The dopamine receptor subtype in brain is DRD1. This receptor modulates several cellular functions and its expression has been studied in detail concerning extracellular signaling. A publication [1] indicates that there is also miRNA regulation (suppression) of DRD1 transcription and translation due to miR-142-3p interaction with the DRD1 3'-untranslated region (1,277 bp) of the DRD1 mRNA. This affects dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa (DARPP-32) expression as well, consequently [1].
DARPP-32 is also known as Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 1B (PPP1R1B). This protein as well as DRD1 is expressed in medium spiny neurons and DARPP-32 is crucial in a number of pathways relating to drug abuse and neuropsychiatric disease. Discovery of DARPP-32 lead to the award of the Nobel Prize to Dr. P. Greengard (Rockefeller University, NY, NY) [3].
Dopamine participates in reward and function in the brain and dopamine pathway dysfunction is involved in drug abuse (e.g. cocaine, amphetamine, nicotine, caffeine, LSD, PCP, ethanol morphine, alcoholism, and smoking), gambling, novelty seeking, and additional neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, Huntington's disease, and Parkinson's disease. Dopamine transporter (SLC6A3) is a participant as well. Signaling pathways interconnect DARPP-32 and dopamine pathways. The kinase, CK2 is also implicated among these pathways [3–5]. It is left as a puzzle for the interested reader to identify the various genes and their functions in the (Figure 1 & Figure 2) [2, 6, 7].
Figure 1.
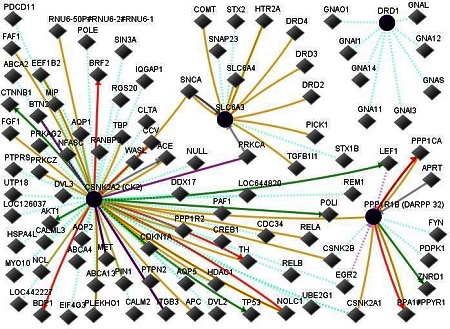
Network of input proteins (DARPP-32, Dopamine receptor DRD1, Dopamine transporter SLC6A3, and casein kinase 2 CK2) with input neighbors of these proteins. In this figure, line-colors and various interactions with other genes are red Down-regulation, green Up-regulation, beige Regulation, purple Co-expression, brown Physical Interaction, turquoise dotted Predicted Protein Interaction, and mauve dotted Predicted TFactor Regulation [2].
Figure 2.
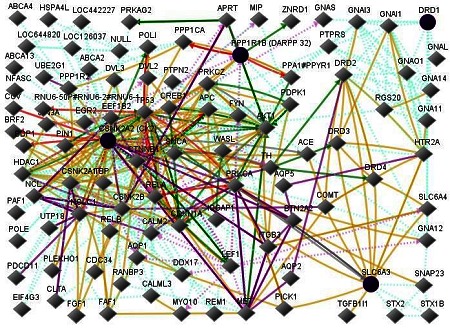
Network of input proteins (DARPP-32, Dopamine receptor DRD1, Dopamine transporter SLC6A3, and casein kinase 2 CK2) and additional neighbors of these proteins. miRNA affects DRD1 expression and probably miRNAs affect several additional proteins in the figure. The study of miRNAs is a new field and much needs to be learned. In this figure, linecolors and various interactions with other genes are red Downregulation, green Up-regulation, beige Regulation, purple Coexpression, brown Physical Interaction, turquoise dotted Predicted Protein Interaction, and mauve dotted Predicted TFactor Regulation [2].
Thus, the continued study of DARPP-32 and related pathways may lead to cures for the many pathologies stemming from diseases as mentioned above.
Acknowledgments
There are no financial conflicts.
Footnotes
Citation:Shapshak, Bioinformation 9(6): 274-275 (2013)
References
- 1.Tobon KE, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. http://www.sabiosciences.com/
- 3. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laure ates/2000/
- 4.Rebholz H, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;3223:8. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Svenningsson P, et al. AAPS J. 2005;7:E353. doi: 10.1208/aapsj070235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. http://www.genecards.org/
- 7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/


