Abstract
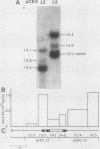
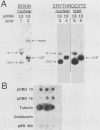
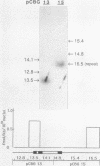
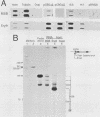
We report active, inappropriate transcription of the chicken beta A-globin gene in normal fibroblasts, cultured MSB cells, and brain. We were unable to detect ovalbumin gene transcription in these same tissues. Most of the globin gene transcripts were found to be truncated near the beginning of the gene, suggesting the existence of a premature termination process that is preferentially active under conditions of inappropriate transcription. The inappropriately transcribed beta A-globin gene chromatin remained DNase I resistant and highly methylated. Thus, the DNase I-sensitive conformation of erythrocyte beta A chromatin was correlated not with beta A transcription per se but with beta A expression. Although both transcribed and nontranscribed genes within the globin domain exhibited the same DNase I sensitivity in erythrocyte nuclei, a housekeeping gene active in erythrocytes exhibited a different level of DNase I sensitivity. However, this gene exhibited the same level of DNase I sensitivity in both erythrocytes and a cultured cell line. These observations are consistent with the proposal (G. Blobel, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:8527-8529, 1985) that the DNase I sensitivity of a gene may reflect properties of chromatin related to cotranscriptional and posttranscriptional aspects of mRNA production rather than to transcription per se.
Full text
PDF

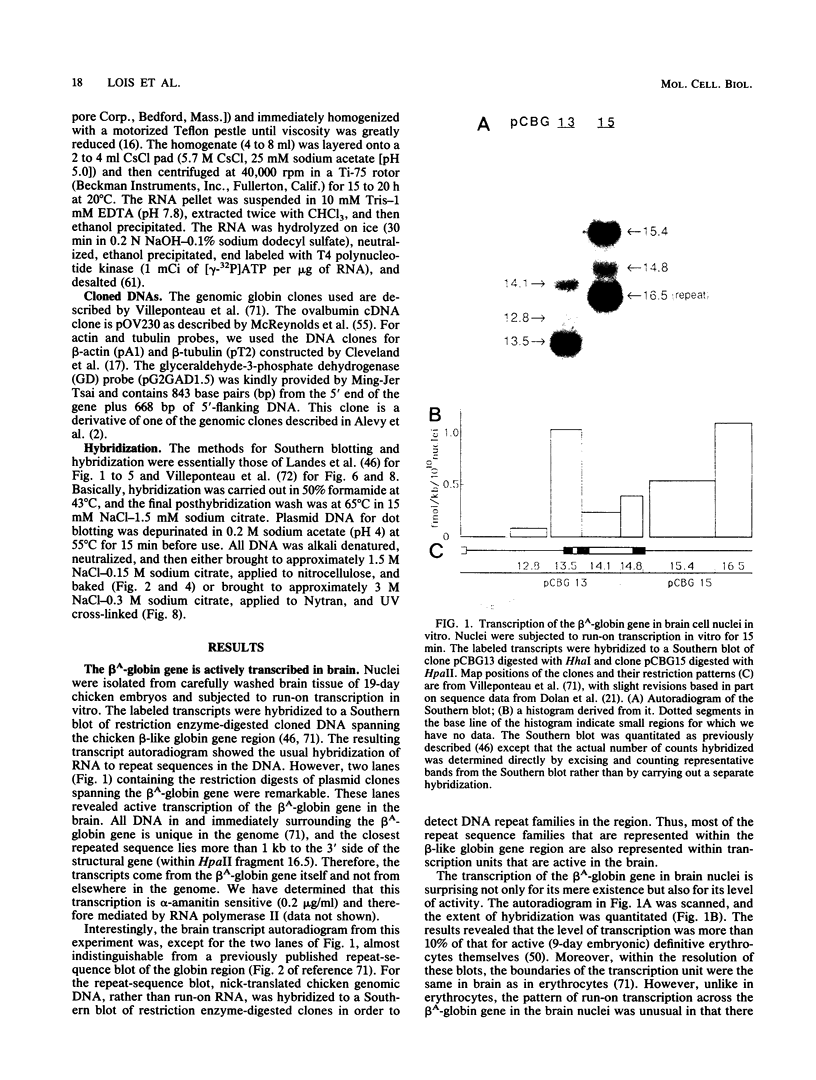


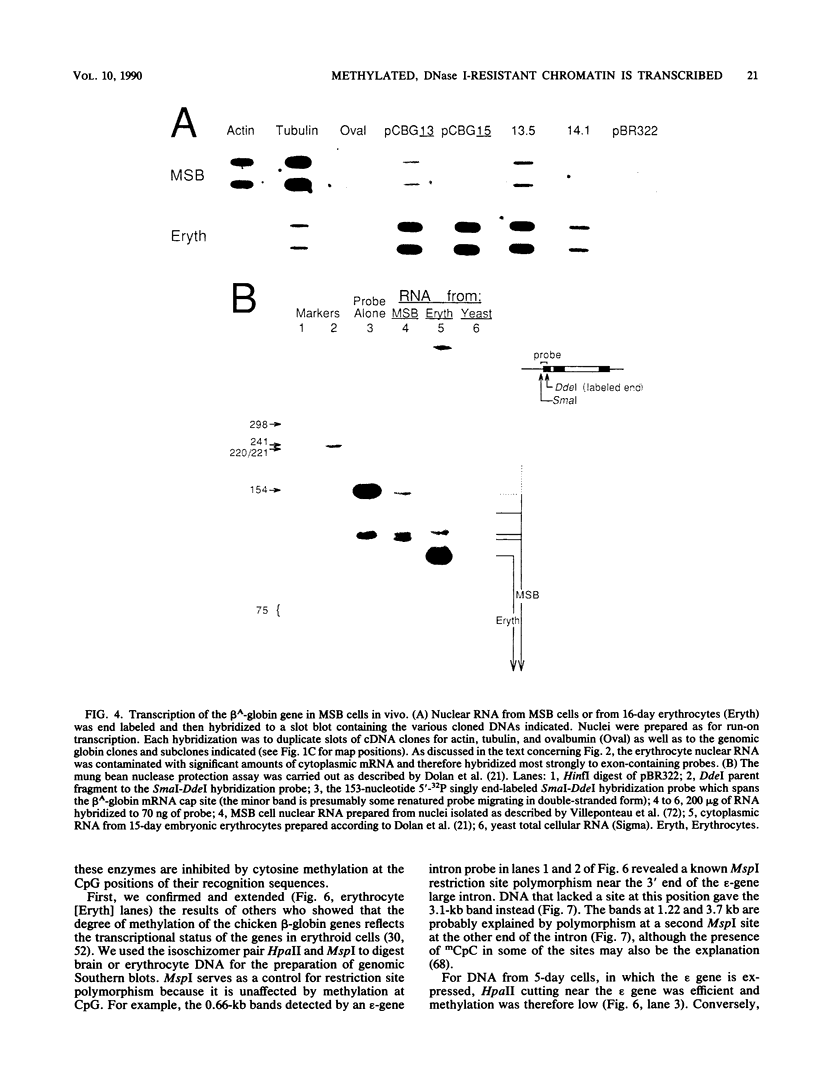
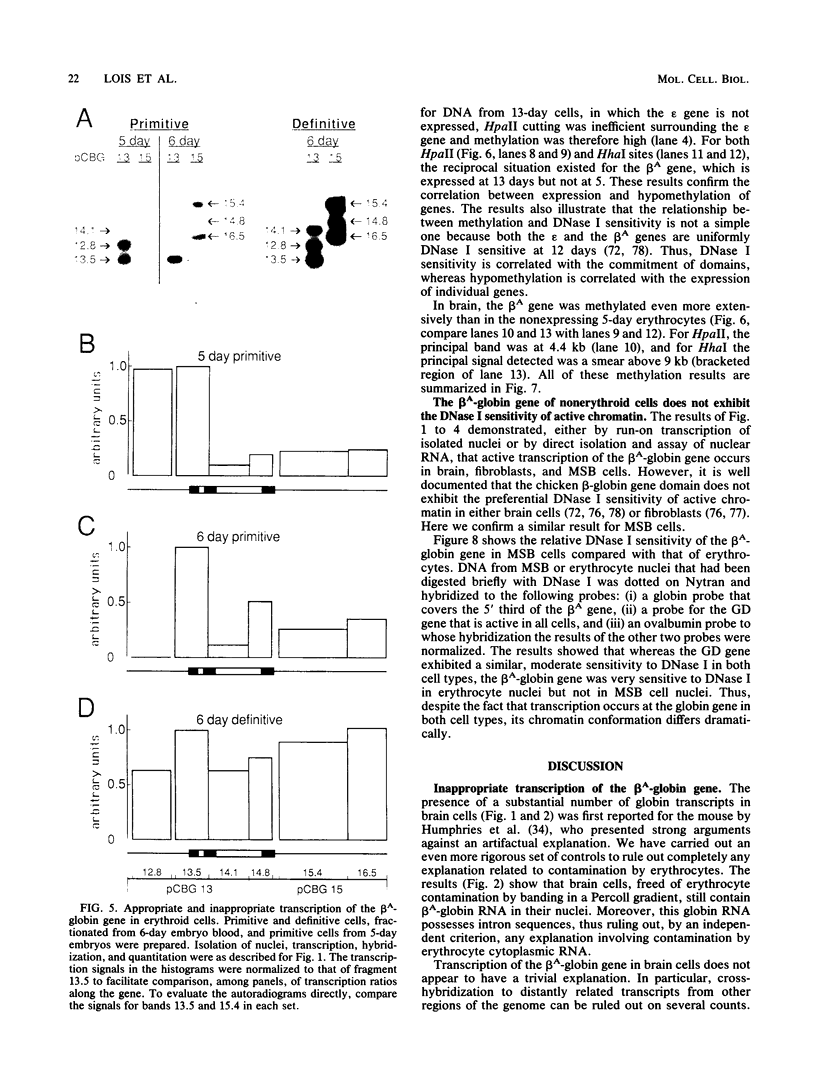
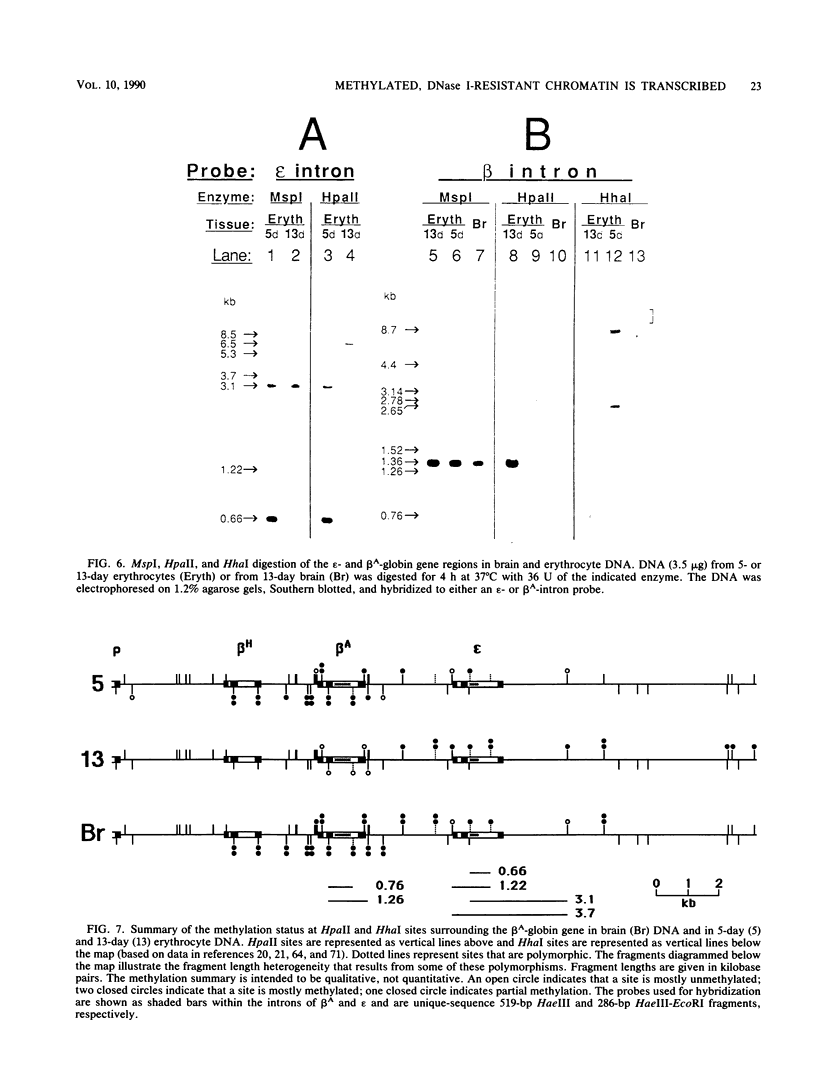
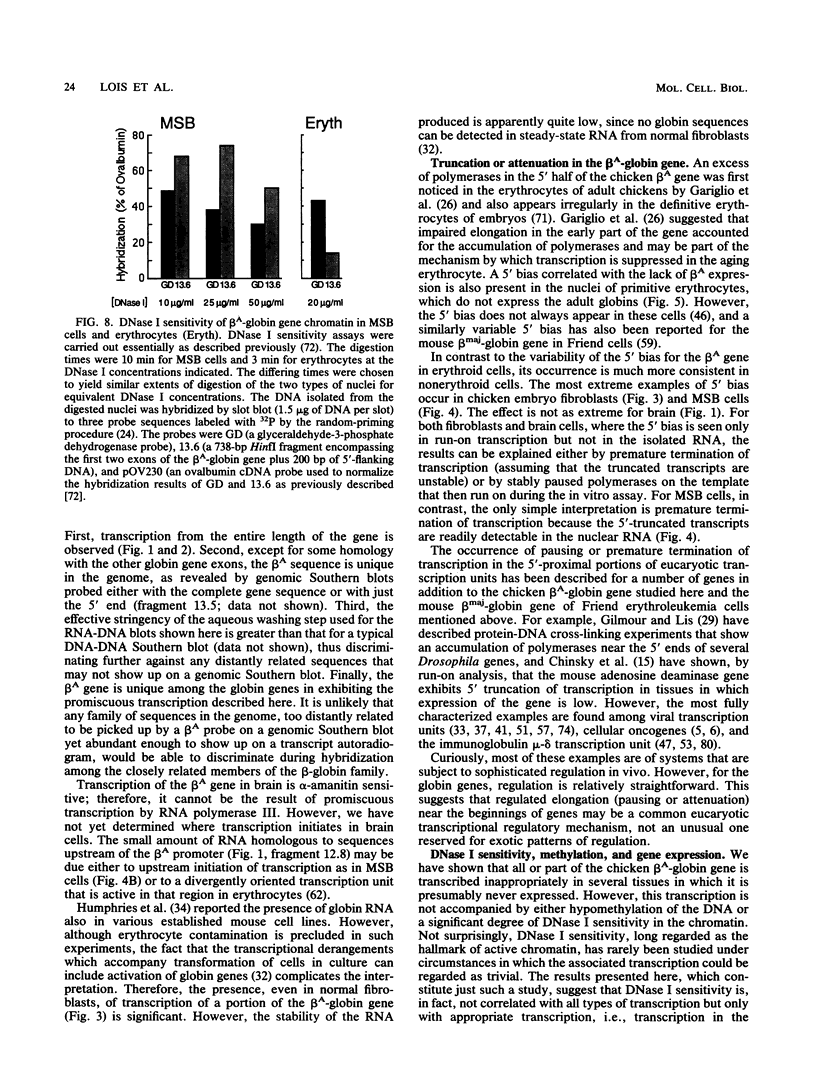



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974 Sep;17(3):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alevy M. C., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. DNase I sensitive domain of the gene coding for the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2309–2314. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra P., Sterner R., Clayton D. F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatographic purification of nucleosomes containing transcriptionally active DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90698-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender T. P., Thompson C. B., Kuehl W. M. Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1473–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.3498214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Sequence requirements for premature termination of transcription in the human c-myc gene. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Gene gating: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8527–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Wittig B., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Chromatin structure is required to block transcription of the methylated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1177–1181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman B. S., Tobin A. J. Distribution of developmentally regulated hemoglobins in embryonic erythroid populations. Dev Biol. 1979 Apr;69(2):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Concordet J. P., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A. Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome structure accompany the activation, repression, and superinduction of murine fibroblast protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinsky J. M., Maa M. C., Ramamurthy V., Kellems R. E. Adenosine deaminase gene expression. Tissue-dependent regulation of transcriptional elongation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14561–14565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Sheffery M. Nucleosome disruption precedes transcription and is largely limited to the transcribed domain of globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):109–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Stadt S. J., Choi O. R., Dolan M., Fischer H. D., Engel J. D. The nucleotide sequence of the embryonic chicken beta-type globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12685–12692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Analysis of the adult chicken beta-globin gene. Nucleotide sequence of the locus, microheterogeneity at the 5'-end of beta-globin mRNA, and aberrant nuclear RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3983–3990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorbic T., Wittig B. Chromatin from transcribed genes contains HMG17 only downstream from the starting point of transcription. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2393–2399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor E. J., Doty P. Highly specific transcription of globin sequences in isolated reticulocyte nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1478–1485. