Abstract
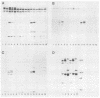
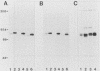
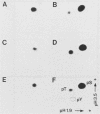
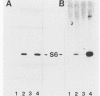
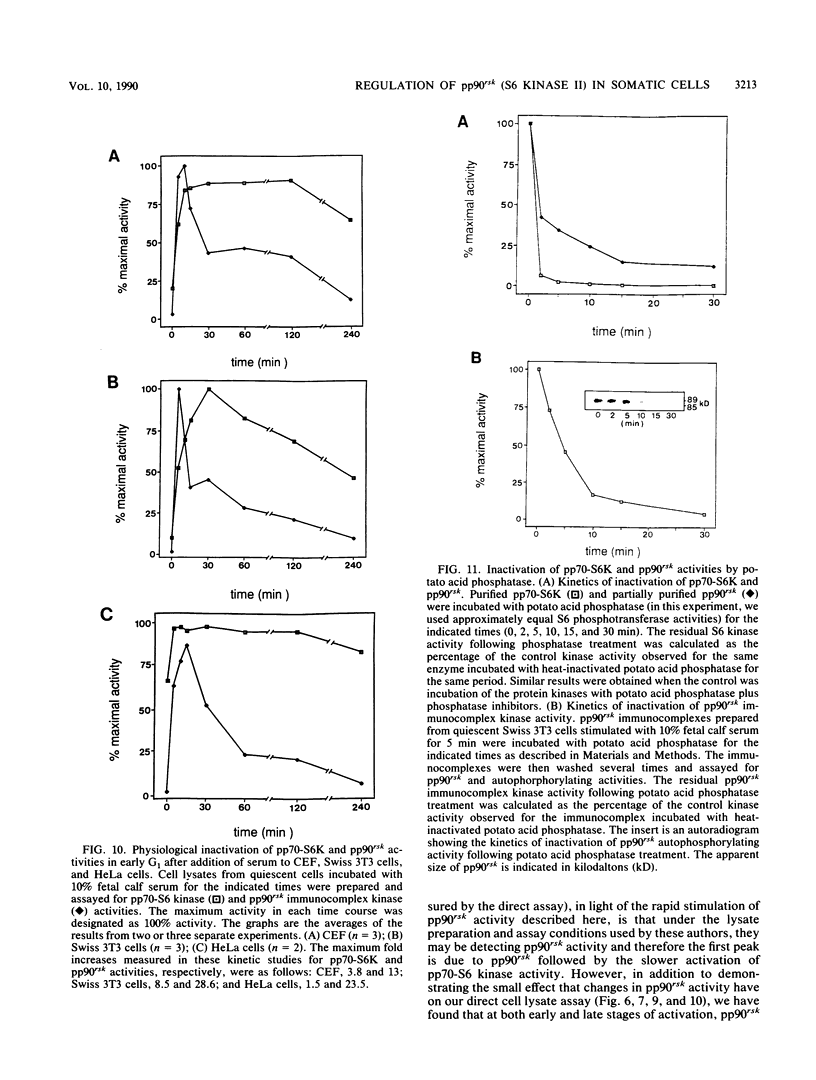
We have identified human, mouse, and chicken homologs to Xenopus S6 protein kinase II (S6KII). In quiescent cells, the apparent molecular mass of the Xenopus homologs (referred to as pp90rsk) increased from a range of 81 to 91 to a range of 85 to 92 kilodaltons following serum addition, which is consistent with an increase in protein phosphorylation. Indeed, serum growth factors stimulated pp90rsk phosphorylation at multiple serine and threonine residues. Furthermore, pp90rsk activity was stimulated within seconds of serum addition. Distinct molecular sizes, chromatographic properties, phosphopeptide maps, and kinetics of activation, the lack of immunological cross-reactivity, and analysis of S6 kinase activities in cells that overexpressed pp90rsk suggest that pp90rsk and pp70-S6 protein kinase, a previously identified mitogen- and oncogene-regulated S6 kinase in cultured cells, are distinct and differentially regulated. The notion that both enzymes are regulated by protein phosphorylation was supported by the ability to inactivate their S6 phosphotransferase activities with potato acid phosphatase. These data demonstrate that homologs to the Xenopus S6 protein kinases are produced and regulated by protein phosphorylation in somatic cells and that, in addition to a proposed role in Xenopus oocyte maturation, these homologs may participate in the initiation of animal cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcorta D. A., Crews C. M., Sweet L. J., Bankston L., Jones S. W., Erikson R. L. Sequence and expression of chicken and mouse rsk: homologs of Xenopus laevis ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Siegmann M., Thomas G. S6 kinase in quiescent Swiss mouse 3T3 cells is activated by phosphorylation in response to serum treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of protein kinase activities in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Stimulation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by pp60v-src or by serum: dissociation from phorbol ester-stimulated activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1733–1737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Activation of multiple protein kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2009–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated ribosomal protein S6 kinase in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12994–12999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. In vivo phosphorylation and activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinases during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13711–13717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Substrate specificity of ribosomal protein S6 kinase II from Xenopus eggs. Second Messengers Phosphoproteins. 