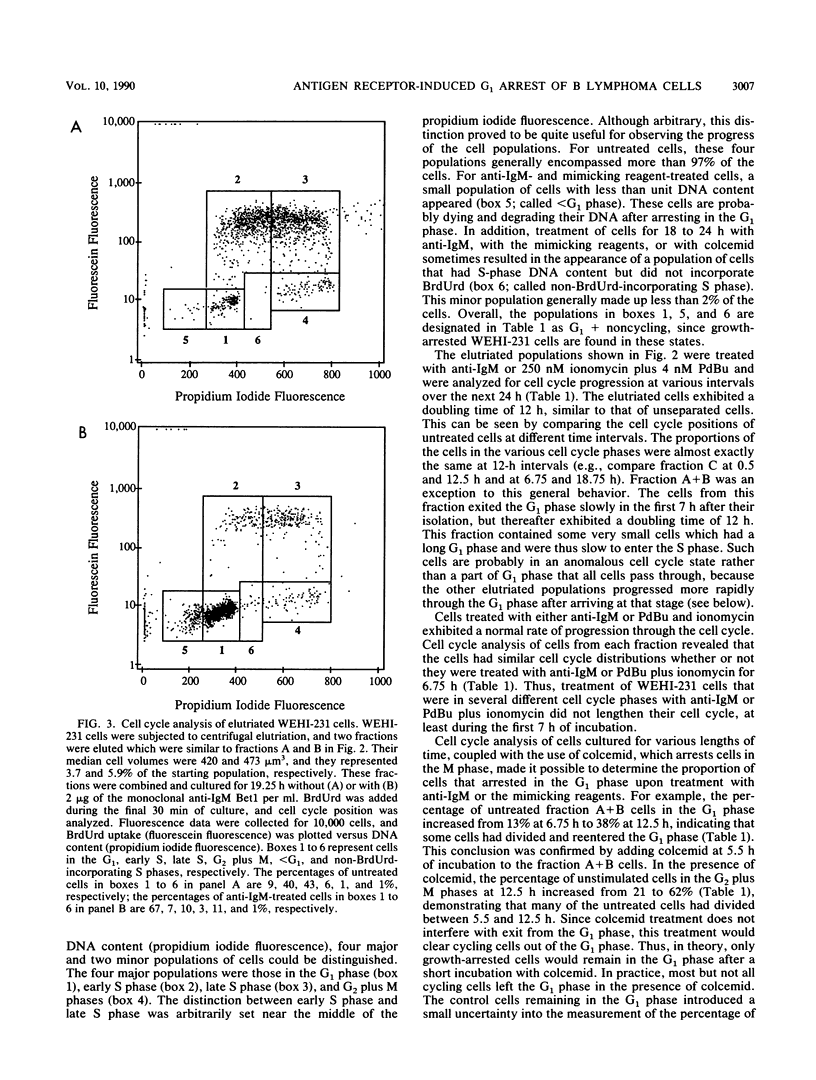
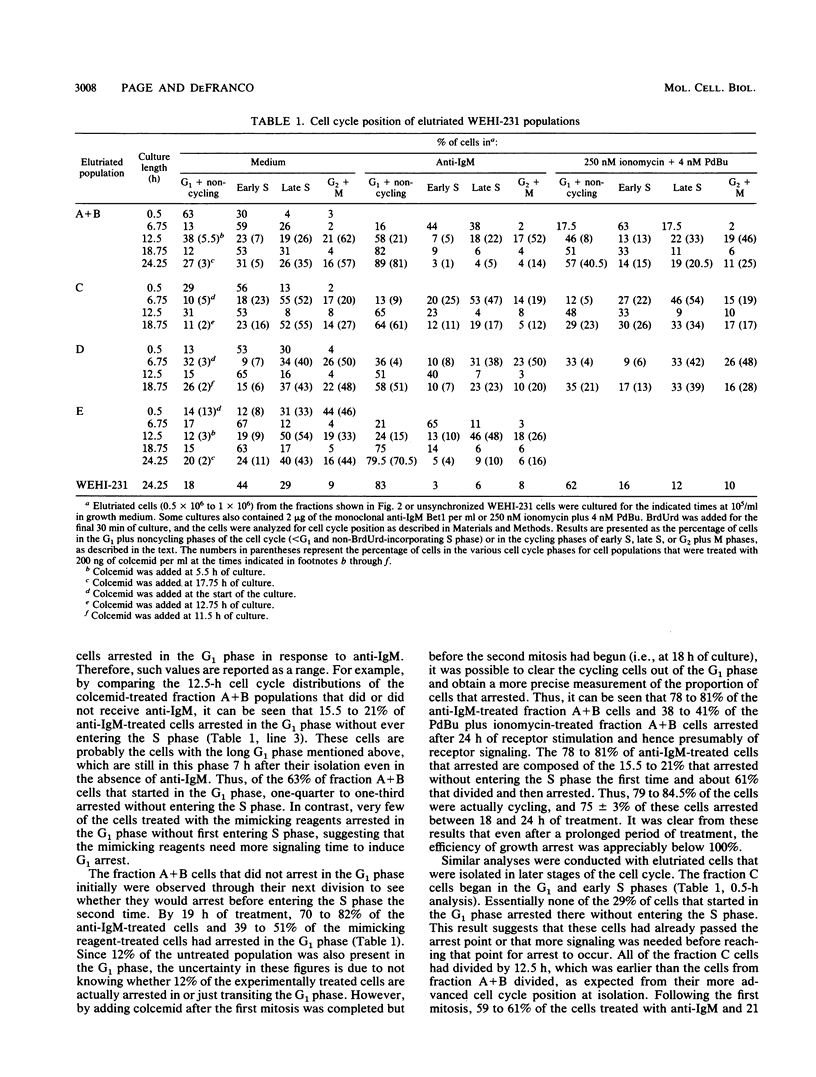
Stimulation of antigen receptors on WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells with anti-receptor antibodies (anti-immunoglobulin M [IgM]) causes irreversible growth arrest. This may be a model for antigen-induced tolerance to self components in the immune system. Antigen receptor stimulation also causes inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, producing diacylglycerol, which activates protein kinase C, and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, which causes release of calcium from intracellular stores. To better understand the nature of the antigen receptor-induced growth arrest of WEHI-231 cells, we have examined the basis for it. WEHI-231 cells in various phases of the cell cycle were isolated by centrifugal elutriation, and their response was evaluated following treatment with either anti-IgM or pharmacologic agents that raise intracellular free calcium levels and activate protein kinase C. Treatment with anti-IgM or the pharmacologic agents did not lengthen the cell cycle. Instead, growth inhibition was solely the result of arrest in the G1 phase. The efficiency of G1 arrest increased with the length of time during which the cells received signaling before reaching the G1 phase arrest point. Maximum efficiency of arrest was achieved after approximately one cell cycle of receptor signaling. These results imply that anti-IgM causes G1 arrest of WEHI-231 cells by slowly affecting components required for S phase progression, rather than by rapidly inhibiting such components or by rapidly activating a suicide mechanism. Antigen receptor stimulation was twice as effective as stimulation via the mimicking reagents phorbol dibutyrate and ionomycin. Thus, although the phosphoinositide second messengers diacylglycerol and calcium probably play roles in mediating the effects of anti-IgM on WEHI-231 cells, other second messengers may also be involved.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Schrader J. W. The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. II. The inhibition of WEHI 231 by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2466–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. DAF1, a mutant gene affecting size control, pheromone arrest, and cell cycle kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4675–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Molecular aspects of B-lymphocyte activation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:143–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defranco A. L., Raveche E. S., Asofsky R., Paul W. E. Frequency of B lymphocytes responsive to anti-immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1523–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeare F., Gratzner H., Pallavicini M. G., Gray J. W. Flow cytometric measurement of total DNA content and incorporated bromodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5573–5577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. A., DeFranco A. L. Cross-linking membrane IgM induces production of inositol trisphosphate and inositol tetrakisphosphate in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3935–3942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein N., Mond J. J. Identification of a prominent nuclear protein associated with proliferation of normal and malignant B cells. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1818–1822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., DeFranco A. L. Phorbol esters and dioctanoylglycerol block anti-IgM-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the murine B cell lymphoma WEHI-231. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):868–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Unger M. W. Unequal division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its implications for the control of cell division. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):422–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornbeck P., Paul W. E. Anti-immunoglobulin and phorbol ester induce phosphorylation of proteins associated with the plasma membrane and cytoskeleton in murine B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14817–14824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakway J. P., Usinger W. R., Gold M. R., Mishell R. I., DeFranco A. L. Growth regulation of the B lymphoma cell line WEHI-231 by anti-immunoglobulin, lipopolysaccharide, and other bacterial products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2225–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. Factors affecting B-cell growth and differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., O'Garra A., Bijsterbosch M. K., Holman M. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. VIII. Induction of DNA synthesis in B cells by a combination of calcium ionophores and phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):92–97. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBaer J., Tsien R. Y., Fahey K. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of the antigen receptor on WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells results in a voltage-independent increase in cytoplasmic calcium. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1836–1844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Hermann T. E. Characterization of ionomycin as a calcium ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5892–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. E., Pepe V. H., Kent R. B., Dean M., Marshak-Rothstein A., Sonenshein G. E. Specific regulation of c-myc oncogene expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5546–5550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Tsang W., Morrison S. L., Beaven M. A., Paul W. E. Membrane IgM, IgD, and IgG act as signal transmission molecules in a series of B lymphomas. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2162–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Kass M. J. Molecular events in B cell activation. I. Signals required to stimulate G0 to G1 transition of resting B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1674–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Seyfert V. L., Owen C. S., Sykes N. Isolation and characterization of a B lymphocyte mutant with altered signal transduction through its antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1059–1070. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. M., DeFranco A. L. Role of phosphoinositide-derived second messengers in mediating anti-IgM-induced growth arrest of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3717–3726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Mizuguchi J., Brown M., Nakanishi K., Hornbeck P., Rabin E., Ohara J. Regulation of B-lymphocyte activation, proliferation, and immunoglobulin secretion. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;99(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell C. A., Scott D. W. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. IV. Growth inhibition by anti-Ig of CH31 and CH33 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P. Functional subsets of murine and human B lymphocyte cell lines. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:107–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein T. L., Baeker T. R., Miller R. A., Kolber D. L. Stimulation of murine B cells by the combination of calcium ionophore plus phorbol ester. Cell Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;102(2):364–373. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., Livnat D., Pennell C. A., Keng P. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. III. Cell cycle dependence for negative signalling of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells by anti-mu. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):156–164. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and glucocorticoids activate an endogenous suicide process in target cells. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):62–64. doi: 10.1038/327062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner G. L., Scott D. W. Lymphoma models for B-cell activation and tolerance. VII. Pathways in anti-Ig-mediated growth inhibition and its reversal. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Daley M. J., Richey J., Spellman C. Flow cytometry analysis of murine B cell lymphoma differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:197–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg A., Larsson O. Kinetic analysis of regulatory events in G1 leading to proliferation or quiescence of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5365–5369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