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio P., Bellard M., Chambon P. Clustering of RNA polymerase B molecules in the 5' moiety of the adult beta-globin gene of hen erythrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2589–2598. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Felsenfeld G., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. Effects of DNA supercoiling on the topological properties of nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2620–2623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber-Huber S., May F. E., Westley B. R., Felber B. K., Hosbach H. A., Andres A. C., Ryffel G. U. In contrast to other Xenopus genes the estrogen-inducible vitellogenin genes are expressed when totally methylated. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Lis J. T. In vivo interactions of RNA polymerase II with genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2009–2018. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Whitters M. J., Pohlman J. K. Activation of a chicken embryonic globin gene in adult erythroid cells by 5-azacytidine and sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3954–3958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Activation of cellular genes by avian RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5351–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Aloni Y. Attenuation of late simian virus 40 mRNA synthesis is enhanced by the agnoprotein and is temporally regulated in isolated nuclear systems. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S., Windass J., Williamson R. Mouse globin gene expression in erythroid and non-erythroid tissues. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. Biological techniques for avian sarcoma viruses. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:379–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison N., Weintraub H. Localization of DNAase I-sensitive sequences to specific regions of interphase nuclei. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto S., Eggerding F., Falck-Pederson E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription unit mapping in adenovirus: regions of termination. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):112–119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.112-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V. Deposition of newly synthesized histones: new histones H2A and H2B do not deposit in the same nucleosome with new histones H3 and H4. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2315–2325. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen K., Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T. The DNase I sensitive domain of the chicken lysozyme gene spans 24 kb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6085–6099. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Sterner R., Allfrey V. G. Altered nucleosomes of active nucleolar chromatin contain accessible histone H3 in its hyperacetylated forms. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6943–6946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Pollok B. A., Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The coupling between enhancer activity and hypomethylation of kappa immunoglobulin genes is developmentally regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):930–937. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landes G. M., Martinson H. G. Transcriptional properties of chick embryonic erythroid nuclei in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11002–11007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landes G. M., Villeponteau B., Pribyl T. M., Martinson H. G. Hemoglobin switching in chickens. Is the switch initiated post-transcriptionally? J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11008–11014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law R., Kuwabara M. D., Briskin M., Fasel N., Hermanson G., Sigman D. S., Wall R. Protein-binding site at the immunoglobulin mu membrane polyadenylylation signal: possible role in transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9160–9164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., Marselle L. M. Highly localized tracks of specific transcripts within interphase nuclei visualized by in situ hybridization. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois R., Martinson H. G. Chicken globin gene transcription is cell lineage specific during the time of the switch. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2281–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Pausing and premature termination of human RNA polymerase II during transcription of adenovirus in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5931–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: organ specific variations in the methylation pattern within and around ovalbumin and other chicken genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2081–2103. