Abstract
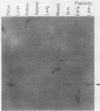
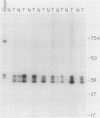
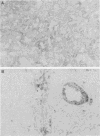
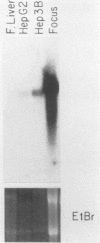
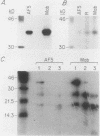
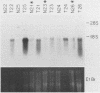
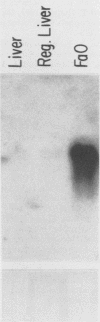
A basic phosphoprotein defined by a monoclonal antibody named AF5 was found to be highly abundant in human hepatocellular carcinoma by Western immunoblotting. Under the same conditions, the levels of this phosphoprotein were low or undetectable in normal liver extracts. The AF5 antibody was used to screen a cDNA expression library of a human hepatoma cell line named FOCUS. A 960-base-pair cDNA was isolated and found to be a partial cDNA encoding the human protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36, also known as lipocortin II. p36 expression was highly abundant in hepatocellular carcinomas at both the transcript and protein levels. Its expression was not induced significantly during rat liver regeneration following a partial hepatectomy. These results suggest that the induction of p36 expression is associated with malignant transformation of hepatocytes. p36 was previously shown to be phosphorylated upon transformation of normal fibroblasts by retroviral oncogenes without significant modulation of expression. We report here the initial description of the association of increased p36 expression with malignant transformation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. M., Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):313–315. doi: 10.1038/340313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Galvin K. M., Liang T. J., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R., Ozturk M. Abnormal structure and expression of p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1973–1977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Calpactin in exocytosis. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):20–20. doi: 10.1038/331020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin C. R., Simon D., Mattison J., Knowles B. B. Expression and biosynthetic variation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):25–34. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C., Howlett A. R., Martin G. S., Bissell M. J. The tyrosine phosphorylation substrate p36 is developmentally regulated in embryonic avian limb and is induced in cell culture. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):2017–2024. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Wilson S. H. Enzymes for modifying and labeling DNA and RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:94–110. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Identification and characterization of cellular targets for tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1108–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Moss S. E., Crumpton M. J. Diversity in the lipocortin/calpactin family. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Shealy D. J., Erikson R. L. Evidence that viral transforming gene products and epidermal growth factor stimulate phosphorylation of the same cellular protein with similar specificity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11381–11384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7884–7888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Two related but distinct forms of the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) that interact with phospholipid and actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4258–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. The 46,000-dalton tyrosine protein kinase substrate is widespread, whereas the 36,000-dalton substrate is only expressed at high levels in certain rodent tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):487–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Changes in the distribution of the 34-kdalton tyrosine kinase substrate during differentiation and maturation of chicken tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):473–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U. Second-strand cDNA synthesis: classical method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:325–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Fitch J. M., Jones J. M., Schlaepfer D. D. Two lipocortin-like proteins, endonexin II and anchorin CII, may be alternate splices of the same gene. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):48–50. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He L., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R., Goodman H. M., Shih C., Quaroni A. Establishment and characterization of a new human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. In Vitro. 1984 Jun;20(6):493–504. doi: 10.1007/BF02619623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber B. E., Glowinski I. B., Thorgeirsson S. S. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the asialoglycoprotein receptor in normal and neoplastic rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12400–12407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. The Ca2+/phospholipid-binding proteins of the submembraneous skeleton. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;234:169–193. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-1980-2_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Trowbridge I. S., Hunter T. Modulation of p36 phosphorylation in human cells: studies using anti-p36 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2745–2751. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasik A., Pepinsky R. B., Shoelson S. E., Kahn C. R. Lipocortins 1 and 2 as substrates for the insulin receptor kinase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11862–11867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug M. S., Berger S. L. First-strand cDNA synthesis primed with oligo(dT). Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:316–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M. Isolation of RNA using guanidinium salts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:219–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Pfeffer D. Direct sequencing of denatured plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motté P., Takahashi H., Ozturk M., Wilson B. E., Wands J. R. Characterization of a malignant phenotype-associated cell surface glycoprotein common to various human tumor cells and preferentially expressed on adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1349–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Tizard R., Mattaliano R. J., Sinclair L. K., Miller G. T., Browning J. L., Chow E. P., Burne C., Huang K. S., Pratt D. Five distinct calcium and phospholipid binding proteins share homology with lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10799–10811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Cheresh D. A. Human tumor antigens. Adv Immunol. 1987;40:323–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulitzeanu D. Human cancer-associated antigens: present status and implications for immunodiagnosis. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:1–42. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai T. F., Yauk Y. K., Chou C. K., Ting L. P., Chang C., Hu C. P., Han S. H., Su T. S. Evidence of autocrine regulation in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Carter E. A., Bucher N. L., Isselbacher K. J. Inhibition of hepatic regeneration in rats by acute and chronic ethanol intoxication. Gastroenterology. 1979 Sep;77(3):528–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B., Ozturk M., Takahashi H., Motté P., Kew M., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R. Cell-surface changes associated with transformation of human hepatocytes to the malignant phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3140–3144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]