1988;12(2-3):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Stefanovic D., Blenis J., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Antibodies to Xenopus egg S6 kinase II recognize S6 kinase from progesterone- and insulin-stimulated Xenopus oocytes and from proliferating chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3147–3155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giugni T. D., Chen K., Cohen S. Activation of a cytosolic serine protein kinase by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18988–18995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Hunter T. Platelet-derived growth factor induces multisite phosphorylation of pp60c-src and increases its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3345–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Ballou L. M., Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Identification and characterization of a mitogen-activated S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):406–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Jäggi N., Luther H., Siegmann M., Thomas G. Purification and characterization of a 40 S ribosomal protein S6 kinase from vanadate-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1293–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P. T., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Perkins A. S., Weinstein I. B. Construction and characterization of a retroviral vector demonstrating efficient expression of cloned cDNA sequences. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):219–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K., Czech M. P. Insulin-like growth factor I and insulin rapidly increase casein kinase II activity in BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15872–15875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Thomas G. Unmasking a growth factor/oncogene-activated S6 phosphorylation cascade. Cell Signal. 1989;1(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Guroff G. Purification and mechanism of activation of a nerve growth factor-sensitive S6 kinase from PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2832–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Differential regulation of histone H1 and ribosomal S6 kinases during sea star oocyte maturation. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7968–7974. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Price D. J., Mendelsohn M. J., Carter E. A., Avruch J. An S6 kinase activated during liver regeneration is related to the insulin-stimulated S6 kinase in H4 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19455–19460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Olwin B. B., Krebs E. G. Fibroblast growth factor treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells activates a subunit S6 kinase that phosphorylates a synthetic peptide substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland E. A., Müller T. H., Goldstein M., Greene L. A. Cell-free detection and characterization of a novel nerve growth factor-activated protein kinase in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7504–7513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Mulligan J. A., Lozeman F. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of casein kinase II in response to insulin and to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
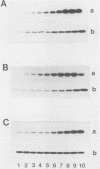
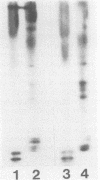
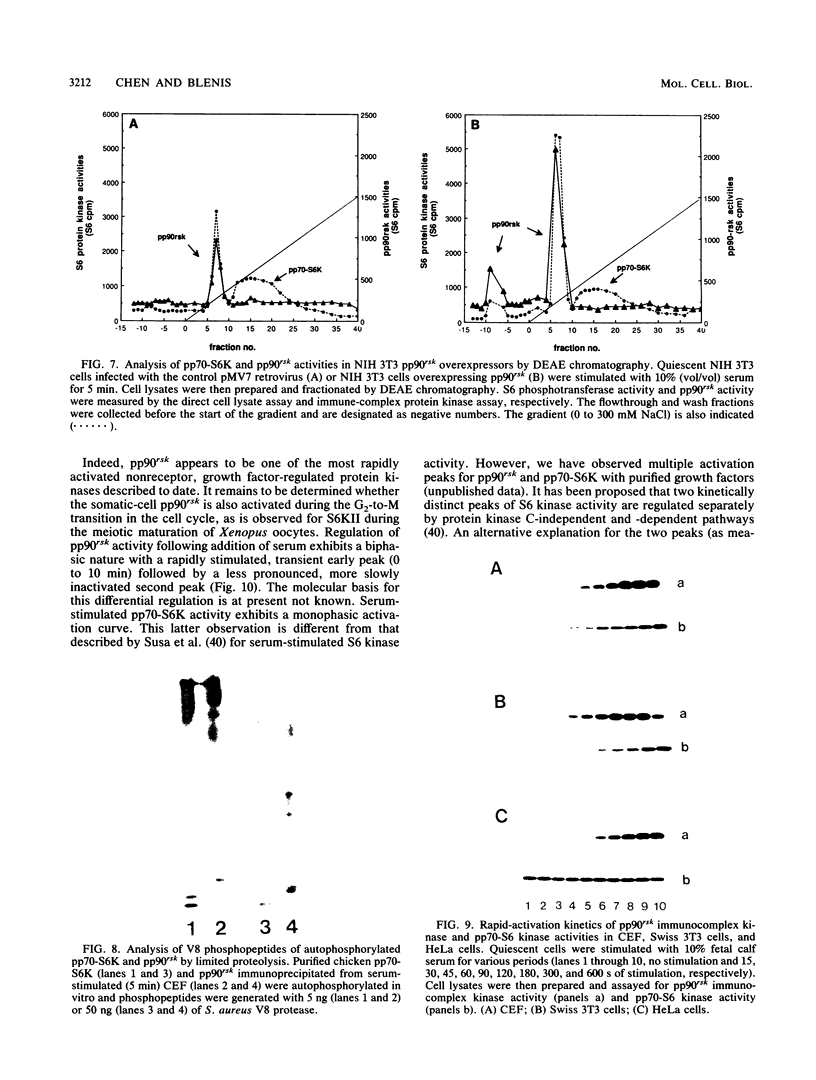
- Susa M., Olivier A. R., Fabbro D., Thomas G. EGF induces biphasic S6 kinase activation: late phase is protein kinase C-dependent and contributes to mitogenicity. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):817–824. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90796-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Garcia de Herreros A., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a bovine liver S6 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):891–899. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]