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Giampaolo A., Carè A., Migliaccio G., Calandrini M., Russo G., Pagliardi G. L., Mastroberardino G., Marinucci M., Peschle C. Molecular mechanisms of human hemoglobin switching: selective undermethylation and expression of globin genes in embryonic, fetal, and adult erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6907–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalowsky L. A., Jones P. A. Gene structure and transcription in mouse cells with extensively demethylated DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):885–892. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok M., Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Premature termination by human RNA polymerase II occurs temporally in the adenovirus major late transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2031–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. L., Chrysogelos S. A., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Reversible changes in the nucleosomal organization of a human H4 histone gene during the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5364–5370. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee R., Molloy G. R. 5,6-Dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits transcription of the beta-hemoglobin gene in vivo at initiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13697–13705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. J., Grosveld F. Site specific demethylation in the promoter of human gamma-globin gene does not alleviate methylation mediated suppression. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2329–2335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl T. M., Martinson H. G. Transcription termination at the chicken beta H-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5369–5377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):343–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B., Ingram V. M. Expression and partial DNA sequence of the chicken beta H-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):802–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Access to a messenger RNA sequence or its protein product is not limited by tissue or species specificity. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):331–334. doi: 10.1126/science.2565599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Maniatis T. Tissue-specific DNA methylation in a cluster of rabbit beta-like globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6634–6638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Yu J., Seale R. L. Chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene family in murine erythroleukemia cells. