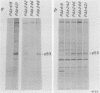
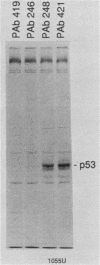
Abstract
The Friend erythroleukemia virus complex contains no cell-derived oncogene. Transformation by this virus may therefore involve mutations affecting cellular gene expression. We provide evidence that inactivating mutations of the cellular p53 gene are a common feature in Friend virus-induced malignancy, consistent with an antioncogene role for p53 in this disease. We have shown that frequent rearrangements of the p53 gene cause loss of expression or synthesis of truncated proteins, whereas overexpression of p53 protein is seen in other Friend cell lines. We now demonstrate that p53 expression in the latter cells is also abnormal, as a result of missense mutations in regions encoding highly conserved amino acids. Three of these aberrant alleles obtained from cells from different mice were cloned and found to function as dominant oncogenes in gene transfer assays, supporting the view that certain naturally occurring missense mutations in p53 confer a dominant negative phenotype on the encoded protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja H., Bar-Eli M., Advani S. H., Benchimol S., Cline M. J. Alterations in the p53 gene and the clonal evolution of the blast crisis of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6783–6787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben David Y., Prideaux V. R., Chow V., Benchimol S., Bernstein A. Inactivation of the p53 oncogene by internal deletion or retroviral integration in erythroleukemic cell lines induced by Friend leukemia virus. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow V., Ben-David Y., Bernstein A., Benchimol S., Mowat M. Multistage Friend erythroleukemia: independent origin of tumor clones with normal or rearranged p53 cellular oncogenes. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2777–2781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2777-2781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks G. G., Mowat M. Integration of Friend murine leukemia virus into both alleles of the p53 oncogene in an erythroleukemic cell line. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4752–4755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4752-4755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Frey A. B., Levine A. J. Immunological evidence for the association of p53 with a heat shock protein, hsc70, in p53-plus-ras-transformed cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2863–2869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Chumakov P., Currie G. A. The cellular oncogene p53 can be activated by mutagenesis. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):816–818. doi: 10.1038/317816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Redmond S., Wade-Evans A. Cloning and expression analysis of full length mouse cDNA sequences encoding the transformation associated protein p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5609–5626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., Maltby V., Mock D., Rossant J., Pawson T., Bernstein A. High incidence of lung, bone, and lymphoid tumors in transgenic mice overexpressing mutant alleles of the p53 oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3982–3991. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Miller C., Koeffler H. P., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7716–7719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F., Tavitian A., Tambourin P. Spi-1 is a putative oncogene in virally induced murine erythroleukaemias. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):277–280. doi: 10.1038/331277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat M., Cheng A., Kimura N., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Rearrangements of the cellular p53 gene in erythroleukaemic cells transformed by Friend virus. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):633–636. doi: 10.1038/314633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D. G., Rovinski B., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Loss of a highly conserved domain on p53 as a result of gene deletion during Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):621–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Benchimol S. Immortalization of rat embryo fibroblasts by the cellular p53 oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Munroe D., Peacock J., Mowat M., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Deletion of 5'-coding sequences of the cellular p53 gene in mouse erythroleukemia: a novel mechanism of oncogene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):847–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., Méchali M., May P., Kress M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA from Xenopus laevis coding for a protein homologous to human and murine p53. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., Stürzbecher H. W., Ullrich S., Jenkins J., May P. Evolutionary conservation of the biochemical properties of p53: specific interaction of Xenopus laevis p53 with simian virus 40 large T antigen and mammalian heat shock proteins 70. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3894–3901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3894-3901.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Addison C., Jenkins J. R. Characterization of mutant p53-hsp72/73 protein-protein complexes by transient expression in monkey COS cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3740–3747. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Wallis J., Levine A. J. Identification of the p53 protein domain involved in formation of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-p53 protein complex. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.574-583.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]