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 14;23(4):785–790. doi: 10.1021/bi00299a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneider T. W. The 5'-cytosine in CCGG1 is methylated in two eukaryotic DNAs and Msp I is sensitive to methylation at this site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3829–3840. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Appella E., Jay G. Developmental activation of the H-2K gene is correlated with an increase in DNA methylation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Landes G. M., Pankratz M. J., Martinson H. G. The chicken beta globin gene region. Delineation of transcription units and developmental regulation of interspersed DNA repeats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11015–11023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Lundell M., Martinson H. Torsional stress promotes the DNAase I sensitivity of active genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Martinson H. G. Gamma rays and bleomycin nick DNA and reverse the DNase I sensitivity of beta-globin gene chromatin in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E., Jr The definition of a large viral transcription unit late in Ad2 infection of HeLa cells: mapping of nascent RNA molecules labeled in isolated nuclei. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):611–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Beug H., Groudine M., Graf T. Temperature-sensitive changes in the structure of globin chromatin in lines of red cell precursors transformed by ts-AEV. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure of the chicken beta-globin gene region. Sensitivity to DNase I, micrococcal nuclease, and DNase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7730–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Simpson R. T. Transient alterations of the chromatin structure of sea urchin early histone genes during embryogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6185–6203. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Gilliam A. C., Tucker P. W. Regulation of expression of immunoglobulins M and D in murine B cells. Fed Proc. 1985 Jul;44(10):2652–2659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Zasloff M. Enhancement of mRNA nuclear transport by promoter elements. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):613–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]